|
Thymus Glabrescens
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to decrease in size and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Pouch (embryology)
In the embryonic development of vertebrates, pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the pharyngeal arches. The pharyngeal grooves (or clefts) form the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches. The pouches line up with the clefts, and these thin segments become gills in fish. Specific pouches First pouch The endoderm lines the future auditory tube (Pharyngotympanic Eustachian tube), middle ear, mastoid antrum, and inner layer of the tympanic membrane. Derivatives of this pouch are supplied by Mandibular nerve. Second pouch * Contributes the middle ear, palatine tonsils, supplied by the facial nerve. Third pouch * The third pouch possesses Dorsal and Ventral wings. Derivatives of the dorsal wings include the inferior parathyroid glands, while the ventral wings fuse to form the cytoreticular cells of the thymus. The main nerve supply to the derivatives of this pouch is Cranial Nerve IX, glossopharyngeal nerve. Fourth pouch Derivatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1), is a subtype of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome (autoimmune polyglandular syndrome). It causes the dysfunction of multiple endocrine glands due to autoimmunity. It is a genetic disorder, inherited in autosomal recessive fashion due to a defect in the ''AIRE'' gene (autoimmune regulator), which is located on chromosome 21 and normally confers immune tolerance. Signs and symptoms APS-1 tends to cause severe symptoms. These are present from early in life, usually around 3.5 years of age. Common symptoms of APS-1 include: * Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. * Hypoparathyroidism. * Addison's disease. * Ectodermal dystrophy (skin, dental enamel, and nails). APS-1 may also cause: * Autoimmune hepatitis. * Hypogonadism. * Vitiligo. * Alopecia. * Malabsorption. * Pernicious anemia. * Cataract. * Cerebellar ataxia. Cause APS-1 is caused by a mutation in the AIRE gene, encoding a protein called autoimmune regulator. This is found o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and ''visceral'' or ''parietal'' fascia, or by its function and anatomical location. Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fascia is made up of fibrous connective tissue containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibers oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fascia is consequently flexible and able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibers has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibers are produced by fibroblasts located within the fascia. Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they have collagen as their major component. They differ in their location and function: ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Vessels
Great vessels are the large vessels that bring blood to and from the heart. These are: *Superior vena cava *Inferior vena cava *Pulmonary arteries *Pulmonary veins *Aorta Transposition of the great vessels is a group of congenital heart defects A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular ... involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels. References Angiology {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
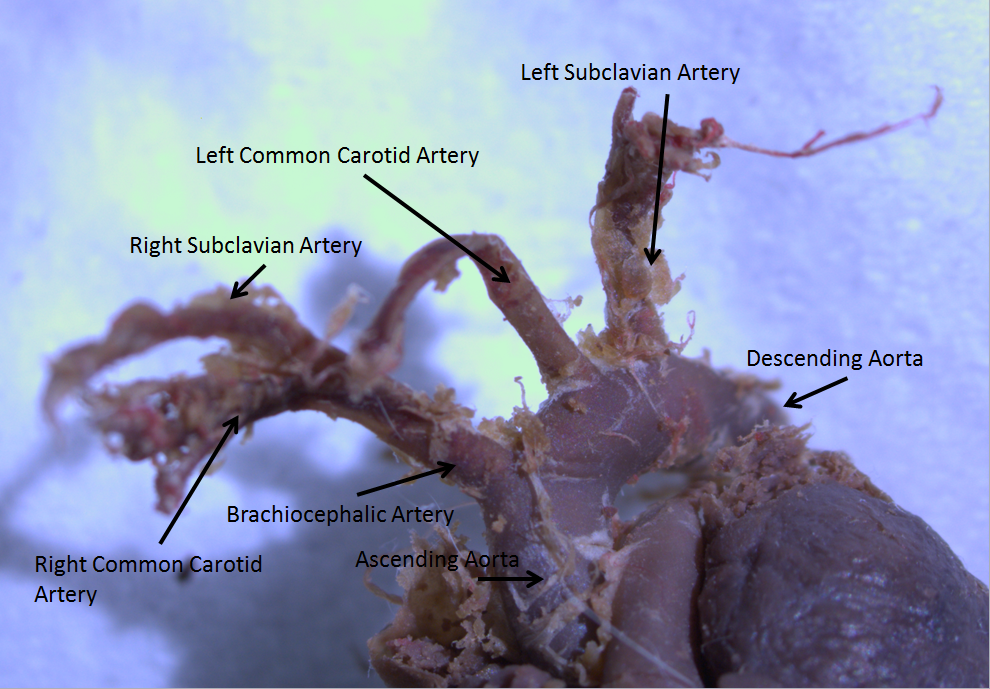
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath. and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix "''peri-''" (περί; "around") and the suffix "''-cardion''" (κάρδιον; "heart"). Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). The fibrous pericardiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane. * The inferior mediastinum from this level to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involution (medicine)
Involution is the shrinking or return of an organ to a former size. At a cellular level, involution is characterized by the process of proteolysis of the basement membrane (basal lamina), leading to epithelial regression and apoptosis, with accompanying stromal fibrosis. The consequent reduction in cell number and reorganization of stromal tissue leads to the reduction in the size of the organ. Examples Thymus The thymus continues to grow between birth and puberty and then begins to atrophy, a process directed by the high levels of circulating sex hormones. Proportional to thymic size, thymic activity (T cell output) is most active before puberty. Upon atrophy, the size and activity are dramatically reduced, and the organ is primarily replaced with fat. The atrophy is due to the increased circulating level of sex hormones, and chemical or physical castration of an adult results in the thymus increasing in size and activity. Uterus Involution is the process by which the uterus is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymectomy
A thymectomy is an operation to remove the thymus. It usually results in remission of myasthenia gravis with the help of medication including steroids. However, this remission may not be permanent. Thymectomy is indicated when thymoma are present in the thymus. Anecdotal evidence suggests MG patients with no evidence of thymoma may still benefit from thymectomy, thus the procedure is (unless and until a much-discussed clinical survey ever reaches a contradictory conclusion) commonly prescribed. Surgical approaches There are a number of surgical approaches to the removal of the thymus gland: transternal (through the breast bone), transcervical (through a small neck incision), transthoracic (through one or both sides of the chest.) * The transternal approach is most common and uses the same length-wise incision through the sternum (breast bone) used for most open-heart surgery. It is espoused by surgeons such as Alfred Jaretzki and is the most commonly performed procedure due to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)