|
Transfusion Therapy (Sickle-cell Disease)
Red blood cells ( erythrocytes) from donors contain normal hemoglobin (HbA), and transfusion of normal red blood cells into people with sickle cell disease reduces the percentage of red cells in the circulation containing the abnormal hemoglobin (HbS). Although transfusion of donor red blood cells can ameliorate and even prevent complications of sickle cell disease in certain circumstances, transfusion therapy is not universally beneficial in sickle cell disease. Types of transfusion therapy There are two main types of transfusion, simple red cell transfusion and exchange transfusion. Simple transfusion Involves transfusing red blood cells without removing any of the patient’s blood. It is used when the patient's hemoglobin is much lower than normal, for example an aplastic crisis. Exchange transfusion Exchange transfusion involves removal of the patient’s blood and replacement with donor red blood cells. It is used to treat life-threatening complications of sickle cell d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvovirus B19
Primate erythroparvovirus 1, generally referred to as B19 virus (B19V), parvovirus B19 or sometimes erythrovirus B19, is the first (and until 2005 the only) known human virus in the family ''Parvoviridae'', genus ''Erythroparvovirus''; it measures only 23–26 nm in diameter. The name is derived from Latin, parvum meaning small, reflecting the fact that B19 ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. B19 virus is most known for causing disease in the pediatric population; however, it can also affect adults. It is the classic cause of the childhood rash called fifth disease or erythema infectiosum, or "slapped cheek syndrome". The virus was discovered by chance in 1975 by Australian virologist Yvonne Cossart. It gained the B19 name because it was discovered in well B19 of a large series of microtiter plates. Virology Erythroviruses belong to the ''Parvoviridae'' family of small DNA viruses. Human parvovirus B19 is a non-enveloped, icosahedral virus that contains a single-stranded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfusion Medicine
Transfusion medicine (or transfusiology) is the branch of medicine that encompasses all aspects of the transfusion of blood and blood components including aspects related to hemovigilance. It includes issues of blood donation, immunohematology and other laboratory testing for transfusion-transmitted diseases, management and monitoring of clinical transfusion practices, patient blood management, therapeutic apheresis, stem cell collections, cellular therapy, and coagulation. Laboratory management and understanding of state and federal regulations related to blood products are also a large part of the field. Overview In most countries, immunohematology and transfusion medicine specialists provide expert opinion on massive transfusions, difficult/incompatible transfusions and rational use of specialised blood product therapy like irradiated blood/ leukodepleted/washed blood products. The blood donor center is the facility that collects blood components from screened blood dono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of Chelation, chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the body. Chelation therapy has a long history of use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific medical treatments, although it is administered under very careful medical supervision due to various inherent risks, including the mobilization of mercury and other metals through the brain and other parts of the body by the use of weak chelating agents that unbind with metals before elimination, exacerbating existing damage. To avoid mobilization, some practitioners of chelation use strong chelators, such as selenium, taken at low doses over a long period of time. Chelation therapy must be administered with care as it has a number of possible side effects, including death. In response to increasing use of chelation therapy as alternative medicine and in circumstances in which the therapy should not be used in conventional medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 43 different blood type (or group) classification systems currently recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusions (ISBT) as of June 2021. A mismatch (very rare in modern medicine) in this, or any other serotype, can cause a potentially fatal adverse reaction after a transfusion, or an unwanted immune response to an organ transplant. The associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually IgM antibodies, produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses. The ABO blood types were discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901; he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930 for this discovery. ABO blood types are also present in other primates such as apes and Old World monkeys. History Discovery The ABO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kell Antigen System
The Kell antigen system (also known as the Kell–Cellano system) is a human blood group system, that is, a group of antigens on the human red blood cell surface which are important determinants of blood type and are targets for autoimmune or alloimmune diseases which destroy red blood cells. The Kell antigens are K, k, Kpa, Kpb, Jsa and Jsb. The Kell antigens are peptides found within the Kell protein, a 93-kilodalton transmembrane zinc-dependent endopeptidase which is responsible for cleaving endothelin-3. Protein The ''KEL'' gene encodes a type II transmembrane glycoprotein that is the highly polymorphic Kell blood group antigen. The Kell glycoprotein links via a single disulfide bond to the XK membrane protein that carries the Kx antigen. The encoded protein contains sequence and structural similarity to members of the neprilysin (M13) family of zinc endopeptidases. There are several alleles of the gene which creates Kell protein. Two such alleles, ''K1'' (Kell) and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rh Blood Group System
The Rh blood group system is a human blood group system. It contains proteins on the surface of red blood cells. After the ABO blood group system, it is the most likely to be involved in transfusion reactions. The Rh blood group system consists of 49 defined blood group antigens, among which the five antigens D, C, c, E, and e are the most important. There is no d antigen. Rh(D) status of an individual is normally described with a ''positive'' (+) or ''negative'' (−) suffix after the ABO type (e.g., someone who is A+ has the A antigen and Rh(D) antigen, whereas someone who is A− has the A antigen but lacks the Rh(D) antigen). The terms ''Rh factor'', ''Rh positive'', and ''Rh negative'' refer to the Rh(D) antigen only. Antibodies to Rh antigens can be involved in hemolytic transfusion reactions and antibodies to the Rh(D) and Rh antigens confer significant risk of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Nomenclature The Rh blood group system has two sets of nomenclature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasian Race
The Caucasian race (also Caucasoid or Europid, Europoid) is an obsolete racial classification of human beings based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. The ''Caucasian race'' was historically regarded as a biological taxon which, depending on which of the historical race classifications was being used, usually included ancient and modern populations from all or parts of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa. First introduced in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, the term denoted one of three purported major races of humankind (those three being Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid). In biological anthropology, ''Caucasoid'' has been used as an umbrella term for phenotypically similar groups from these different regions, with a focus on skeletal anatomy, and especially cranial morphology, without regard to skin tone. Ancient and modern "Caucasoid" populations were thus not exclusively "white", but rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulatory system, circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosome, ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain staining, stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain. Clinical significance To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated flow cytometry, counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorophore, fluorescent dye that marks RNA and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine). Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin S
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years. Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (''HBB'') that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
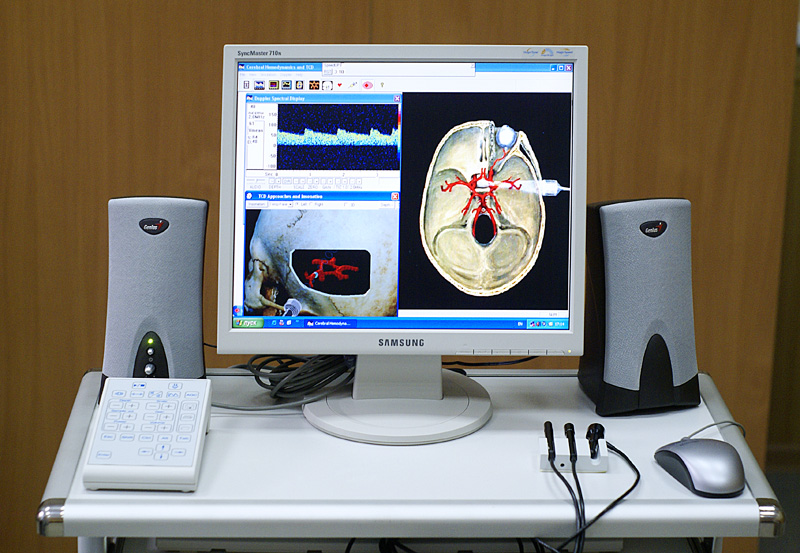
Transcranial Doppler
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) and transcranial color Doppler (TCCD) are types of Doppler ultrasonography that measure the velocity of blood flow through the brain's blood vessels by measuring the echoes of ultrasound waves moving transcranially (through the cranium). These modes of medical imaging conduct a spectral analysis of the acoustic signals they receive and can therefore be classified as methods of active acoustocerebrography. They are used as tests to help diagnose emboli, stenosis, vasospasm from a subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding from a ruptured aneurysm), and other problems. These relatively quick and inexpensive tests are growing in popularity. The tests are effective for detecting sickle cell disease, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, subarachnoid hemorrhage, arteriovenous malformations, and cerebral circulatory arrest. The tests are possibly useful for perioperative monitoring and meningeal infection. The equipment used for these tests is becoming increasingly portab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |