|
Tomb Of Judgement, Lefkadia
The Tomb of Judgement ( el, τάφος της Κρίσεως, tafos tis kriseōs), also known as the Great Tomb of Lefkadia is an ancient Macedonian tomb of the Hellenistic period in Mieza (modern Lefkadia, near Naousa, Imathia), noted for its monumental painted facade. It was probably built at the beginning of the third century BC. Description The tomb consists of two vaulted chambers: an antechamber and a burial chamber and a disproportionately large monumental facade. The structure was covered by an earthen tumulus, which was 1.5 m high and had a diameter of about 10 m; it was removed during excavation. Facade The facade is 8.68 m wide and 8.6 m high. It once had a triangular pediment with a tympanum containing relief decoration, but this is almost entirely lost as a result of severe damage suffered by the facade in antiquity. Below this, there is an upper story with six Ionic columns ''in antis'', which are 1.46 m high. In between these columns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20160518 040 Mieza
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: * 16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * ''Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band *Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from ''Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", by Hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
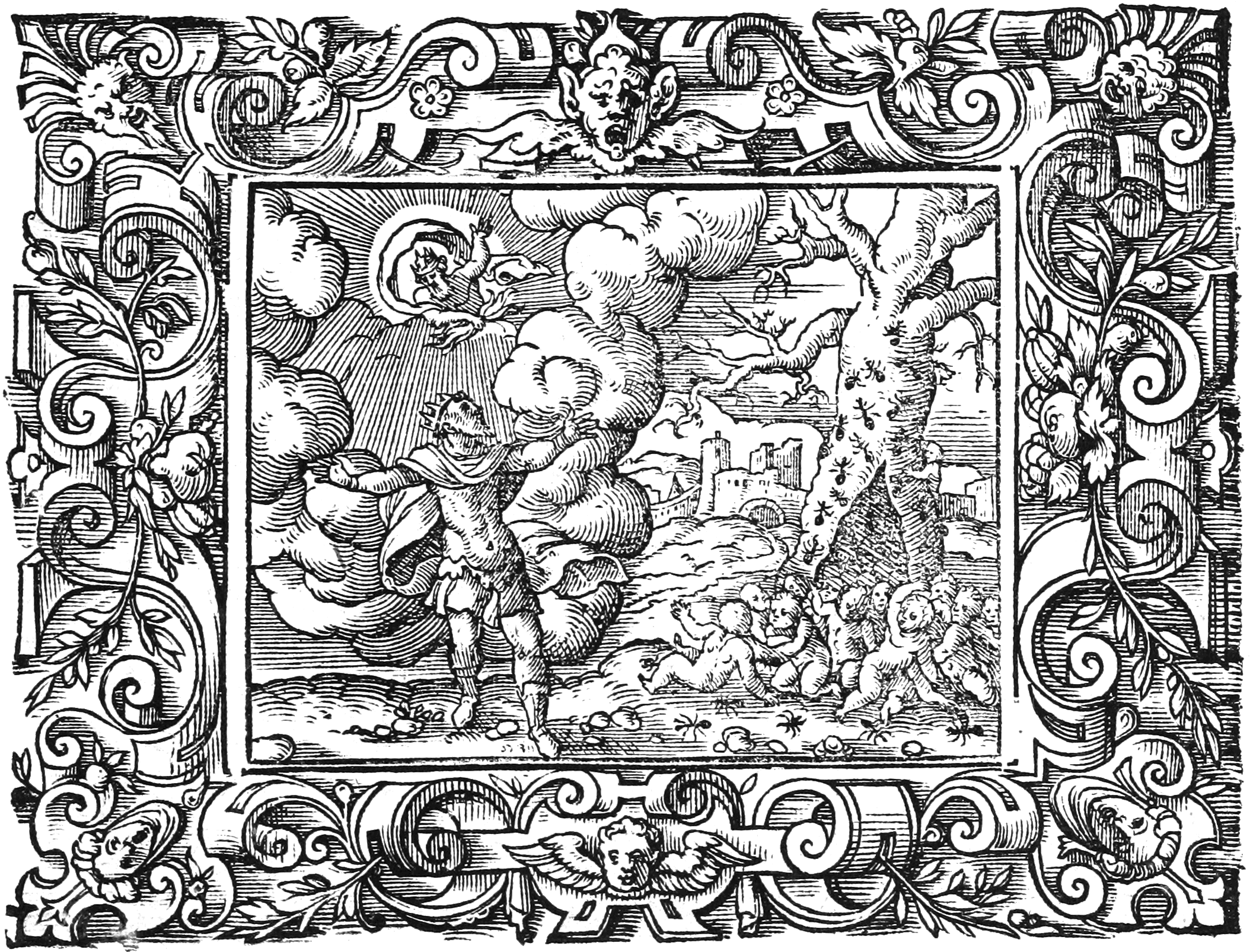
Rhadamanthys
In Greek mythology, Rhadamanthus () or Rhadamanthys ( grc, Ῥαδάμανθυς) was a wise king of Crete. As the son of Zeus and Europa he was considered a demigod. His name means "showing stern and inflexible judgement". He later became one of the judges of the dead and an important figure in Greek mythology. Family Rhadamanthus was, according to mythology, the son of Zeus and Europa and brother to Sarpedon and Minos (also a king and later a judge of the dead). Together with his brother, Rhadamanthus was raised by Asterion, their stepfather. He had two sons, Gortys (associated with Gortyn, Crete) and Erythrus (founder of Erythrae). Other sources (e.g. Plutarch, ''Theseus'' 20) credit Rhadamanthys rather than Dionysus as the husband of Ariadne, and the father of Oenopion, Staphylus and Thoas. In this account, Ariadne was the daughter of Minos, Rhadamanthys' brother; another Ariadne was the daughter of Minos's grandson and namesake, who features in Theseus's legend and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeacus
Aeacus (; also spelled Eacus; Ancient Greek: Αἰακός) was a mythological king of the island of Aegina in the Saronic Gulf. He was a son of Zeus and the nymph Aegina, and the father of the heroes Peleus and Telamon. According to legend, he was famous for his justice, and after he died he became one of the three judges in Hades alongside Minos and Rhadamanthos. In another story, he assisted Poseidon and Apollo in building the walls of Troy. He had sanctuaries in Athens and Aegina, and the Aeginetan festival of the Aeacea (Αἰάκεια) was celebrated in his honour. Family Aeacus was the son of Zeus by Aegina, a daughter of the river-god Asopus, and thus, brother of Damocrateia. In some accounts, his mother was Europa and thus possible brother to Minos, Rhadamanthus and Sarpedon. He was the father of Peleus, Telamon and Phocus and was the grandfather of the Trojan war warriors Achilles and Telemonian Ajax. In some accounts, Aeacus had a daughter called Alcima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petasus
A ''petasos'' or petasus ( el, πέτασος) is a broad brimmed hat of Thessalian origin worn by ancient Greeks, Thracians and Etruscans, often in combination with the chlamys cape. It was made of wool felt, leather, straw or animal skin. Women's versions had a high crown while those for men featured a lower crown. It was worn primarily by farmers, travellers and hunters, and was considered characteristic of rural people. Elite Greek men generally chose not to wear hats. As a winged hat, it became the symbol of Hermes, the Greek mythological messenger god. Along with the pileus, the petasos was the most common hat worn in Greece between 1200 and 146 B.C.E. Its wide brim protected the wearer from the sun and rain while a lengthy strap allowed wearers to secure it under the chin. When not needed, the hat was often worn hanging behind the head. Its popularity later extended to the Etruscans, the Byzantine Empire and the Roman Empire, in slightly modified forms. A type of metal he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also borne by heralds in general, for example by Iris, the messenger of Hera. It is a short staff entwined by two serpents, sometimes surmounted by wings. In Roman iconography, it was often depicted being carried in the left hand of Mercury, the messenger of the gods. Some accounts suggest that the oldest known imagery of the caduceus has its roots in Mesopotamia with the Sumerian god Ningishzida; his symbol, a staff with two snakes intertwined around it, dates back to 4000 BC to 3000 BC. As a symbolic object, it represents Hermes (or the Roman Mercury), and by extension trades, occupations, or undertakings associated with the god. In later Antiquity, the caduceus provided the basis for the astrological symbol representing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermes Psychopompus
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine, aided by his winged sandals. Hermes plays the role of the psychopomp or "soul guide"—a conductor of souls into the afterlife. In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. Hermes is regarded as "the divine trickster," about which the '' Homeric Hymn to Hermes'' offers the most well-known account. His attributes and symbols include the herma, the rooster, the tortoise, satchel or pouch, talaria (winged sandals), and winged helmet or simple petasos, as well as the palm tree, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish, and incense. However, his main symbol is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamys
The chlamys (Ancient Greek: χλαμύς : chlamýs, genitive: χλαμύδος : chlamydos) was a type of an ancient Greek cloak.Ancient Greek Dress ''Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History'', , 2000–2013. Retrieved 7 October 2013. By the time of the it was, although in a much larger form, part of the state costume of the emperor and high officials. It survived as such until at least the 12th century AD. The ephaptis (Ancient Greek: ἐφαπτίς) was a similar garment, typically worn by infantrymen.
|
Cuirass
A cuirass (; french: cuirasse, la, coriaceus) is a piece of armour that covers the torso, formed of one or more pieces of metal or other rigid material. The word probably originates from the original material, leather, from the French '' cuirace'' and Latin word '' coriacea''. The use of the term "cuirass" generally refers to both the chest plate (or breastplate) and the back piece together; whereas a breastplate only protects the front, a cuirass protects both the front and the back. Description In Hellenistic and Roman times, the musculature of the male torso was idealized in the form of the muscle cuirass or "heroic cuirass" (in French the ''cuirasse esthétique'') sometimes further embellished with symbolic representation in relief, familiar in the Augustus of Prima Porta and other heroic representations in official Roman sculpture. As parts of the actual military equipment of classical antiquity, cuirasses and corsets of bronze, iron, or some other rigid substance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiton
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora (), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized. They are also sometimes known as gumboots or sea cradles or coat-of-mail shells or suck-rocks, or more formally as loricates, polyplacophorans, and occasionally as polyplacophores. Chitons have a shell composed of eight separate shell plates or valves. These plates overlap slightly at the front and back edges, and yet articulate well with one another. Because of this, the shell provides protection at the same time as permitting the chiton to flex upward when needed for locomotion over uneven surfaces, and even allows the animal to curl up into a ball when dislodged from rocks. The shell plates are encircled by a skirt known as a girdle. Habitat Chitons live worldwide, from cold waters through to the tropics. They live on hard surfaces, such as on or under rocks, or in rock crevices. Some species live quite h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercolumniation
In architecture, intercolumniation is the proportional spacing between columns in a colonnade, often expressed as a multiple of the column diameter as measured at the bottom of the shaft. In Classical, Renaissance, and Baroque architecture, intercolumniation was determined by a system described by the first-century BC Roman architect Vitruvius (Vitruvius, ''De architectura'', iii.3.3-10). Vitruvius named five systems of intercolumniation (Pycnostyle, Systyle, Eustyle, Diastyle, and Araeostyle), and warned that when columns are placed three column-diameters or more apart, stone architraves break. According to Vitruvius, the Hellenistic architect Hermogenes (ca. 200 BC) formulated these proportions ("''symmetriae''") and perfected the Eustyle arrangement, which has an enlarged bay in the center of the façade. Standard intercolumniations The standard intercolumniations are: ; Pycnostyle : One and a half diameters ; Systyle : Two diameters ; Eustyle : Two and a quarter dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |