|
Tidarren Argo
''Tidarren argo'' is a spider from Yemen. The species is remarkable by its male amputating one of its palps before maturation and entering his adult life with one palp only. It adopts exceptional copulatory behaviour: when the male achieves genitalia coupling with his palp, the latter is torn off by the female. The separated gonopod remains attached to the female's epigynum for approximately 4 hours and continues to function independently, serving as a mating plug. While this happens, the female feeds on the male. Emasculation thus synchronizes sexual cannibalism and sperm transfer, lengthening the interval between copulations. This mating behaviour might allow for the continuation of insemination Insemination is the introduction of sperm into a female’s reproductive system for the purpose of impregnating, also called fertilizing, the female for sexual reproduction. The sperm is introduced into the uterus of a mammal or the oviduct of an ... by the dismembered palp. Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palps
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
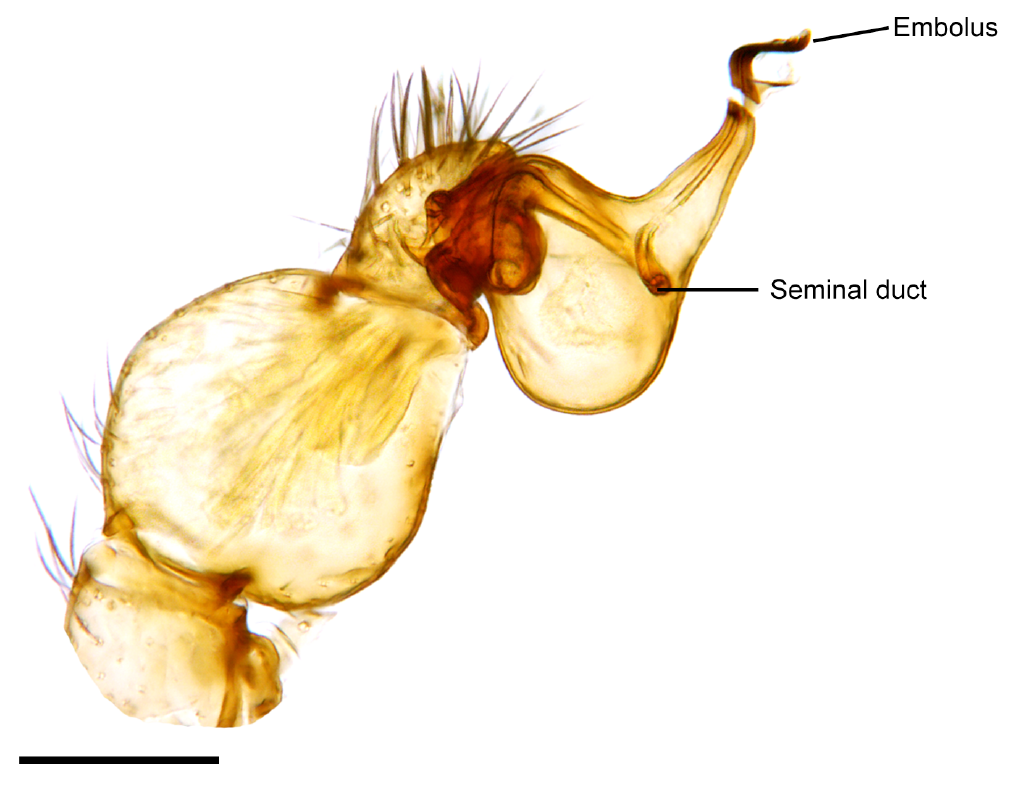
Gonopod
Gonopods are specialized appendages of various arthropods used in reproduction or egg-laying. In males, they facilitate the transfer of sperm from male to female during mating, and thus are a type of intromittent organ. In crustaceans and millipedes, gonopods are modified walking or swimming legs. Gonopods may be highly decorated with elaborate structures which may play roles in sperm competition, and can be used to differentiate and identify closely related species. Gonopods generally occur in one or more pairs, as opposed to the single (un-paired) reproductive organs such as the aedeagus of insects or the Opiliones penis, penis of harvestmen. Insects In insects, gonopods are appendages of the genital segment that may be used in insemination, or that comprise the egg-laying apparatus. Crustaceans In male decapoda, decapod crustaceans, gonopods are modified swimming appendages (pleopods). The anterior two pair of pleopods in males are modified for sperm transferring, with dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigynum (spider)
The epigyne or epigynum is the external genital structure of female spiders. As the epigyne varies greatly in form in different species, even in closely related ones, it often provides the most distinctive characteristic for recognizing species. It consists of a small, hardened portion of the exoskeleton located on the underside of the abdomen, in front of the epigastric furrow and between the epigastric plates. Functions The primary function of the epigyne is to receive and direct the palpal organ of the male during copulation. The various specific forms of epigynes are correlated, in each case, with corresponding specific differences in the palpus of the male. This specialization prevents individuals of different species from mating. The epigyne covers or accompanies the openings of the spermathecae, which are pouches for receiving and retaining sperm. Frequently, the openings of the spermathecae are on the outer face of the epigyne and can be easily seen. A secondary functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating Plug
A mating plug, also known as a copulation plug, sperm plug, vaginal plug, or sphragis (Latin, from Greek σφραγίς ''sphragis'', "a seal"), is gelatinous secretion used in the mating of some species. It is deposited by a male into a female genital tract, such as the vagina, and later hardens into a plug or glues the tract together. While females can expel the plugs afterwards, the male's sperm still gets a time advantage in getting to the egg, which is often the deciding factor in fertilization. The mating plug plays an important role in sperm competition and may serve as an alternative and more advantageous strategy to active mate guarding. In some species, such a passive mate-guarding strategy may reduce selection on large male size. Such a strategy may be advantageous because it would allow a male to increase reproductive success by spending more time pursuing new female mates rather than active mate guarding. Composition The mating plug of the ''Bombus terrestris'' was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emasculation
Emasculation is the removal of both the penis and the testicles, the external male sex organs. It differs from castration, which is the removal of the testicles only, although the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. The potential medical consequences of emasculation are more extensive than those associated with castration, as the removal of the penis gives rise to a unique series of complications. There are a range of religious, cultural, punitive, and personal reasons why someone may choose to emasculate themselves or another person. Consensual emasculation may be seen as a form of body modification that enhances a recipient's identification with their community or sense of self. By comparison, non-consensual emasculations, such as those performed punitively or accidentally, may constitute genital mutilation. The medical treatment for an emasculated person differs depending on whether the procedure was consensual. The term ''emasculation'' may be used metaphorically to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Cannibalism
Sexual cannibalism is when an animal, usually the female, cannibalizes its mate prior to, during, or after copulation.Polis, G.A. & Farley, R.D. Behavior and Ecology of Mating in the journal of Arachnology 33-46 (1979). It is a trait observed in many arachnid orders and several insect orders. Several hypotheses to explain this seemingly paradoxical behavior have been proposed. The adaptive foraging hypothesis,Blamires, S.J. Nutritional implications for sexual cannibalism in a sexually dimorphic orb web spider. Austral Ecology 36, 389-394 (2011). aggressive spillover hypothesisArnqvist, G. Courtship behaviour and sexual cannibalism in the semi-aquatic fishing spider, DOLOMEDES FIMBRIATUS (CLERCK) (ARANEAE: PISAURIDAE).pdf. The journal of Arachnology 20, 222-226 (1992). and mistaken identity hypothesisGould, S. Only his wings remained. Natural History 93, 10-18 (1984). are among the proposed hypotheses to explain how sexual cannibalism evolved. This behavior is believed to have evolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copulation (zoology)
In zoology, copulation is animal sexual behavior in which a male introduces sperm into the female's body, especially directly into her reproductive tract. This is an aspect of mating. Many animals that live in water use external fertilization, whereas internal fertilization may have developed from a need to maintain gametes in a liquid medium in the Late Ordovician epoch. Internal fertilization with many vertebrates (such as all reptiles, some fish, and most bird Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...s) occurs via cloacal copulation, known as cloacal kiss (see also hemipenis), while mammals copulate vaginally, and many primitive (biology), basal vertebrates reproduce sexually with external fertilization. In spiders and insects Spiders are often confused with insects, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insemination
Insemination is the introduction of sperm into a female’s reproductive system for the purpose of impregnating, also called fertilizing, the female for sexual reproduction. The sperm is introduced into the uterus of a mammal or the oviduct of an oviparous (egg-laying) animal. In mammals, insemination normally occurs during sexual intercourse or copulation, but insemination can take place in other ways, such as by artificial insemination. In humans, the act and form of insemination has legal, moral and interpersonal implications. However, whether insemination takes place naturally or by artificial means, the pregnancy and the progress of it will be the same. Insemination may be called ''in vivo'' fertilisation (from ''in vivo'' meaning "within the living") because an egg is fertilized inside the body, this is in contrast with in vitro fertilisation (IVF). In plants, the fertilization process is referred to as pollination. It is the process of transfer of pollen grains from one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theridiidae
Theridiidae, also known as the tangle-web spiders, cobweb spiders and comb-footed spiders, is a large family of Araneomorphae, araneomorph spiders first described by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833. This diverse, globally distributed family includes over 3,000 species in 124 genus, genera, and is the most common arthropod found in human dwellings throughout the world. Theridiid spiders are both Entelegynae, entelegyne, meaning that the females have a genital plate, and Cribellum, ecribellate, meaning that they spin sticky capture silk instead of woolly silk. They have a comb of serrated bristles (setae) on the Arthropod leg, tarsus of the fourth leg. The family includes some model organisms for research, including the List of medically significant spider bites, medically important Latrodectus, widow spiders. They are important to studies characterizing their venom and its clinical manifestation, but widow spiders are also used in research on spider silk and sexual biology, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Of Asia
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all Order (biology), orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 Family (biology), families have been recorded by Taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segmentation (biology), segments are fused into two Tagma (biology), tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |