|
Tokanui, Waikato
Tokanui is a rural locality in the Waipa District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It is located southwest of Te Awamutu. runs to the east of the locality. History Te Mawhai railway station operated from 1887 to 1962, originally as Te Puhi railway station. Tokanui is the site of the former Tokanui Psychiatric Hospital, which operated from 1912 to 1997. The closure of the hospital resulted in the loss of 600 jobs, and there was little alternative employment available in the area. Tokanui Crossroads Hall The hall, at 4 Te Kawa Road, about south of Tokanui, opened on 18 January 1928. It is a converted casein factory, which had been working since at least 1919. Demographics Tokanui settlement is in an SA1 statistical area which covers . The SA1 area is part of the larger Tokanui statistical area. The SA1 area had a population of 144 at the 2018 New Zealand census, a decrease of 18 people (−11.1%) since the 2013 census, and a decrease of 9 people (− ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakepuku
Kakepuku (Kakipuku-o-kahurere) is a volcanic cone which rises from the plain between the Waipā and Puniu rivers, about NW of Te Kawa and SW of Te Awamutu in the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. Geology The 'Geology of the Waikato Area' says, "The Alexandra Volcanic Group consists of several low-angle composite cones, including Karioi, Pirongia, Kakepuku, Te Kawa and Tokanui volcanoes, aligned southeast from Mount Karioi on the coast to Tokanui. They comprise about 55 km3 of mainly basaltic material erupted from at least 40 volcanic centres. The Alexandra Volcanic Group is the product oflate Pliocene to earliest Pleistocene back-arc volcanism, when both subduction-related basaltic magmas (Karioi, Pirongia, Kakepuku and Te Kawa) and intraplate alkalic basalts (Okete) were erupted. K-Ar ages range from 2.74 to 1.6 Ma, with the ages of the different magma series overlapping". It goes on to say Kakepuku is "composed mainly of basalt lava with minor tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people with an estimated 60% of Māori pledging allegiance to the Christian message within the first 35 years. It remains New Zealand's largest religious group despite there being no official state church. Today, slightly less than half the population identify as Christian. The largest Christian groups are Catholic, Anglican and Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian services conducted in New Zealand were carried out by Father Paul-Antoine Léonard de Villefeix, the Dominican chaplain on the ship ''Saint Jean Baptiste'' commanded by the French navigator and explorer Jean-François-Marie de Surville. Villefeix was the first Christian minister to set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Aggregate
Construction aggregate, or simply aggregate, is a broad category of coarse- to medium-grained particulate material used in construction, including sand, gravel, crushed stone, slag, recycled concrete and geosynthetic aggregates. Aggregates are the most mined materials in the world. Aggregates are a component of composite materials such as concrete and asphalt; the aggregate serves as reinforcement to add strength to the overall composite material. Due to the relatively high hydraulic conductivity value as compared to most soils, aggregates are widely used in drainage applications such as foundation and French drains, septic drain fields, retaining wall drains, and roadside edge drains. Aggregates are also used as base material under foundations, roads, and railroads. In other words, aggregates are used as a stable foundation or road/rail base with predictable, uniform properties (e.g. to help prevent differential settling under the road or building), or as a low-cost exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987. In European lithostratigraphy, the name "Malm" indicates rocks of Late Jurassic age. In the past, ''Malm'' was also used to indicate the unit of geological time, but this usage is now discouraged to make a clear distinction between lithostratigraphic and geochronologic/chronostratigraphic units. Subdivisions The Late Jurassic is divided into three ages, which correspond with the three (faunal) stages of Upper Jurassic rock: Paleogeography During the Late Jurassic Epoch, Pangaea broke up into two supercontinents, Laurasia to the north, and Gondwana to the south. The result of this break-up was the spawning of the Atlantic Ocean. However, at this time, the Atlantic Ocean was relatively narrow. Life forms of the epoch This epoch is well known for many famous types of dinosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
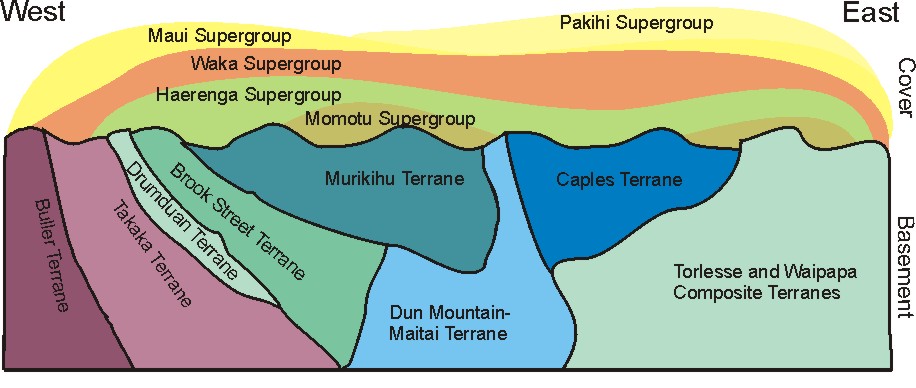
Stratigraphy Of New Zealand
This is a list of the units into which the rock succession of New Zealand is formally divided. As new geological relationships have been discovered new names have been proposed and others are made obsolete. Not all these changes have been universally adopted. This table is based on the 2014 New Zealand Stratigraphic Lexicon (Litho2014). However, obsolete names that are still in use and names postdating the lexicon are included if it aids in understanding. Names for particular rock units have two parts, a proper name which is almost always a geographic location where the rock is found and a hierarchical rank (e.g. Waitematā Group). This ranking system starts with individual 'beds' of rock which can be grouped into 'members', members are grouped into 'formations', formations into 'subgroups' then 'groups'. In New Zealand, groups are further combined into 'supergroups' or for basement rocks into terranes. Not all of these hierarchical layers are necessarily present within a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke (German ''grauwacke'', signifying a grey, earthy rock) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness, dark color, and poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or lithic fragments set in a compact, clay-fine matrix. It is a texturally immature sedimentary rock generally found in Paleozoic strata. The larger grains can be sand- to gravel-sized, and matrix materials generally constitute more than 15% of the rock by volume. The term "greywacke" can be confusing, since it can refer to either the immature (rock fragment) aspect of the rock or its fine-grained (clay) component. The origin of greywacke was unknown until turbidity currents and turbidites were understood, since, according to the normal laws of sedimentation, gravel, sand and mud should not be laid down together. Geologists now attribute its formation to submarine avalanches or strong turbidity currents. These actions churn sediment and cause mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argillaceous Mineral
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates (e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4), sometimes with variable amounts of iron, magnesium, alkali metals, alkaline earths, and other cations found on or near some planetary surfaces. Clay minerals form in the presence of water and have been important to life, and many theories of abiogenesis involve them. They are important constituents of soils, and have been useful to humans since ancient times in agriculture and manufacturing. Properties Clay is a very fine-grained geologic material that develops plasticity when wet, but becomes hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. It is a very common material, and is the oldest known ceramic. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. The chemistry of clay, including its capacity to retain nutrient cations such as potassium and ammonium, is important to soil fertility. Because the individual particles in clay are less than i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandra Volcanic Group
The Alexandra Volcanic Group (also known as Alexandra volcanic lineament or Alexandra Volcanics) is a chain of extinct calc-alkalic basaltic stratovolcanoes that were most active between 2.74 to 1.60 million years ago but is now known to have had more recent activity between 1.6 to 0.9 million years ago. They extend inland from Mount Karioi near Raglan with Mount Pirongia being the largest, with Pukehoua on the eastern slopes of Pirongia, Kakepuku, Te Kawa, and Tokanui completing the definitive lineament. The associated, but usually separated geologically basaltic monogenetic Okete volcanic field (also known as the Okete Volcanic Formation or Okete Volcanics), lies mainly between Karioi and Pirongia but extends to the east and is quite scattered. Geology The chain extends in the Alexandra volcanic lineament, an alignment striking north-west to south-east over in length and is an example of backarc, intraplate basaltic volcanism that is very rare on land. This is because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In New Zealand
Hinduism is the second largest religion in New Zealand. It is also one of the fastest-growing religions in New Zealand. According to the 2018 census, Hindus form 2.65% of the population of New Zealand. There are about 123,534 Hindus in New Zealand. Hindus from all over India continue to immigrate today, with the largest Indian ethnic subgroup being Gujaratis. A later wave of immigrants also includes Hindu immigrants who were of Indian descent from nations that were historically under European colonial rule, such as Fiji. Today there are Hindu temples in all major New Zealand cities. History Early settlement In 1836 the missionary William Colenso saw Māori women near Whangarei using a broken bronze bell to boil potatoes. The inscription is in very old Tamil script. This discovery has led to speculation that Tamil-speaking Hindus may have visited New Zealand hundreds of years ago. However, the first noted settlement of Hindus in New Zealand dates back to the arrival of sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |