|
Tiazesim
Tiazesim (), or thiazesim (, ), previously sold under the brand name Altinil, is a heterocyclic antidepressant related to the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) which, first introduced in 1966 by Squibb Corporation (now Bristol-Myers Squibb), has since been discontinued and is no longer marketed. See also * Diltiazem * Tofenacin Tofenacin is an antidepressant drug with a tricyclic-like structure which was developed and marketed in the United Kingdom and Italy in 1971 and 1981, respectively, by Brocades-Stheeman & Pharmacia (now part of Astellas Pharma). It acts as a ser ... References Dimethylamino compounds Benzothiazepines Antidepressants Lactams {{Nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tofenacin
Tofenacin is an antidepressant drug with a tricyclic-like structure which was developed and marketed in the United Kingdom and Italy in 1971 and 1981, respectively, by Brocades-Stheeman & Pharmacia (now part of Astellas Pharma). It acts as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and based on its close relation to orphenadrine, may also possess anticholinergic and antihistamine properties. Tofenacin is also the major active metabolite of orphenadrine and likely plays a role in its beneficial effects against depressive symptoms seen in Parkinson's disease patients. See also * Clemastine * Orphenadrine * Tiazesim Tiazesim (), or thiazesim (, ), previously sold under the brand name Altinil, is a heterocyclic antidepressant related to the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) which, first introduced in 1966 by Squibb Corporation (now Bristol-Myers Squibb), has ... References Abandoned drugs Amines Astellas Pharma Antidepressants Ethers Muscarinic antagonists Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amines into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. Additionally, many hydrochlorides of amines have a longer shelf-life than their respective free bases. Amine hydrochlorides represent latent forms of a more reactive free base. In this regard, formation of an amine hydrochloride confers protection. This eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan are quinol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is a slight increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Discontinuation syndrome may occur after stopping any antidepressant which resembles recurrent depression. Some research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults has found benefits, whilst other research has not. Evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear. The twenty-one most commonly prescribed antidepressant medications are more effective than placebo for the short-term (acute) treatments of adults with major depressive disorder. There is debate in the medical community about how much of the observed effects of antidep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricyclic Antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), which contain four rings of atoms, are a closely related group of antidepressant compounds. Although TCAs are sometimes prescribed for depressive disorders, they have been largely replaced in clinical use in most parts of the world by newer antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs). Adverse effects have been found to be of a similar level between TCAs and SSRIs. Another class of antidepressants, tetracyclic antidepressants, are also used around the world, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol-Myers Squibb
The Bristol Myers Squibb Company (BMS) is an American multinational pharmaceutical company. Headquartered in New York City, BMS is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies and consistently ranks on the ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest U.S. corporations. For fiscal 2021, it had a total revenue of $46.4 billion. Bristol Myers Squibb manufactures prescription pharmaceuticals and biologics in several therapeutic areas, including cancer, HIV/AIDS, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psychiatric disorders. BMS's primary research and development (R&D) sites are located in Lawrence, New Jersey (formerly Squibb, near Princeton), Summit, New Jersey, formerly HQ of Celgene, New Brunswick, New Jersey, Redwood City, California, and Seville in Spain, with other sites in Devens and Cambridge, Massachusetts, East Syracuse, New York, Braine-l'Alleud, Belgium, Tokyo, Japan, Bangalore, India, and Wirral, United Kingdom. BMS previously had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
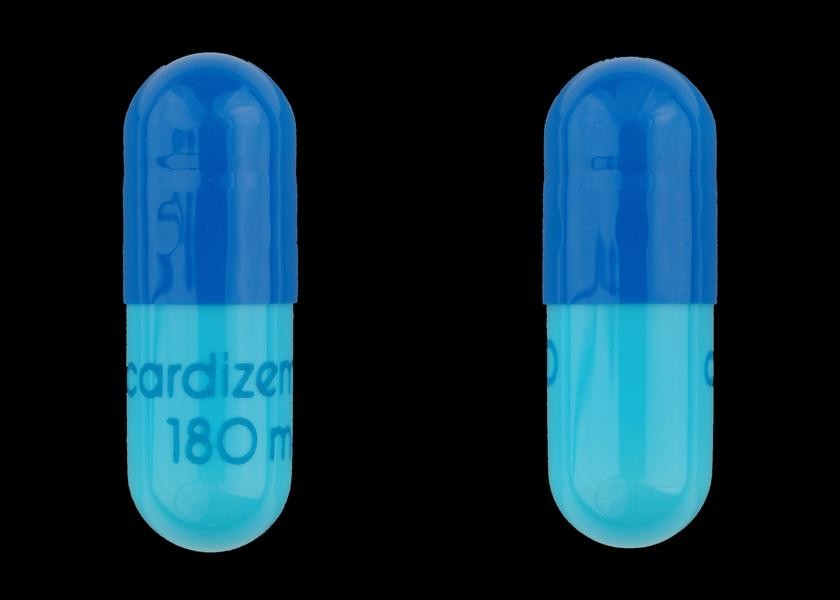
Diltiazem
Diltiazem, sold under the brand name Cardizem among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to treat high blood pressure, angina, and certain heart arrhythmias. It may also be used in hyperthyroidism if beta blockers cannot be used. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. When given by injection, effects typically begin within a few minutes and last a few hours. Common side effects include swelling, dizziness, headaches, and low blood pressure. Other severe side effects include an overly slow heart beat, heart failure, liver problems, and allergic reactions. Use is not recommended during pregnancy. It is unclear if use when breastfeeding is safe. Diltiazem works by relaxing the smooth muscle in the walls of arteries, resulting in them opening and allowing blood to flow more easily. Additionally, it acts on the heart to prolong the period until it can beat again. It does this by blocking the entry of calcium into the cells of the heart and blood vessels. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylamino Compounds
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005. Structure and synthesis The molecule consists of a nitrogen atom with two methyl substituents and one proton. Dimethylamine is a weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3--CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79). Dimethylamine reacts with acids to form salts, such as dimethylamine hydrochloride, an odorless white solid with a melting point of 171.5 °C. Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia at elevated temperatures and high pressure: :2 CH3OH + NH3 → (CH3)2NH + 2 H2O Natural occurrence Dimethylamine is found quite widely distributed in animals and plants, and is present in many foods at the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is a slight increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Discontinuation syndrome may occur after stopping any antidepressant which resembles recurrent depression. Some research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults has found benefits, whilst other research has not. Evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear. The twenty-one most commonly prescribed antidepressant medications are more effective than placebo for the short-term (acute) treatments of adults with major depressive disorder. There is debate in the medical community about how much of the observed effects of antidepre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)