|
Tian'anmen
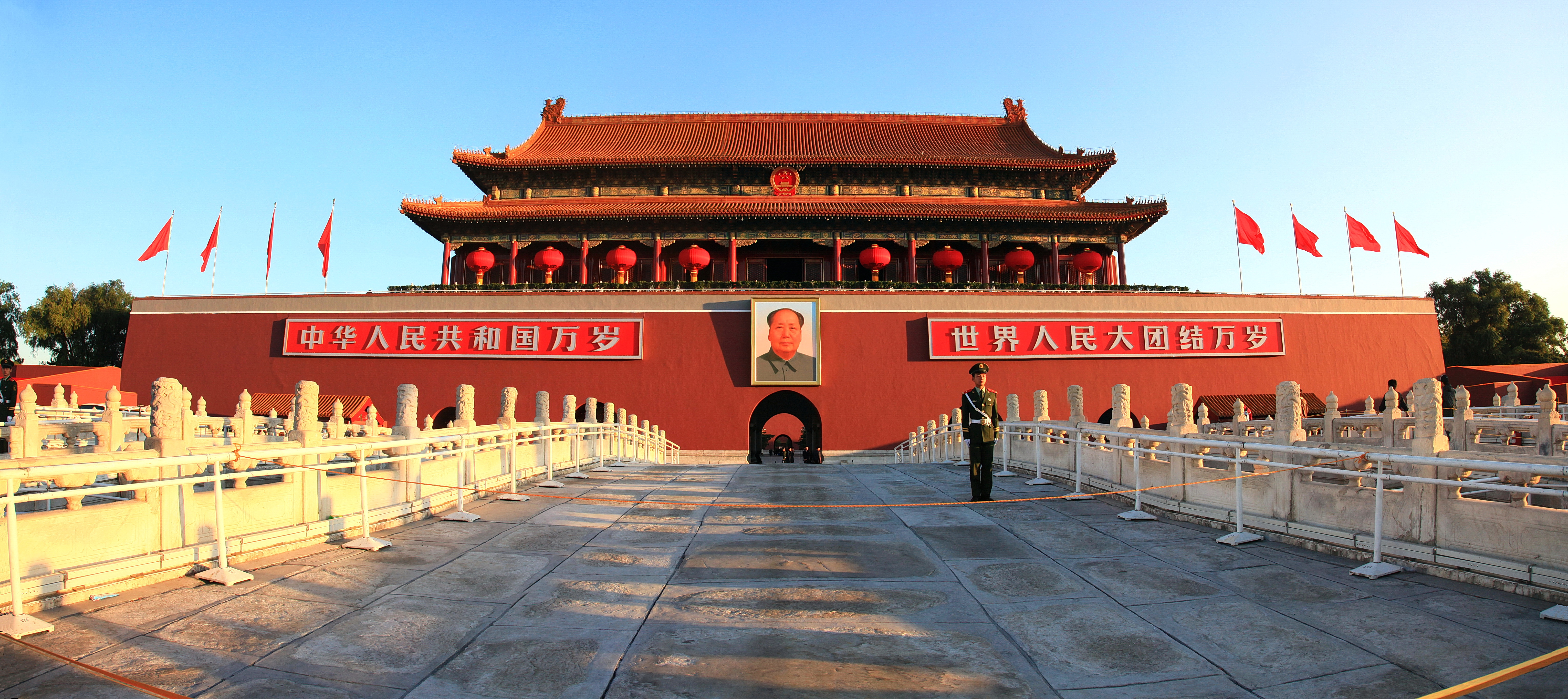
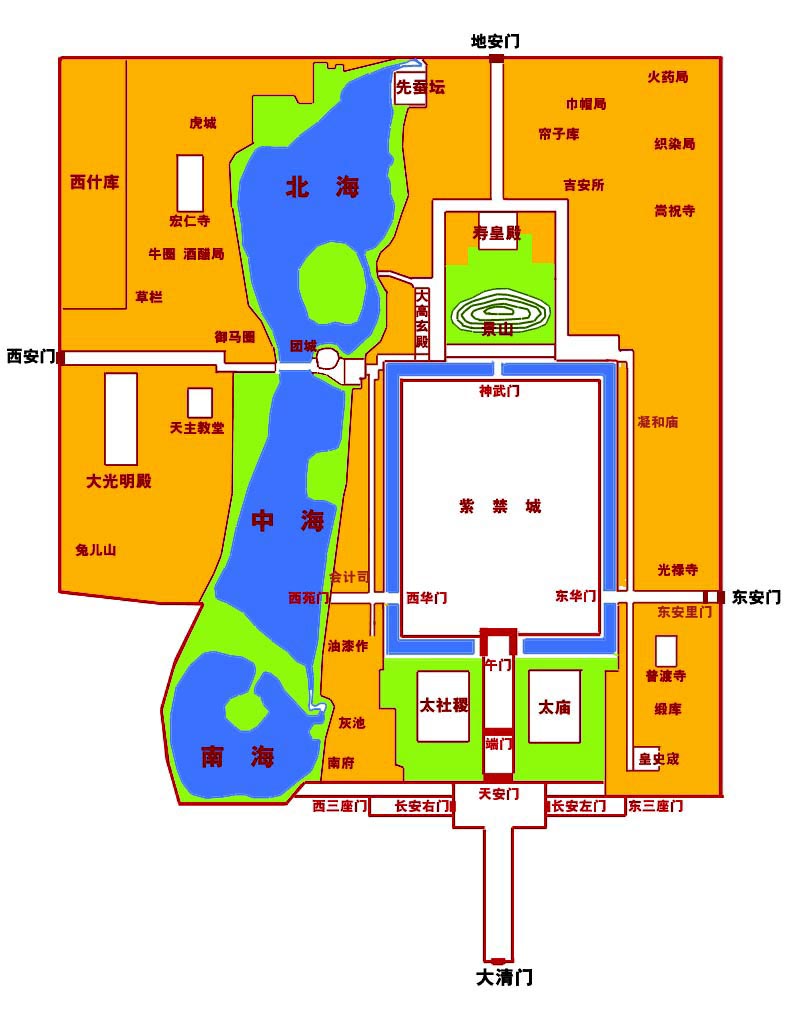
The Tiananmen (also Tian'anmen (天安门), Tienanmen, T’ien-an Men; ), or the Gate of Heaven-Sent Pacification, is a monumental gate in the city center of Beijing, China, the front gate of the Imperial City of Beijing, located near the city's Central Business District, and widely used as a national symbol. First built during the Ming dynasty in 1420, Tiananmen was the entrance to the Imperial City, within which the Forbidden City was located. Tiananmen is located to the north of Tiananmen Square, and is separated from the plaza by Chang'an Avenue. Name The Chinese name of the gate (/), is made up of the Chinese characters for "heaven", "peace" and "gate" respectively, which is why the name is conventionally translated as "Gate of Heavenly Peace". However, this translation is somewhat misleading, since the Chinese name is derived from the much longer phrase "receiving the mandate from heaven, and pacifying the dynasty". (). The Manchu translation, ''Abkai elhe obure d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'an Avenue
250px, Chang'an Avenue hosts military parades. Here are 50th anniversary of the People's Republic of China">1999 National Day parade. Chang'an Avenue (), literally "Eternal Peace Street", is a major thoroughfare in Beijing, China. Chang'an () is also the old name for Xi'an which was the capital of China during the Western Han dynasty, the Tang dynasty and other periods. The Avenue has also been referred to as the Shili Changjie (), meaning the Ten Li Long Street, China's No. 1 Avenue and No. 1 Avenue of the Divine Land. Chang'an Avenue is a synonym for Beijing and China politics because its political importance. Chang'an Avenue starts from Dongdan in the east and ends at Xidan in the west. Tiananmen and Tiananmen Square are located at the north and south of the center of the Avenue, respectively. The Avenue consists of two parts, West Chang'an Avenue and East Chang'an Avenue. The extension line extends east-west with Tiananmen Square as the center, extends westward to S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiananmen Square
Tiananmen Square or Tian'anmen Square (; 天安门广场; Pinyin: ''Tiān'ānmén Guǎngchǎng''; Wade–Giles: ''Tʻien1-an1-mên2 Kuang3-chʻang3'') is a city square in the city center of Beijing, China, named after the eponymous Tiananmen ("Gate of Heavenly Peace") located to its north, which separates it from the Forbidden City. The square contains the Monument to the People's Heroes, the Great Hall of the People, the National Museum of China, and the Mausoleum of Mao Zedong. Mao Zedong proclaimed the founding of the People's Republic of China in the square on October 1, 1949; the anniversary of this event is still observed there. The size of Tiananmen Square is 765 x 282 meters (215,730 m2 or 53.31 acres). It has great cultural significance as it was the site of several important events in Chinese history. Outside China, the square is best known for the 1989 protests and massacre that ended with a military crackdown, which is also known as the Tiananmen Square M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial City, Beijing
The Imperial City () is a section of the city of Beijing in the Ming and Qing dynasties, with the Forbidden City at its center. It refers to the collection of gardens, shrines, and other service areas between the Forbidden City and the Inner City of ancient Beijing. The Imperial City was surrounded by a wall and accessed through seven gates and it includes historical places such as the Forbidden City, Tiananmen, Zhongnanhai, Beihai Park, Zhongshan Park, Jingshan, Imperial Ancestral Temple, and Xiancantan. China Through A Lens Construction [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai (; 5 March 1898 – 8 January 1976) was a Chinese statesman and military officer who served as the first premier of the People's Republic of China from 1 October 1949 until his death on 8 January 1976. Zhou served under Chairman Mao Zedong and helped the Communist Party rise to power, later helping consolidate its control, form its foreign policy, and develop the Chinese economy. As a diplomat, Zhou served as the Chinese foreign minister from 1949 to 1958. Advocating peaceful coexistence with the West after the Korean War, he participated in the 1954 Geneva Conference and the 1955 Bandung Conference, and helped orchestrate Richard Nixon's 1972 visit to China. He helped devise policies regarding disputes with the United States, Taiwan, the Soviet Union ( after 1960), India, Korea, and Vietnam. Zhou survived the purges of other top officials during the Cultural Revolution. While Mao dedicated most of his later years to political struggle and ideological work, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Conquest Of The Ming
The transition from Ming to Qing, alternatively known as Ming–Qing transition or the Manchu conquest of China, from 1618 to 1683, saw the transition between two major dynasties in Chinese history. It was a decades-long conflict between the emerging Qing dynasty, the incumbent Ming dynasty, and several smaller factions (like the Shun dynasty and Xi dynasty). It ended with the consolidation of Qing rule, and the fall of the Ming and several other factions. Overview The transition from the Ming to Qing was a decades-long period of conflict between: # the Qing dynasty, established by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in contemporary Northeast China; # the Ming dynasty, the incumbent dynasty led by the Zhu clan; # and various other rebel powers in China, such as the short-lived Xi dynasty led by Zhang Xianzhong and the short-lived Shun dynasty led by Li Zicheng. Leading up to the Qing, in 1618, the Later Jin khan Nurhaci commissioned a document entitled the Seven Grievances, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions populated by the dominant Han population and the "frontier" regions of China, sometimes known as "Outer China". There is no fixed extent for China proper, as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in Chinese history. One definition refers to the original area of Chinese civilization, the Central Plain (in the North China Plain); another to the Eighteen Provinces of the Qing dynasty. There is no direct translation for "China proper" in the Chinese language due to differences in terminology used by the Qing to refer to the regions. The expression is controversial among scholars, particularly in China, due to issues pertaining to territorial integrity. Outer China usually includes the geographical regions of Dzunga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di'anmen
Di'anmen () or Bei'anmen was an imperial gate in Beijing, China. The gate was first built in the Yongle period of the Ming dynasty, and served as the main northern gate to the Imperial City (the southern gate is the much more famed Tiananmen). The gate is located north of Jingshan Park Jingshan Park is an imperial park covering immediately north of the Forbidden City in the Imperial City area of Beijing, China. The focal point is the artificial hill Jingshan (), literally "Prospect Hill". Formerly a private imperial garden a ... and south of the Drum Tower. The gate was demolished in 1954. Efforts to restore it have been under way since 2013. Chinese architectural history Gates of Beijing Neighbourhoods of Beijing Demolished buildings and structures in China Buildings and structures demolished in 1954 {{Beijing-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-lived Shun dynasty before his death a year later. Biography Li Zicheng was born in 1606 as Li Hongji to an impoverished family of farmers in Li Jiqian village, Yan'an prefecture, northeast Shaanxi province. Li Zicheng had a brother who was 20 years his senior and raised Li Zicheng alongside his son and Zicheng’s nephew, Li Guo. While Li Zicheng was literate, the source of his education is disputed. Over the course of his late adolescence and early adulthood, Li worked on a farm, in a wine shop, in a blacksmith's shop, and as a mailman for the state courier system. According to folklore, in 1630, Li was put on public display in an iron collar and shackles for failing to repay loans to a usurious magistrate. The magistrate, a man by the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paifang
A ''paifang'', also known as a ''pailou'', is a traditional style of Chinese architectural arch or gateway structure. Evolved from the Indian subcontinent's '' torana'' through the introduction of Buddhism to China, it has developed many styles and has been introduced to other East Asian countries, such as Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. Etymology The word ''paifang'' () was originally a collective term for the top two levels of administrative division and subdivisions of ancient Chinese cities. The largest division within a city in ancient China was a ''fang'' (), equivalent to a current day ward. Each ''fang'' was enclosed by walls or fences, and the gates of these enclosures were shut and guarded every night. Each ''fang'' was further divided into several ''pai'' (), which is equivalent to a current day (unincorporated) community. Each ''pai'', in turn, contained an area including several hutongs (alleyways). This system of urban administrative division and subdivision reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


