|
Triple Witching
Triple witching hour is the last hour of the stock market trading session (3:00-4:00 P.M., New York City local Time) on the third Friday of every March, June, September, and December. Those days are the expiration of three kinds of securities: * Stock market index futures; * Stock market index options; * Stock options. The simultaneous expirations generally increases the trading volume of options, futures, and their underlying stocks, occasionally increasing the volatility of prices of related securities. On those same days single-stock futures also expire, so that the final hour is sometimes referred to as the quadruple witching hour. Concept and usage The term "triple witching" refers to the extra volatility resulting from the expiration dates of the three financing instruments, and is based on the ''witching hour'' denoting the active time for witches. It is used often and is considered industry jargon, along with the synonym, ''Freaky Friday''.{{cite web , url=https://hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange, as well as stock that is only traded privately, such as shares of private companies which are sold to investors through equity crowdfunding platforms. Investment is usually made with an investment strategy in mind. Size of the market The total market capitalization of all publicly traded securities worldwide rose from US$2.5 trillion in 1980 to US$93.7 trillion at the end of 2020. , there are 60 stock exchanges in the world. Of these, there are 16 exchanges with a market capitalization of $1 trillion or more, and they account for 87% of global market capitalization. Apart from the Australian Securities Exchange, these 16 exchanges are all in North America, Europe, or Asia. By country, the largest stock markets as of January 2022 are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small portion of westernmost Brazil in South America, along with certain Caribbean and Atlantic islands. Places that use: * Eastern Standard Time (EST), when observing standard time (autumn/winter), are five hours behind Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−05:00). * Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), when observing daylight saving time (spring/summer), are four hours behind Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−04:00). On the second Sunday in March, at 2:00 a.m. EST, clocks are advanced to 3:00 a.m. EDT leaving a one-hour "gap". On the first Sunday in November, at 2:00 a.m. EDT, clocks are moved back to 1:00 a.m. EST, thus "duplicating" one hour. Southern parts of the zone (Panama and the Caribbean) do not observe daylight saving time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Market Index Future
In finance, a stock market index future is a cash-settled futures contract on the value of a particular stock market index. The turnover for the global market in exchange-traded equity index futures is notionally valued, for 2008, by the Bank for International Settlements at US$130 trillion. Uses Stock index futures are used for hedging, trading, and investments. Index futures are also used as leading indicators to determine market sentiment. Hedging using stock index futures could involve hedging against a portfolio of shares or equity index options. Trading using stock index futures could involve, for instance, volatility trading (The greater the volatility, the greater the likelihood of profit taking – usually taking relatively small but regular profits). Investing via the use of stock index futures could involve exposure to a market or sector without having to actually purchase shares directly. There are cases of equity hedging with index futures. One case is where a portf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Market Index Option
Stock market index option is a type of option, a financial derivative, that is based on stock indices like the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average. They give an investor the right to buy or sell the underlying stock index for a defined time period. Because index options are based on a large basket of stocks, investors are able to gain exposure to the market as a whole and take advantage of diversification. Index options may be tied to the price of either "broad-based indexes" like the S&P 500 or the Russell 3000 or to "narrow-based indexes", which are limited to a particular industry. The global market for exchange-traded stock market index options is notionally valued by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) at $368,900 million in 2005. A stock index option provides the right to trade a specific stock index at a specified price by a specified expiration date. A call option on a stock index In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Option
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in ''over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financial instrument at a specified strike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
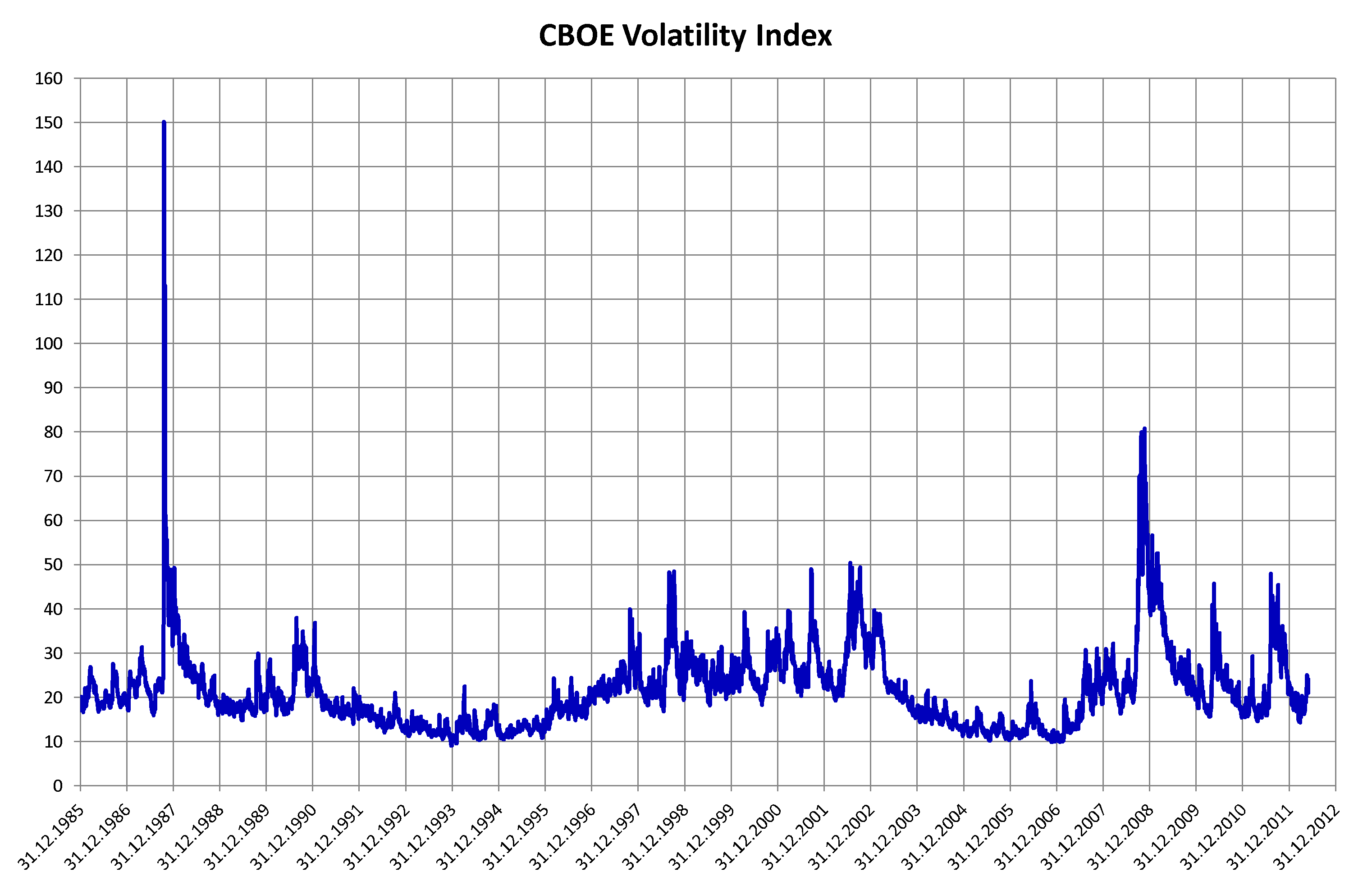
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn calculated using the sum of squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-stock Future
In finance, a single-stock future (SSF) is a type of futures contract between two parties to exchange a specified number of stocks in a company for a price agreed today (the futures price or the strike price) with delivery occurring at a specified future date, the delivery date. The contracts can be later traded on a futures exchange. The party agreeing to take delivery of the underlying stock in the future, the "buyer" of the contract, is said to be "long", and the party agreeing to deliver the stock in the future, the "seller" of the contract, is said to be "short". The terminology reflects the expectations of the parties - the buyer hopes or expects that the stock price is going to increase, while the seller hopes or expects that it will decrease. Because entering the contract itself costs nothing, the buy/sell terminology is a linguistic convenience reflecting the position each party is taking - long or short. SSFs are usually traded in increments/lots/batches of 100. When pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expiration (options)
In finance, the expiration date of an option contract (represented by Greek letter tau, τ) is the last date on which the holder of the option may exercise it according to its terms. In the case of options with "automatic exercise", the net value of the option is credited to the long and debited to the short position holders. Typically, exchange-traded option contracts expire according to a pre-determined calendar. For instance, for U.S. exchange-listed equity stock option contracts, the expiration date is always the Saturday that follows the third Friday of the month, unless that Friday is a market holiday, in which case the expiration is on Thursday right before that Friday. The clearing firm may automatically exercise by exception any option that is in the money at expiration to preserve its value for the holder of the option and at the same time, benefit from the commission fees collected from the account holder. However, the holder or the holder's broker may request t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witching Hour
In folklore, the witching hour or devil's hour is a time of night that is associated with supernatural events, whereby witches, demons and ghosts are thought to appear and be at their most powerful. Definitions vary, and include the hour immediately after midnight, and the time between 3:00am and 4:00am. The term now has a widespread colloquial and idiomatic usage that is associated with human physiology and behaviour to more superstitious phenomena such as luck. Origins The phrase "witching hour" began at least as early as 1775, in the poem "Night, an Ode." by Rev. Matthew West, though its origins may go further back to 1535 when the Catholic Church prohibited activities during the 3:00 am and 4:00 am timeframe due to emerging fears about witchcraft in Europe.Should You be Afraid of the Witchin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witch
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of Magic (supernatural), magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In Middle Ages, medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have used Black magic, malevolent magic against their own community, and often to have communed with evil beings. It was thought witchcraft could be thwarted by Apotropaic magic, protective magic or counter-magic, which could be provided by cunning folk or folk healers. Suspected witches were also intimidated, banished, attacked or killed. Often they would be formally prosecuted and punished, if found guilty or simply believed to be guilty. European witch-hunts and witch trials in the early modern period led to tens of thousands of executions. In some regions, many of those accused of witchcraft were folk healers or midwife, midwives. European belief in witchcraft gradually dwindled during and after the Age of Enl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jargon
Jargon is the specialized terminology associated with a particular field or area of activity. Jargon is normally employed in a particular Context (language use), communicative context and may not be well understood outside that context. The context is usually a particular occupation (that is, a certain trade, profession, vernacular or academic field), but any ingroups and outgroups, ingroup can have jargon. The main trait that distinguishes jargon from the rest of a language is special vocabulary—including some words specific to it and often different word sense, senses or meanings of words, that outgroups would tend to take in another sense—therefore misunderstanding that communication attempt. Jargon is sometimes understood as a form of technical slang and then distinguished from the official terminology used in a particular field of activity. The terms ''jargon'', ''slang,'' and ''argot'' are not consistently differentiated in the literature; different authors interpret the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program Trading
Program trading is a type of trading in securities, usually consisting of baskets of fifteen stocks or more that are executed by a computer program simultaneously based on predetermined conditions. Program trading is often used by hedge funds and other institutional investors pursuing index arbitrage or other arbitrage strategies. There are essentially two reasons to use program trading, either because of the desire to trade many stocks simultaneously (for example, when a mutual fund receives an influx of money it will use that money to increase its holdings in the multiple stocks which the fund is based on), or alternatively to arbitrage temporary price discrepancies between related financial instruments, such as between an index and its constituent parts. According to the New York Stock Exchange, in 2006 program trading accounts for about 30% and as high as 46.4% of the trading volume on that exchange every day. Barrons breaks down its weekly figures for program trading betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
