|
Time Crystal
In condensed matter physics, a time crystal is a quantum system of particles whose lowest-energy state is one in which the particles are in repetitive motion. The system cannot lose energy to the environment and come to rest because it is already in its quantum ground state. Time crystals were first proposed theoretically by Frank Wilczek in 2012 as a time-based analogue to common crystals – whereas the atoms in crystals are arranged periodically in space, the atoms in a time crystal are arranged periodically in both space and time. Several different groups have demonstrated matter with stable periodic evolution in systems that are periodically driven. In terms of practical use, time crystals may one day be used as quantum computer memory. The existence of crystals in nature is a manifestation of spontaneous symmetry breaking, which occurs when the lowest-energy state of a system is less symmetrical than the equations governing the system. In the crystal ground state, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid State of matter, phases, that arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms and electrons. More generally, the subject deals with condensed phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions among them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconductivity, superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at extremely low cryogenic temperatures, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of Spin (physics), spins on crystal lattices of atoms, the Bose–Einstein condensates found in ultracold atomic systems, and liquid crystals. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theoretical physics, physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; it is said to be Conservation law, ''conserved'' over time. In the case of a Closed system#In thermodynamics, closed system, the principle says that the total amount of energy within the system can only be changed through energy entering or leaving the system. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy is Energy conversion, converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, the conservation of energy was distinct from the conservation of mass. However, special relativity shows that mass is related to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Many-body Problem
The many-body problem is a general name for a vast category of physical problems pertaining to the properties of microscopic systems made of many interacting particles. Terminology ''Microscopic'' here implies that quantum mechanics has to be used to provide an accurate description of the system. ''Many'' can be anywhere from three to infinity (in the case of a practically infinite, homogeneous or periodic system, such as a crystal), although three- and four-body systems can be treated by specific means (respectively the Faddeev and Faddeev–Yakubovsky equations) and are thus sometimes separately classified as few-body systems. Explanation of the problem In general terms, while the underlying physical laws that govern the motion of each individual particle may (or may not) be simple, the study of the collection of particles can be extremely complex. In such a quantum system, the repeated interactions between particles create quantum correlations, or entanglement. As a consequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period-doubling Bifurcation
In dynamical systems theory, a period-doubling bifurcation occurs when a slight change in a system's parameters causes a new periodic trajectory to emerge from an existing periodic trajectory—the new one having double the period of the original. With the doubled period, it takes twice as long (or, in a discrete dynamical system, twice as many iterations) for the numerical values visited by the system to repeat themselves. A period-halving bifurcation occurs when a system switches to a new behavior with half the period of the original system. A period-doubling cascade is an infinite sequence of period-doubling bifurcations. Such cascades are one route by which dynamical systems can develop chaos. In hydrodynamics, they are one of the possible routes to turbulence. Examples Logistic map The logistic map is :x_ = r x_n (1 - x_n) where x_n is a function of the (discrete) time n = 0, 1, 2, \ldots. The parameter r is assumed to lie in the interval ,4/math>, in which case x_n is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametric Down-conversion
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion (also known as SPDC, parametric fluorescence or parametric scattering) is a nonlinear instant optical process that converts one photon of higher energy (namely, a ''pump'' photon) into a pair of photons (namely, ''signal'' and ''idler'' photons) of lower energy, in accordance with the laws of law of conservation of energy, energy conservation and law of conservation of momentum, momentum conservation. It is an important process in quantum optics, for the generation of photon entanglement, entangled photon pairs and of single photons. Description A Nonlinear optics, nonlinear crystal is used to produce pairs of photons from a photon beam. In accordance with conservations of energy and momentum, the pairs need to have combined energies and momenta equal to the energy and momentum of the original photon. Because the index of refraction changes with frequency (Dispersion (optics), dispersion), only certain triplets of frequencies will be phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
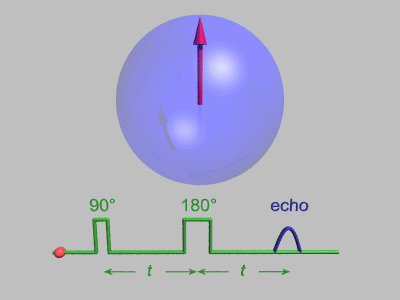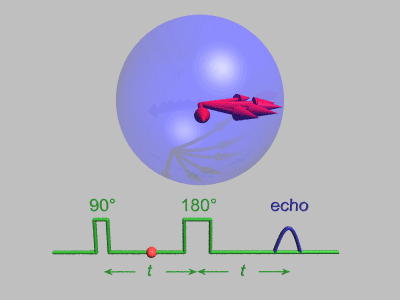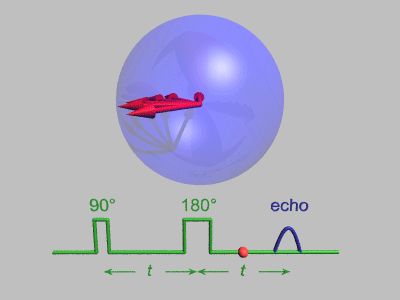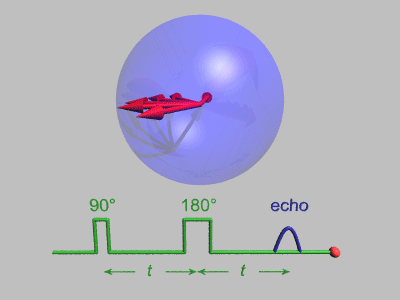
Spin Echo
In magnetic resonance, a spin echo or Hahn echo is the refocusing of spin magnetisation by a pulse of resonant electromagnetic radiation. Modern nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make use of this effect. The NMR signal observed following an initial excitation pulse decays with time due to both spin relaxation and any ''inhomogeneous'' effects which cause spins in the sample to precess at different rates. The first of these, relaxation, leads to an irreversible loss of magnetisation. But the inhomogeneous dephasing can be removed by applying a 180° ''inversion'' pulse that inverts the magnetisation vectors. Examples of inhomogeneous effects include a magnetic field gradient and a distribution of chemical shifts. If the inversion pulse is applied after a period ''t'' of dephasing, the inhomogeneous evolution will rephase to form an echo at time 2''t''. In simple cases, the intensity of the echo relative to the initial signal is given by '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crysta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Wave
Faraday waves, also known as Faraday ripples, named after Michael Faraday (1791–1867), are nonlinear standing waves that appear on liquids enclosed by a vibrating receptacle. When the vibration frequency exceeds a critical value, the flat hydrostatic surface becomes unstable. This is known as the Faraday instability. Faraday first described them in an appendix to an article in the ''Philosophical Transactions'' of the Royal Society of London in 1831. If a layer of liquid is placed on top of a vertically oscillating piston, a pattern of standing waves appears which oscillates at half the driving frequency, given certain criteria of instability. This relates to the problem of parametric resonance. The waves can take the form of stripes, close-packed hexagons, or even squares or quasiperiodic patterns. Faraday waves are commonly observed as fine stripes on the surface of wine in a wine glass that is ringing like a bell. Faraday waves also explain the 'fountain' phenomenon on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroelasticity
Aeroelasticity is the branch of physics and engineering studying the interactions between the inertial, elastic, and aerodynamic forces occurring while an elastic body is exposed to a fluid flow. The study of aeroelasticity may be broadly classified into two fields: ''static aeroelasticity'' dealing with the static or steady state response of an elastic body to a fluid flow, and ''dynamic aeroelasticity'' dealing with the body's dynamic (typically vibrational) response. Aircraft are prone to aeroelastic effects because they need to be lightweight while enduring large aerodynamic loads. Aircraft are designed to avoid the following aeroelastic problems: # divergence where the aerodynamic forces increase the twist of a wing which further increases forces; # control reversal where control activation produces an opposite aerodynamic moment that reduces, or in extreme cases reverses, the control effectiveness; and # flutter which is uncontained vibration that can lead to the destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Oscillator
In chemistry, a chemical oscillator is a complex mixture of reacting chemical compounds in which the concentration of one or more components exhibits periodic changes. They are a class of reactions that serve as an example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics with far-from-equilibrium behavior. The reactions are theoretically important in that they show that chemical reactions do not have to be dominated by equilibrium thermodynamic behavior. In cases where one of the reagents has a visible color, periodic color changes can be observed. Examples of oscillating reactions are the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction (BZ reaction), the Briggs–Rauscher reaction, and the Bray–Liebhafsky reaction. History The earliest scientific evidence that such reactions can oscillate was met with extreme scepticism. In 1828, G.T. Fechner published a report of oscillations in a chemical system. He described an electrochemical cell that produced an oscillating current. In 1899, W. Ostwald observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection Cells
In fluid dynamics, a convection cell is the phenomenon that occurs when density differences exist within a body of liquid or gas. These density differences result in rising and/or falling convection currents, which are the key characteristics of a convection cell. When a volume of fluid is heated, it expands and becomes less dense and thus more buoyant than the surrounding fluid. The colder, denser part of the fluid descends to settle below the warmer, less-dense fluid, and this causes the warmer fluid to rise. Such movement is called convection, and the moving body of liquid is referred to as a ''convection cell''. This particular type of convection, where a horizontal layer of fluid is heated from below, is known as Rayleigh–Bénard convection. Convection usually requires a gravitational field, but in microgravity experiments, thermal convection has been observed without gravitational effects. Fluids are generalized as materials that exhibit the property of flow; however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Ball
Philip Ball (born 1962) is a British science writer. For over twenty years he has been an editor of the journal ''Nature'', for which he continues to write regularly. He is a regular contributor to '' Prospect'' magazine and a columnist for ''Chemistry World'', '' Nature Materials'', and ''BBC Future''. Biography Ball holds a degree in chemistry from Oxford and a doctorate in physics from Bristol University. Ball's 2004 book '' Critical Mass: How One Thing Leads to Another'' won the 2005 Aventis Prize for Science Books. It examines a wide range of topics including the business cycle, random walks, phase transitions, bifurcation theory, traffic flow, Zipf's law, Small world phenomenon, catastrophe theory, the Prisoner's dilemma. The overall theme is one of applying modern mathematical models to social and economic phenomena.Harkin, James. (2004)''Critical Mass – How One Thing Leads to Another'' ''The Independent''. In 2011, Ball published ''The Music Instinct'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |