|
Tortula Muralis
''Tortula muralis'', commonly known as wall- screw moss, is a species of moss in the family Pottiaceae. ''T. muralis'' is found throughout the world. Taxonomy Due to the diversity of the genus ''Tortula'', there are groups of taxa within the genus that are more closely related than others. The genus ''Tortula'' and the genus '' Barbula'' were previously used interchangeably, and some species have since been reclassified. The ''T. muralis'' complex consists of four taxa (''T. lingulate'', ''T. obtusifolia'', ''T. muralis var. aestiva'', ''T. muralis var. muralis''), two of which are ''T. muralis'' varieties. They are similar in appearance and are commonly mistaken for each other. * ''T. lingulate'' have a relatively large spore size (10 – 18.5 µm) compared to the other three (7.5 – 13.5 µm). * ''T. obtusifolia'' and ''T. muralis var. aestiva'' both have short hairpoints and difficult to distinguish. * ''T. muralis var. muralis'' are very similar to ''T. muralis v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Hedwig
Johann Hedwig (8 December 1730 – 18 February 1799), also styled as Johannes Hedwig, was a German botanist notable for his studies of mosses. He is sometimes called the "father of bryology". He is known for his particular observations of sexual reproduction in the cryptogams. Many of his writings were in Latin, and his name is rendered in Latin as Ioannis Hedwig or Ioanne Hedwig. Early life Hedwig was born in Brașov, Transylvania, on 8 December 1730. As the son of a shoemaker, he grew up in poverty. It was in his childhood he became fascinated with mosses.Isely, Duane. One Hundred and One Botanists. Purdue University Press, 2002. He went on to study medicine at the University of Leipzig, and received his medical degree in 1759. Career After receiving his degree, Hedwig worked as a physician for the next twenty years. When he was not granted a license to practice in Transylvania with his Leipzig degree, he worked as a general practitioner in Chemnitz. It was during this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternation Of Generations
Alternation of generations (also known as metagenesis or heterogenesis) is the predominant type of Biological life cycle, life cycle in plants and algae. It consists of a Multicellular organism, multicellular haploid sexual phase, the gametophyte, which has a single set of chromosomes alternating with a multicellular diploid asexual phase, the sporophyte which has two sets of chromosomes. A mature sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis, a process which reduces the number of chromosomes to half, from two sets to one. The resulting haploid spores germinate and grow into multicellular haploid gametophytes. At maturity, a gametophyte produces gametes by mitosis, the normal process of cell division in eukaryotes, which maintains the original number of chromosomes. Two haploid gametes (originating from different organisms of the same species or from the same organism) fertilisation, fuse to produce a diploid zygote, which divides repeatedly by mitosis, developing into a multice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternation Of Generations Simpler
Alternation or AlterNation may refer to: * Alternation (complexity), a resource in computational complexity theory * Alternation (formal language theory), the set union of two sets of strings in formal language theory and pattern matching * Alternation (geometry), a geometric operation for deriving polytopes from other polytopes * Alternation (linguistics), a variation in the phonological form of a morpheme * Diathesis alternation, a linguistics term relating to verb use * R/N alternation; see Rhotacism (sound change) * Logical disjunction, the ''or'' function * ''AlterNation'', a show on NE1 FM * WSTB, a radio station in Streetsboro, Ohio known as ''The AlterNation'' {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheridium
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cells and spermatogenous tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
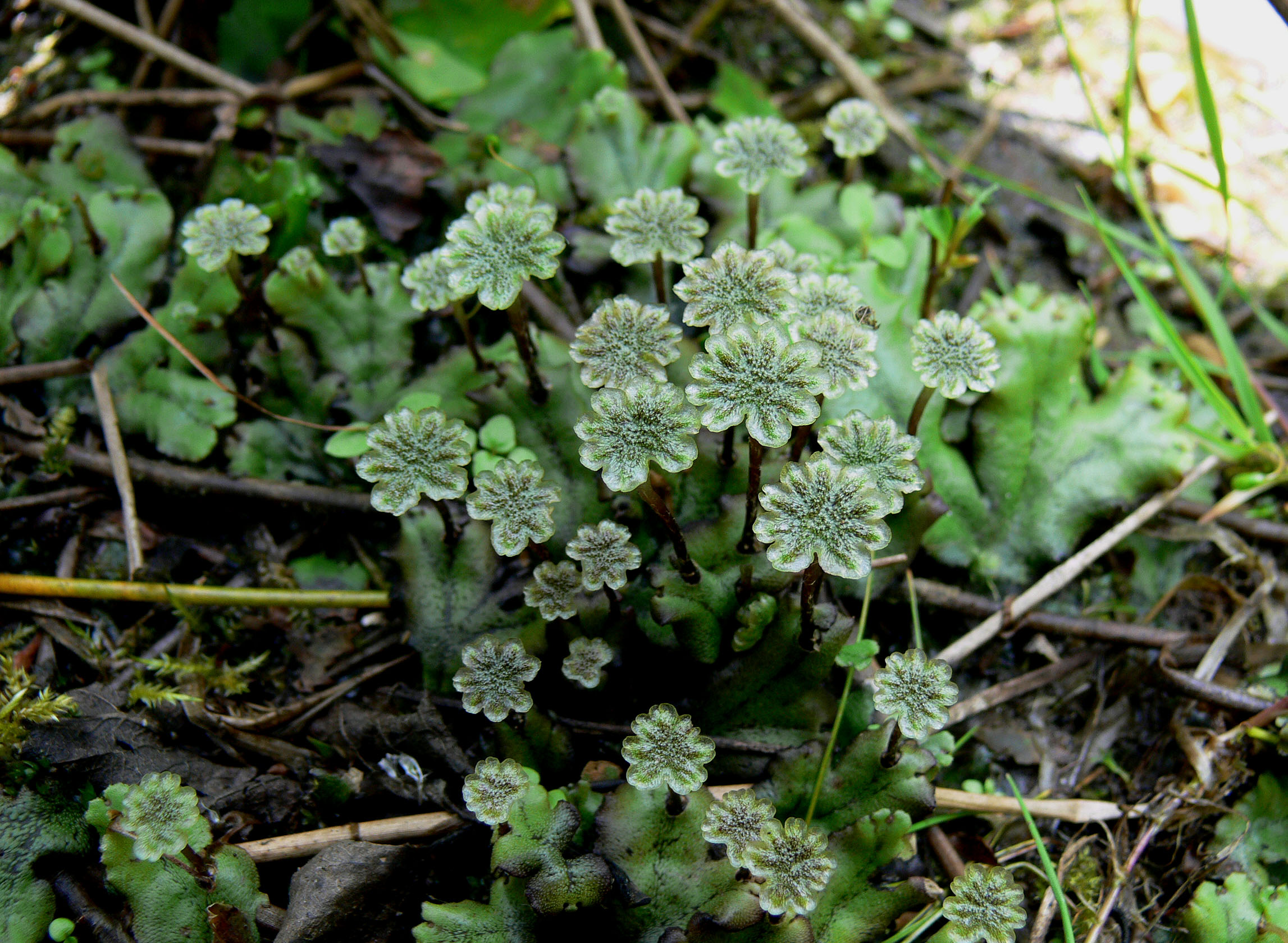
Archegonium
An archegonium (pl: archegonia), from the ancient Greek ''ἀρχή'' ("beginning") and ''γόνος'' ("offspring"), is a multicellular structure or organ of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the ovum or female gamete. The corresponding male organ is called the antheridium. The archegonium has a long neck canal or venter and a swollen base. Archegonia are typically located on the surface of the plant thallus, although in the hornworts they are embedded. Bryophytes In bryophytes and other cryptogams sperm reach the archegonium by swimming in water films, whereas in Pinophyta and Angiosperms the pollen are delivered by wind or animal vectors and the sperm are delivered by means of a pollen tube. In the moss ''Physcomitrella patens'', archegonia are not embedded but are located on top of the leafy gametophore (s. Figure). The Polycomb protein FIE is expressed in the unfertilized egg cell (right) as the blue colour after GUS staining reveals. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonema
A protonema (plural: protonemata) is a thread-like chain of cells that forms the earliest stage of development of the gametophyte (the haploid phase) in the life cycle of mosses. When a moss first grows from a spore, it starts as a ''germ tube'', which lengthens and branches into a filamentous complex known as a ''protonema'', which develops into a leafy gametophore, the adult form of a gametophyte in bryophytes. Moss spores germinate to form an alga-like filamentous structure called the protonema. It represents the juvenile gametophyte. While the protonema is growing by apical cell division, at some stage, under the influence of the phytohormone cytokinin, buds are induced which grow by three-faced apical cells. These give rise to gametophores, stems and leaf like structures. Bryophytes do not have true leaves (megaphylls A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
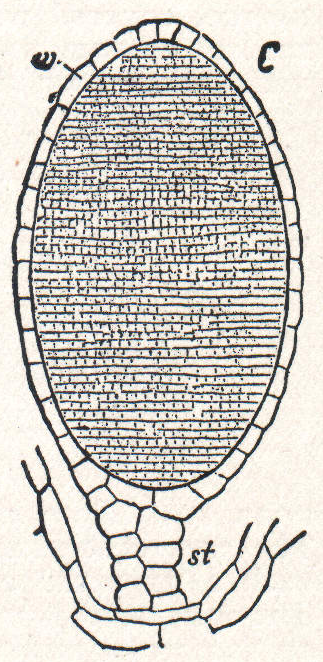
Sporophyte
A sporophyte () is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. Life cycle The sporophyte develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the seed plants, the largest groups of which are the gymnosperms and flowering plants (angiosperms), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, stem, leaves and cones or flowers. In flowering plants the gametophytes are very reduced in size, and are represented by the germinated pollen and the embryo sac. The sporophyte produces spores (hence t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
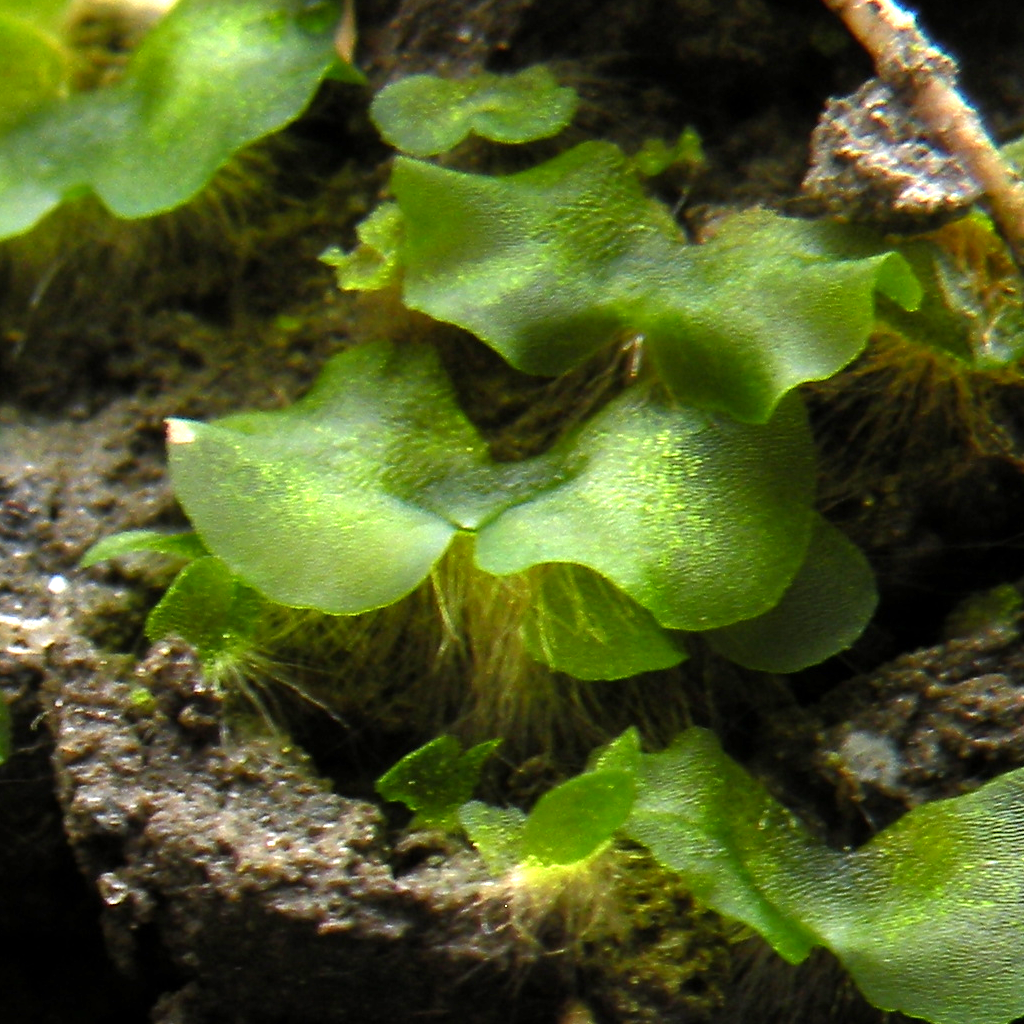
Gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the Sexual reproduction of plants, sexual phase in the life cycle of plants and algae. It develops sex organs that produce gametes, haploid sex cells that participate in fertilization to form a diploid zygote which has a double set of chromosomes. Cell division of the zygote results in a new diploid multicellular organism, the second stage in the life cycle known as the sporophyte. The sporophyte can produce haploid spores by meiosis that on germination produce a new generation of gametophytes. Algae In some multicellular green algae (''Ulva lactuca'' is one example), red algae and brown algae, sporophytes and gametophytes may be externally indistinguishable (isomorphic). In ''Ulva (genus), Ulv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in size and prefer moist habitats although they can survive in drier environments. The bryophytes consist of about 20,000 plant species. Bryophytes produce enclosed reproductive structures (gametangia and sporangia), but they do not produce flowers or seeds. They reproduce sexually by spores and asexually by fragmentation or the production of gemmae. Though bryophytes were considered a paraphyletic group in recent years, almost all of the most recent phylogenetic evidence supports the monophyly of this group, as originally classified by Wilhelm Schimper in 1879. The term ''bryophyte'' comes . Terminology The term "Bryophyta" was first suggested by Braun in 1864. G.M. Smith placed this group between Algae and Pteridophyta. Features The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
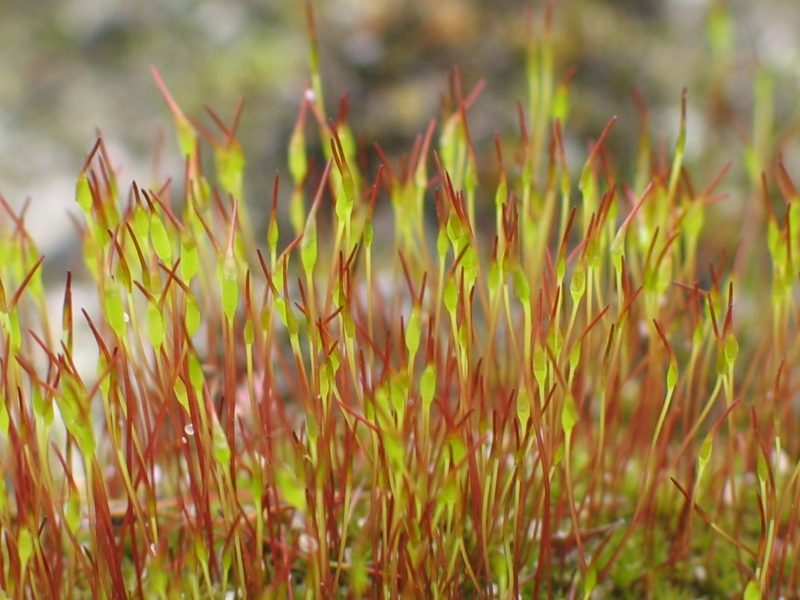
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)