|
Ts–ch Merger
In phonology, the ts–ch merger is the merger of the voiceless alveolar affricate and the voiceless postalveolar affricate . In Russian, it is the merger of the consonants rendered by letters Che and Tse. If the shift is towards Tse, it is called ''tsokanye'' (russian: цоканье); the shift towards Che is called ''chokanye'' (russian: чоканье). It is a regular sound change of Lower Sorbian, but not Upper Sorbian, as seen in the difference between Lower Sorbian and Upper Sorbian , both meaning "time". In Polish the merger is part of a more general dialectal feature called (mazuration), present in many Polish dialects but named after the Masovian dialect.Stanislaw Gogolewski, "Dialectology in Poland, 1873-1997", In: ''Towards a History of Linguistics in Poland'', by E. F. K. Koerner, A. J. Szwedek (eds.) (2001) p. 128/ref> It also occurs in a few areas of the Chakavian dialect of Serbo-Croatian, known as '' tsakavism''. The ''sabesdiker losn'' feature of Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
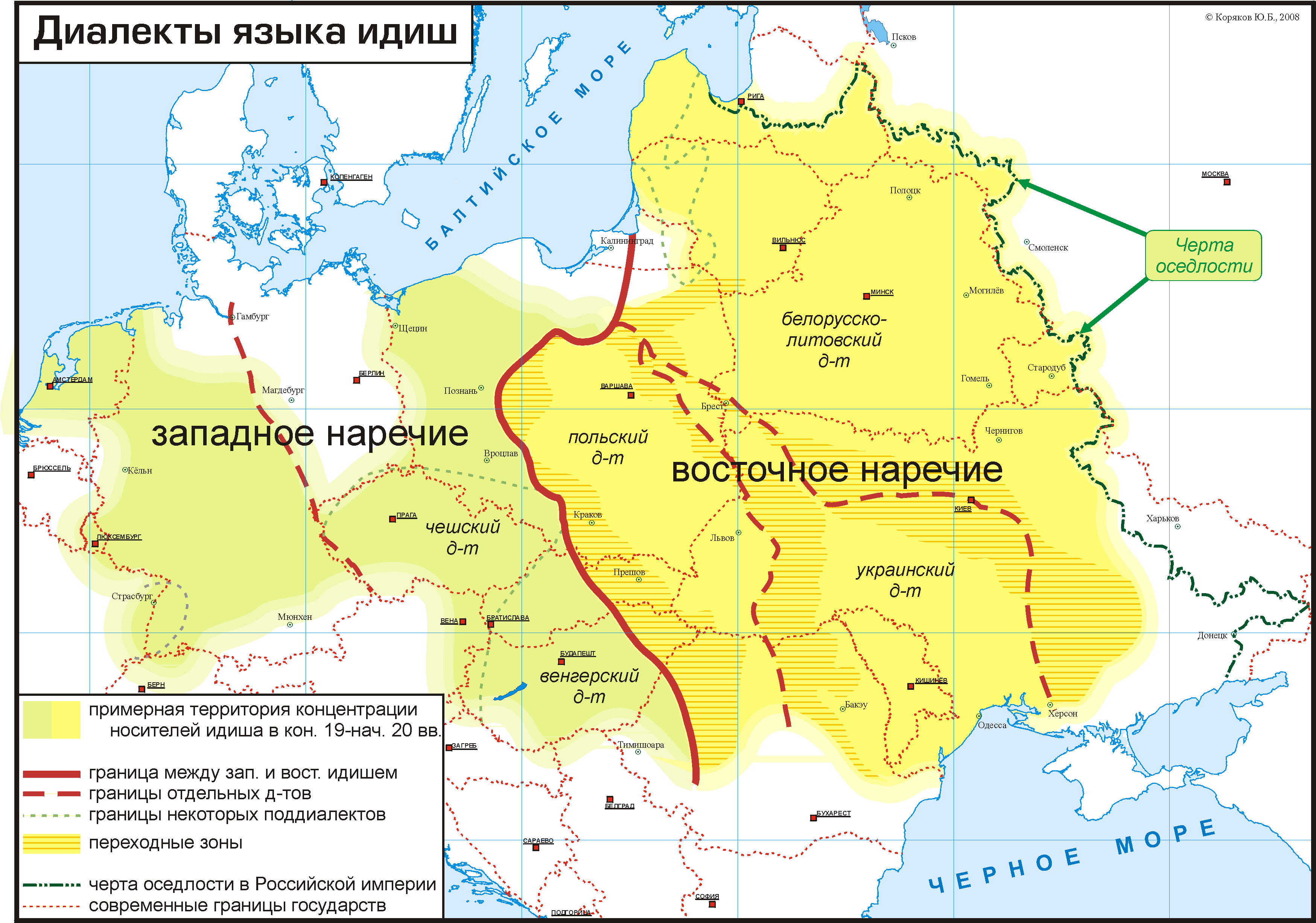
Northeastern Yiddish
Yiddish dialects are variants of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Shoah. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, since Yiddish is largely dying out everywhere due to language assimilation, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic communities, have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in Western-Central Europe, in the region which was called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabesdiker Losn
Der sabesdiker-losn (Yiddish: דער סאַבעסדיקער לשון (לאָסן)) is a dialectal feature characteristic of the Northeastern dialect of the Yiddish language ( NEY, ''Litvisher-vaysrusisher dialekt'', צפֿון ייִדיש ''Tsofn-yidish''), which is the replacement, or merger of the "hushing" (post-alveolar) consonants "ch", "sh" ( IPA: /tʃ/, /ʃ/), with the "hissing" (alveolar) ones, "ts", "s" (IPA: /ts/, /s/). The name of the term is a shibboleth: the phrase ''"דאָס שבתֿדיקע לשון" "dos shabesdike loshn"'' (in standard Yiddish) means " Sabbath speech", hinting at the perception that this feature is substandard. "History of the Yiddish Language", by Max Weinreichbr>p. 534/ref> In addition to the shibboleth, the use of the masculine article ''der'' indicates NEY's tendency to use either the masculine or the feminine gender for nouns where Standard Yiddish uses the neuter. It is similar to the dialectical feature of Polish language called ''mazurze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakavian Dialect
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , sh-Latn, čakavski proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic regiolect or language spoken primarily by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia). Chakavian, like Kajkavian, is not spoken in Serbo-Croatian-speaking regions beyond Croatia. Chakavian was the basis for early literary standards in Croatia. Today, it is spoken almost entirely within Croatia's borders, apart from the Burgenland Croatian in Austria and Hungary and a few villages in southern Slovenia. History Chakavian is one of the oldest written South Slavic varieties that had made a visible appearance in legal documents—as early as 1275 ( Istrian land survey) and 1288 (Vinodol codex), the predominantly vernacular Chakavian is recorded, mixed with elements of Church Slavic. Many of these a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a continuum. The turbulent history of the area, particularly due to expansion of the Ottoman Empire, resulted in a patchwork of dialectal and religious differences. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread dialect in the western Balkans, intruding westwards into the area previously occupied by Chakavian and Kajkavian (which further blend into Slovenian in the northwest). Bosniaks, Croats and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural circles, although a large part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
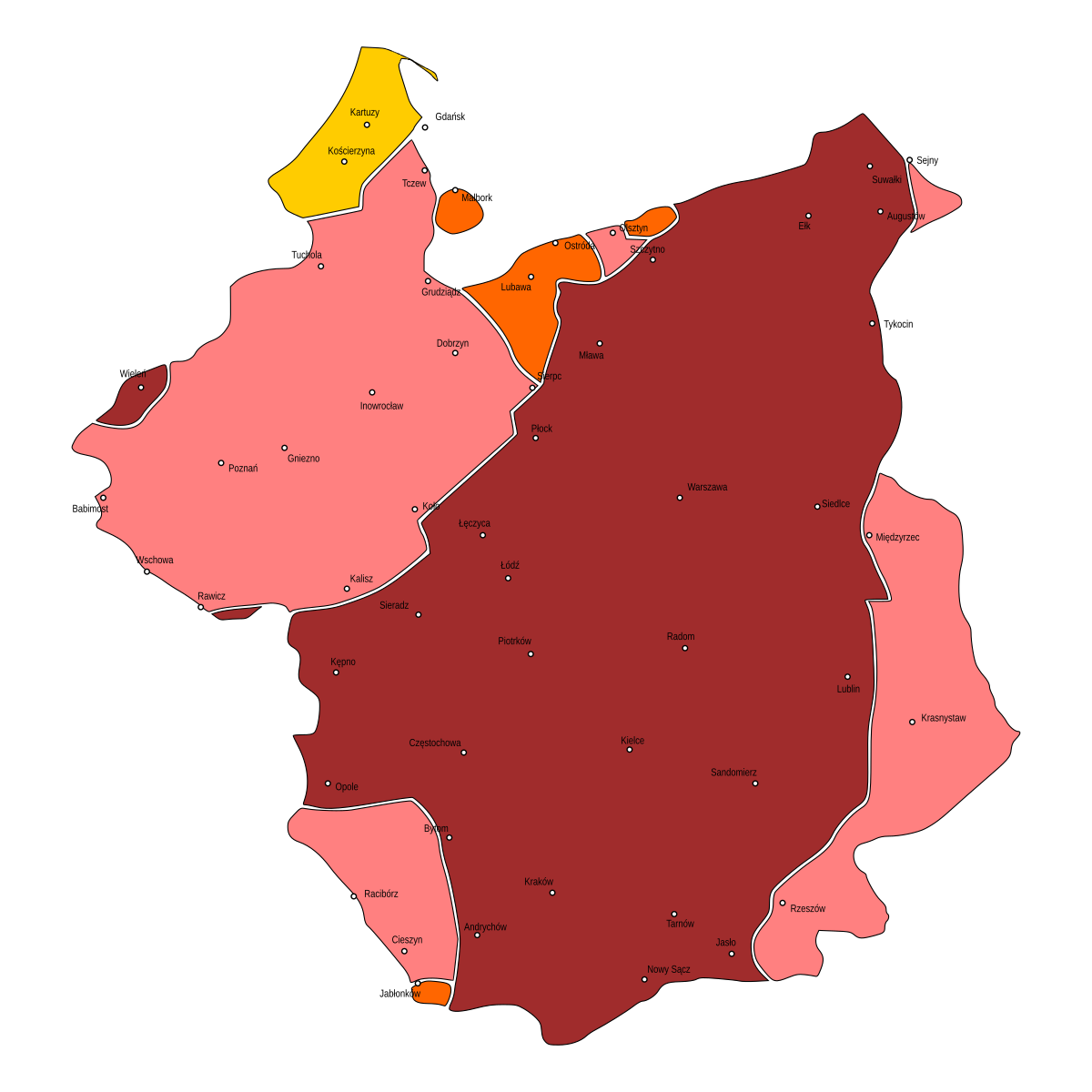
Masovian Dialect
The Masovian dialect ( pl, dialekt mazowiecki), also written Mazovian, is the dialect of Polish spoken in Mazovia and historically related regions, in northeastern Poland. It is the most distinct of the Polish dialects and the most expansive. Mazovian dialects may exhibit such features as mazurzenie, sandhi (intervocalic voicing of obstruents on word boundaries), and asynchronous palatal pronunciation of labial consonants (so-called softening). The Kurpie region has some of the most distinctive phonetic features due to isolation. Characteristics include: * Depalatalization of velars before and palatalization of velars before historical ; e.g. standard Polish ''rękę'', ''nogę'' ('arm', 'leg', in the accusative case) is rendered , respectively instead of , ; * sequences realized instead of ; * merger of the retroflex series sz, ż, cz, dż into the alveolar s, z, c, dz; * > before certain consonants; * the Old Polish dual number marker -''wa'' continues to be attached to v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazurzenie
Mazurzenie () or mazuration is the replacement or merger of Polish's series of postalveolar fricatives and affricates (written ) into the dentialveolar series (written ). This merger is present in many dialects, but is named for the Masovian dialect.Stanislaw Gogolewski, "Dialectology in Poland, 1873-1997", In: ''Towards a History of Linguistics in Poland'', by E. F. K. Koerner, A. J. Szwedek (eds.) (2001) p. 128/ref> This phonological feature is observed in dialects of Masuria and Masovia (Masovian dialect), as well as in most of Lesser Poland and parts of Silesia. There are also some peripheral mazurating islands in Greater Poland. The boundary of runs from north-east to south-west. It may have originated between the 14th and 16th centuries in the Masovian dialect. The feature is linked to the process of depalatalization (reducing of the number of palatalized consonants) similar to the phenomena of and ' in other dialects. A rarer term for mazuration is sakanie. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety (linguistics), variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. Under this definition, the dialects or varieties of a particular language are closely related and, despite their differences, are most often largely Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, especially if close to one another on the dialect continuum. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors, such as social class or ethnicity. A dialect that is associated with a particular social class can be termed a sociolect, a dialect that is associated with a particular ethnic group can be termed an ethnolect, and a geographical/regional dialect may be termed a regiolectWolfram, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Scientific Publishers PWN
Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN (''Polish Scientific Publishers PWN''; until 1991 ''Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe'' - ''National Scientific Publishers PWN'', PWN) is a Polish book publisher, founded in 1951, when it split from the Wydawnictwa Szkolne i Pedagogiczne. Adam Bromberg, who was the enterprise's director between 1953 and 1965, made it into communist Poland's largest publishing house. The printing house is best known as a publisher of encyclopedias, dictionaries and university handbooks. It is the leading Polish provider of scientific, educational and professional literature as well as works of reference. It authored the Wielka Encyklopedia Powszechna PWN, by then the largest Polish encyclopedia, as well as its successor, the Wielka Encyklopedia PWN, which was published between 2001 and 2005. There is also an online PWN encyclopedia – Internetowa encyklopedia PWN. Initially state-owned, since 1991 it has been a private company. The company is a member of International Associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merger (phonology)
In historical linguistics, phonological change is any sound change that alters the distribution of phonemes in a language. In other words, a language develops a new system of oppositions among its phonemes. Old contrasts may disappear, new ones may emerge, or they may simply be rearranged. Sound change may be an impetus for changes in the phonological structures of a language (and likewise, phonological change may sway the process of sound change). One process of phonological change is ''rephonemicization'', in which the distribution of phonemes changes by either addition of new phonemes or a reorganization of existing phonemes. Mergers and splits are types of rephonemicization and are discussed further below. Types In a typological scheme first systematized by Henry M. Hoenigswald in 1965, a historical sound law can only affect a phonological system in one of three ways: * Conditioned merger (which Hoenigswald calls "primary split"), in which some instances of phoneme A beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |