|
Timor And Wetar Deciduous Forests
The Timor and Wetar deciduous forests is a tropical dry forest ecoregion in Indonesia and East Timor. The ecoregion includes the islands of Timor, Wetar, Rote, Savu, and adjacent smaller islands. Geography Timor, Wetar, Rote, and Savu are part of the Lesser Sunda Islands. The ecoregion is part of Wallacea, a group of islands that are part of the Australasian realm, but were never joined to either the Australian or Asian continents. The islands of Wallacea are home to a mix of plants and animals from both terrestrial realms, and have many unique species that evolved in isolation. Timor is the largest of the islands at 30,777 km². Timor is politically divided; The independent country of Timor Leste is on the eastern portion of Timor, and western Timor and the other islands are part of Indonesia. Western Timor, Rote, and Savu are part of East Nusa Tenggara province, while Wetar is part of Maluku Province. The islands are mostly mountainous, and Tatamailau on Timor is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corypha Utan
''Corypha utan'', the cabbage palm, buri palm or gebang palm, is a species of palm native to Asia and Oceania. Description It grows up to tall, and, on the York Peninsula of Queensland, up to 1.5 meters (4' 11") thick (exceeded only by Borassus aethiopum and Jubaea chilensis.) and bears fronds long. Like other palms of genus ''Corypha'', this species flowers at the end of its lifetime (monocarpy), producing a massive inflorescence up to 5 m tall containing up to one million flowers.''Corypha utan'' Palm and Cycad Societies of Australia web page Accessed 20 June 2009 Distribution and habitat It is distributed from the region of |
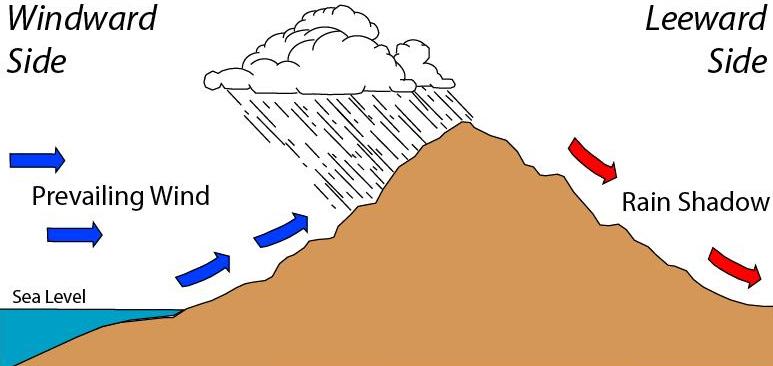
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands or even deserts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
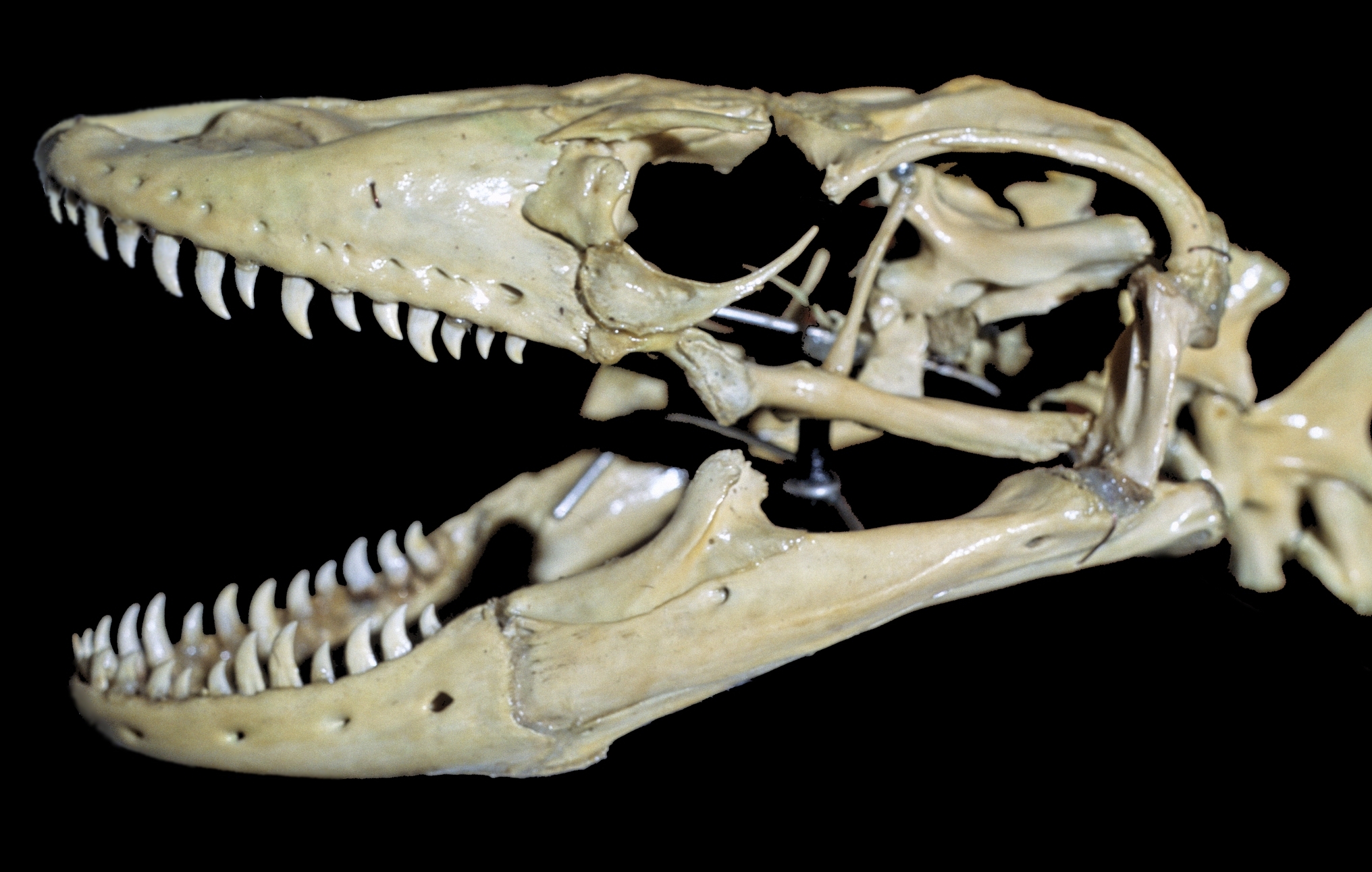
Komodo Dragon
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant species of lizard, growing to a maximum length of , and weighing up to . As a result of their size, Komodo dragons are apex predators, and dominate the ecosystems in which they live. Komodo dragons hunt and ambush prey including invertebrates, birds, and mammals. It has been claimed that they have a venomous bite; there are two glands in the lower jaw that secrete several toxic proteins. The biological significance of these proteins is disputed, but the glands have been shown to secrete an anticoagulant. Komodo dragons' group behavior in hunting is exceptional in the reptile world. The diet of Komodo dragons mainly consists of Javan rusa (''Rusa timorensis''), though they also eat considerable amounts of carrion. Komodo dragons also occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
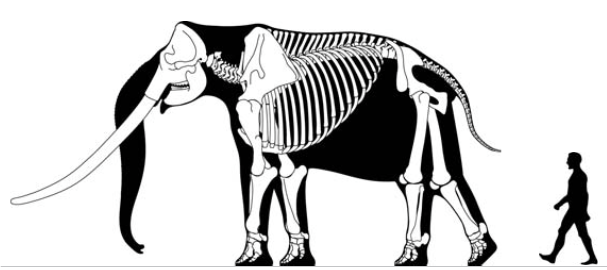
Stegodon
''Stegodon'' ("roofed tooth" from the Ancient Greek words , , 'to cover', + , , 'tooth' because of the distinctive ridges on the animal's molars) is an extinct genus of proboscidean, related to elephants. It was originally assigned to the family Elephantidae along with modern elephants but is now placed in the extinct family Stegodontidae. Like elephants, ''Stegodon'' had teeth with plate-like lophs that are different from those of more primitive proboscideans like gomphotheres and mastodons. The oldest fossils of the genus are found in Late Miocene strata in Asia, likely originating from the more archaic ''Stegolophodon,'' shortly afterwards migrating into Africa. While the genus became extinct in Africa during the Pliocene, ''Stegodon'' remained widespread in Asia until the end of the Pleistocene. Morphology Size Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the Yellow River that is tall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coryphomys
''Coryphomys'' is an extinct genus of rats, known from sub-fossils found on Timor. Its name is Greek for "top-of-the-head mouse A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ..." or "summit mouse". Species include '' Coryphomys buhleri'' and '' Coryphomys musseri''. Archaeological research on East Timor has revealed the bones of rats weighing up to 6 kilograms (13.2 pounds) when adult. They seem to have died out between 1000 and 2000 years ago, perhaps due to large-scale forest clearance for farming. In 2015, the discovery of fossils of "seven new species of giant rat", including the "largest rat ever" on the island of East Timor was announced. The biggest of these rats was described as weighing "five kilos (11 pounds), the size of a small dog," and was referred to as the "Giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javan Rusa
The Javan rusa or Sunda sambar (''Rusa timorensis'') is a deer native to Indonesia and East Timor. Introduced populations exist in a wide variety of locations in the Southern Hemisphere. Taxonomy Seven subspecies of the Javan rusa are recognised: *''R. t. timorensis'' (Timor rusa deer) – Timor. *''R. t. djonga'' – Muna and Butung Islands. *''R. t. floresiensis'' (Flores rusa deer) – Flores and other islands. *''R. t. macassaricus'' (Celebes rusa deer) – Celebes. *''R. t. moluccensis'' (Moluccan rusa deer) – Molucca Islands. *''R. t. renschi'' – Bali. *''R. t. russa'' (Javan rusa deer) – Java. Characteristics The Javan rusa is dark blackish brown and has a grey forehead. Its back is almost black, the underparts and inner thighs are yellowish brown. The abdomen is lighter brown, and the tail tuft is dark blackish brown. The hair is coarse and longer on the chest than on the remaining body. Its ears are wide and a little shorter than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Common Cuscus
The northern common cuscus (''Phalanger orientalis''), also known as the gray cuscus, is a species of marsupial in the family Phalangeridae native to northern New Guinea and adjacent smaller islands, but is now also found in the Bismarck Archipelago, southeast and central Moluccas, the Solomons, and Timor, where it is believed to have been introduced in prehistoric times from New Guinea. It was formerly considered conspecific with the allopatric '' P. intercastellanus'' and '' P. mimicus''. It is hunted for human consumption in New Guinea. Names It is known as ''laku ita'' in the Naueti language or ''meda'' in the Tetum Terik Tetum language of Timor-Leste. Habitat The northern common cuscus normally inhabits disturbed habitats. These would include secondary forest, plantations, and gardens. This species is also found in primary tropical forests.Leary, T., Singadan, R., Menzies, J., Helgen, K., Wright, D., Allison, A., Hamilton, S., Salas, L. & Dickman, C. 2008. Phalanger orie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timor Rat
The Timor rat (''Rattus timorensis'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae found in Indonesian West Timor, where it lives in the teak forests. It is known from a specimen collected near the summit of Mount Mutis Mount Mutis ( id: Gunung Mutis), also known as Nuaf Nefomasi, is a mountain and highest point of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia, at above sea level. It is located in the Gunung Mutis Nature Reserve in the South Central Timor Regency, from Kupang, .... References Rattus Rats of Asia Endemic fauna of Indonesia Rodents of Indonesia Mammals of Timor Fauna of the Lesser Sunda Islands Vulnerable fauna of Asia Mammals described in 1991 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Rattus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timor Shrew
The Timor shrew or thin shrew (''Crocidura tenuis'') is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Timor Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, .... References Crocidura Mammals of Timor Mammals of Indonesia Fauna of the Lesser Sunda Islands Vulnerable fauna of Asia Mammals described in 1840 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{whitetoothed-shrew-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleurites Moluccanus
''Aleurites moluccanus'', the candlenut, is a flowering tree in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, also known as candleberry, Indian walnut, ''kemiri'', varnish tree, ''nuez de la India'', ''buah keras'', ''godou'', kukui nut tree, and ''rata kekuna''. Description The candlenut grows to a height of up to , with wide spreading or pendulous branches. The leaves are pale green, simple, and ovate or heart-shaped on mature shoots, but may be three-, five-, or seven-lobed on saplings. They are up to long and wide and young leaves are densely clothed in rusty or cream stellate hairs. Petioles measure up to long and stipules about . Flowers are small—male flowers measure around in diameter, female flowers about . The fruit is a drupe about in diameter with one or two lobes; each lobe has a single soft, white, oily, kernel contained within a hard shell which is about in diameter. The kernel is the source of candlenut oil. Taxonomy This plant was first described by Carl Linnaeu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santalum Album
''Santalum album'', or Indian sandalwood, is a small tropical tree, and the traditional source of sandalwood oil. It is native to southern India and Southeast Asia. It is considered sacred in some religions like Hinduism, and some cultures place great significance on its fragrant qualities. However, the high value of the species has caused over-exploitation, to the point where the wild population is vulnerable to extinction. Indian sandalwood still commands high prices for its essential oil owing to its high alpha santalol content, but due to lack of sizable trees it is no longer used for fine woodworking as before. The plant is long-lived, but harvest is only viable after many years. Description The height of the evergreen tree is between 4 and 9 metres. They may live to one hundred years of age. The tree is variable in habit, usually upright to sprawling, and may intertwine with other species. The plant parasitises the roots of other tree species, with a haustorium adaptatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |