|
Thomas–Fermi Screening
Thomas–Fermi screening is a theoretical approach to calculate the effects of electric field screening by electrons in a solid.N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, ''Solid State Physics'' (Thomson Learning, Toronto, 1976) It is a special case of the more general Lindhard theory; in particular, Thomas–Fermi screening is the limit of the Lindhard formula when the wavevector (the reciprocal of the length-scale of interest) is much smaller than the Fermi wavevector, i.e. the long-distance limit. It is named after Llewellyn Thomas and Enrico Fermi. The Thomas–Fermi wavevector (in Gaussian-cgs units) is k_0^2 = 4\pi e^2 \frac, where ''μ'' is the chemical potential ( Fermi level), ''n'' is the electron concentration and ''e'' is the elementary charge. Under many circumstances, including semiconductors that are not too heavily doped, , where ''k''B is Boltzmann constant and ''T'' is temperature. In this case, k_0^2 = \frac, i.e. is given by the familiar formula for Debye length. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field Screening
In physics, screening is the damping of electric fields caused by the presence of mobile charge carriers. It is an important part of the behavior of charge-carrying fluids, such as ionized gases (classical plasmas), electrolytes, and charge carriers in electronic conductors (semiconductors, metals). In a fluid, with a given permittivity , composed of electrically charged constituent particles, each pair of particles (with charges and ) interact through the Coulomb force as \mathbf = \frac\hat, where the vector is the relative position between the charges. This interaction complicates the theoretical treatment of the fluid. For example, a naive quantum mechanical calculation of the ground-state energy density yields infinity, which is unreasonable. The difficulty lies in the fact that even though the Coulomb force diminishes with distance as , the average number of particles at each distance is proportional to , assuming the fluid is fairly isotropic. As a result, a charge fluctu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Energy
The Fermi energy is a concept in quantum mechanics usually referring to the energy difference between the highest and lowest occupied single-particle states in a quantum system of non-interacting fermions at absolute zero temperature. In a Fermi gas, the lowest occupied state is taken to have zero kinetic energy, whereas in a metal, the lowest occupied state is typically taken to mean the bottom of the conduction band. The term "Fermi energy" is often used to refer to a different yet closely related concept, the Fermi ''level'' (also called electrochemical potential).The use of the term "Fermi energy" as synonymous with Fermi level (a.k.a. electrochemical potential) is widespread in semiconductor physics. For example:''Electronics (fundamentals And Applications)''by D. Chattopadhyay''Semiconductor Physics and Applications''by Balkanski and Wallis. There are a few key differences between the Fermi level and Fermi energy, at least as they are used in this article: * The Fermi energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Fermi–Dirac Integral
In mathematics, the complete Fermi–Dirac integral, named after Enrico Fermi and Paul Dirac, for an index ''j '' is defined by :F_j(x) = \frac \int_0^\infty \frac\,dt, \qquad (j > -1) This equals :-\operatorname_(-e^x), where \operatorname_(z) is the polylogarithm. Its derivative is :\frac = F_(x) , and this derivative relationship is used to define the Fermi-Dirac integral for nonpositive indices ''j''. Differing notation for F_j appears in the literature, for instance some authors omit the factor 1/\Gamma(j+1). The definition used here matches that in thNIST DLMF Special values The closed form of the function exists for ''j'' = 0: :F_0(x) = \ln(1+\exp(x)). For ''x = 0'', the result reduces to F_j(0) = \eta(j+1), where \eta is the Dirichlet eta function. See also * Incomplete Fermi–Dirac integral * Gamma function * Polylogarithm In mathematics, the polylogarithm (also known as Jonquière's function, for Alfred Jonquière) is a special functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventionally called ''electrostatic force'' or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, hence the name. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism, maybe even its starting point, as it made it possible to discuss the quantity of electric charge in a meaningful way. The law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Coulomb studied the repulsive force between bodies having electrical charges of the same sign: Coulomb also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauss's Law
In physics and electromagnetism, Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem, (or sometimes simply called Gauss's theorem) is a law relating the distribution of electric charge to the resulting electric field. In its integral form, it states that the flux of the electric field out of an arbitrary closed surface is proportional to the electric charge enclosed by the surface, irrespective of how that charge is distributed. Even though the law alone is insufficient to determine the electric field across a surface enclosing any charge distribution, this may be possible in cases where symmetry mandates uniformity of the field. Where no such symmetry exists, Gauss's law can be used in its differential form, which states that the divergence of the electric field is proportional to the local density of charge. The law was first formulated by Joseph-Louis Lagrange in 1773, followed by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1835, both in the context of the attraction of ellipsoids. It is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson Equation
Poisson's equation is an elliptic partial differential equation of broad utility in theoretical physics. For example, the solution to Poisson's equation is the potential field caused by a given electric charge or mass density distribution; with the potential field known, one can then calculate electrostatic or gravitational (force) field. It is a generalization of Laplace's equation, which is also frequently seen in physics. The equation is named after French mathematician and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson. Statement of the equation Poisson's equation is \Delta\varphi = f where \Delta is the Laplace operator, and f and \varphi are real or complex-valued functions on a manifold. Usually, f is given and \varphi is sought. When the manifold is Euclidean space, the Laplace operator is often denoted as and so Poisson's equation is frequently written as \nabla^2 \varphi = f. In three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates, it takes the form \left( \frac + \frac + \frac \right)\varph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Function
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in response to an applied electric field than a material with low permittivity, thereby storing more energy in the material. In electrostatics, the permittivity plays an important role in determining the capacitance of a capacitor. In the simplest case, the electric displacement field D resulting from an applied electric field E is :\mathbf = \varepsilon \mathbf. More generally, the permittivity is a thermodynamic function of state. It can depend on the frequency, magnitude, and direction of the applied field. The SI unit for permittivity is farad per meter (F/m). The permittivity is often represented by the relative permittivity ''ε''r which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity ''ε'' and the vacuum permittivity ''ε''0 :\kappa = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Potential
In electrochemistry, the electrochemical potential (ECP), ', is a thermodynamic measure of chemical potential that does not omit the energy contribution of electrostatics. Electrochemical potential is expressed in the unit of J/ mol. Introduction Each chemical species (for example, "water molecules", "sodium ions", "electrons", etc.) has an electrochemical potential (a quantity with units of energy) at any given point in space, which represents how easy or difficult it is to add more of that species to that location. If possible, a species will move from areas with higher electrochemical potential to areas with lower electrochemical potential; in equilibrium, the electrochemical potential will be constant everywhere for each species (it may have a different value for different species). For example, if a glass of water has sodium ions (Na+) dissolved uniformly in it, and an electric field is applied across the water, then the sodium ions will tend to get pulled by the electric fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
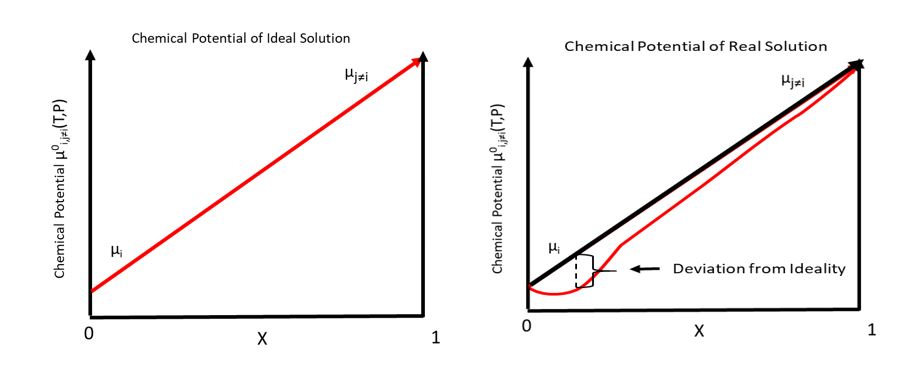
Total Chemical Potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species in a mixture is defined as the rate of change of free energy of a thermodynamic system with respect to the change in the number of atoms or molecules of the species that are added to the system. Thus, it is the partial derivative of the free energy with respect to the amount of the species, all other species' concentrations in the mixture remaining constant. When both temperature and pressure are held constant, and the number of particles is expressed in moles, the chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibrium, the total sum of the product of chemical potentials and stoichiometric coefficients is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum. In a system in diffusion equilibrium, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Surface
In condensed matter physics, the Fermi surface is the surface in reciprocal space which separates occupied from unoccupied electron states at zero temperature. The shape of the Fermi surface is derived from the periodicity and symmetry of the crystalline lattice and from the occupation of electronic energy bands. The existence of a Fermi surface is a direct consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, which allows a maximum of one electron per quantum state. The study of the Fermi surfaces of materials is called fermiology. Theory Consider a spin-less ideal Fermi gas of N particles. According to Fermi–Dirac statistics, the mean occupation number of a state with energy \epsilon_i is given by :\langle n_i\rangle =\frac, where, *\left\langle n_i\right\rangle is the mean occupation number of the i^ state *\epsilon_i is the kinetic energy of the i^ state *\mu is the chemical potential (at zero temperature, this is the maximum kinetic energy the particle can have, i.e. Fermi ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavepacket
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short "burst" or "envelope" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating. Quantum mechanics ascribes a special significance to the wave packet; it is interpreted as a probability amplitude, its norm squared describing the probability density that a particle or particles in a particular state will be measured to have a given position or momentum. The wave equation is in this case the Schrödinger equation, and through its ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.gif)