|
This Way For The Gas, Ladies And Gentlemen
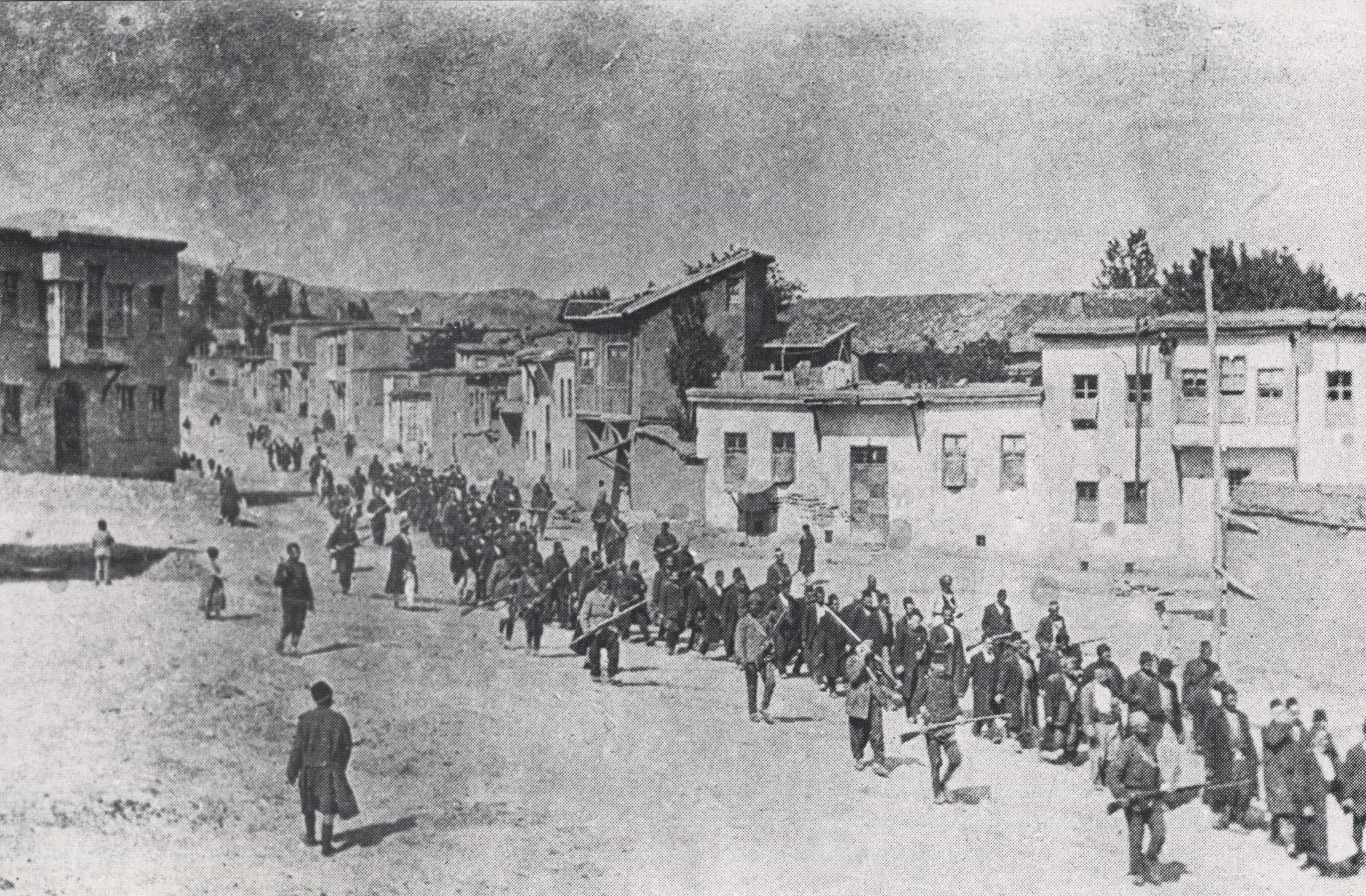
''This Way for the Gas, Ladies and Gentlemen,'' also known as ''Ladies and Gentlemen, to the Gas Chamber,'' is a collection of short stories by Tadeusz Borowski, which were inspired by the author's concentration camp experience. The original title in the Polish language was ''Pożegnanie z Marią'' (''Farewell to Maria''). at Following two year imprisonment at Auschwitz, Borowski had been liberated from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadeusz Borowski
Tadeusz Borowski (; 12 November 1922 – 3 July 1951) was a Polish writer and journalist. His wartime poetry and stories dealing with his experiences as a prisoner at Auschwitz are recognized as classics of Polish literature. Early life Borowski was born in 1922 into the Polish community in Zhytomyr, Ukrainian SSR (today Ukraine). In 1926, his father, whose bookstore had been nationalized by the communists, was sent to a camp in the Gulag system in Russian Karelia because he had been a member of a Polish military organization during World War I. In 1930, Borowski's mother was deported to a settlement on the shores of the Yenisey, in Siberia, during Collectivization. During this time Tadeusz lived with his aunt. Borowski and his family were targeted (as Poles) by the Soviet Union during Stalin's Great Terror. In 1932, the Borowskis were expatriated to Poland by the Polish Red Cross in an exchange for Communist prisoners. Impoverished, the family settled in Warsaw. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death March
A death march is a forced march of prisoners of war or other captives or deportees in which individuals are left to die along the way. It is distinguished in this way from simple prisoner transport via foot march. Article 19 of the Geneva Convention requires that prisoners must be moved away from a danger zone such as an advancing front line, to a place that may be considered more secure. It is not required to evacuate prisoners that are too unwell or injured to move. In times of war such evacuations can be difficult to carry out. Death marches usually feature harsh physical labor and abuse, neglect of prisoner injury and illness, deliberate starvation and dehydration, humiliation, torture, and execution of those unable to keep up the marching pace. The march may end at a prisoner-of-war camp or internment camp, or it may continue until all the prisoners are dead. Lieutenant General Masaharu Homma was charged with failure to control his troops in 1945 in connection with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Short Story Collections
Polish may refer to: * Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe * Polish language * Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent * Polish chicken * Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwriters Polish may refer to: * Polishing, the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing or chemical action ** French polishing, polishing wood to a high gloss finish * Nail polish * Shoe polish * Polish (screenwriting), improving a script in smaller ways than in a rewrite See also * * * Polonaise (other) A polonaise ()) is a stately dance of Polish origin or a piece of music for this dance. Polonaise may also refer to: * Polonaises (Chopin), compositions by Frédéric Chopin ** Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53 (french: Polonaise héroïque, ... {{Disambiguation, surname Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Literature
Polish literature is the literary tradition of Poland. Most Polish literature has been written in the Polish language, though other languages used in Poland over the centuries have also contributed to Polish literary traditions, including Latin, Yiddish, Lithuanian, Russian, German and Esperanto. According to Czesław Miłosz, for centuries Polish literature focused more on drama and poetic self-expression than on fiction (dominant in the English speaking world). The reasons were manifold but mostly rested on the historical circumstances of the nation. Polish writers typically have had a more profound range of choices to motivate them to write, including past cataclysms of extraordinary violence that swept Poland (as the crossroads of Europe), but also, Poland's collective incongruities demanding an adequate reaction from the writing communities of any given period.Czesław Miłosz ''The History of Polish Literature.''Google Books preview. ''University of California Press'', Ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zofia Nałkowska
Zofia Nałkowska (, Warsaw, Congress Poland, 10 November 1884 – 17 December 1954, Warsaw) was a Polish prose writer, dramatist, and prolific essayist. She served as the executive member of the prestigious Polish Academy of Literature (1933–1939) during the interwar period. Biography Nałkowska was born into a family of intellectuals dedicated to issues of social justice, and studied at the clandestine Flying University under the Russian partition. Upon Poland's return to independence she became one of the country's most distinguished feminist writers of novels, novellas and stage-plays characterized by socio-realism and psychological depth. Literary output Nałkowska's first literary success was the ''Romans Teresy Hennert'' (The Romance of Teresa Hennert, 1923) followed by a slew of popular novels. She is best known for her books ''Granica'' (Boundary, 1935), the ''Węzły życia'' (Bonds of Life, 1948) and ''Medaliony'' ('' Medallions'', 1947). In her writing, Nałkowska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanna Krall
Hanna Krall (born 1935), is a Polish writer with a degree in journalism from the University of Warsaw, specializing among other subjects in the history of the Holocaust in occupied Poland. Personal life Krall is of Jewish origin, the daughter of Salomon Krall and Felicia Jadwiga ''née'' Reichold. She was born in Warsaw, Poland, but her date of birth is contested between 20 May 1935 and 20 May 1937. She was four years old, living in Lublin, when the World War II began with the Nazi German invasion of Poland. Krall lost most of her close relatives in the Holocaust, including her mother and father, who were murdered in Majdanek. She survived deportations to death camps only because she was hidden from the Germans by the Polish rescuers. After the war, she stayed in her childhood home in Otwock until going to the University of Warsaw for her education from 1951-1955. She is married to reporter Jerzy Szperkowicz and together have one daughter, Katarzyna. Career Journalism After K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Although disagreement exists as to how to precisely define behavior in a biological context, one common interpretation based on a meta-analysis of scientific literature states that "behavior is the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to internal and/or externa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan Kundera
Milan Kundera (, ; born 1 April 1929) is a Czech writer who went into exile in France in 1975, becoming a naturalised French citizen in 1981. Kundera's Czechoslovak citizenship was revoked in 1979, then conferred again in 2019. He "sees himself as a French writer and insists his work should be studied as French literature and classified as such in book stores". Kundera's best-known work is '' The Unbearable Lightness of Being''. Prior to the Velvet Revolution of 1989, the communist régime in Czechoslovakia banned his books. He leads a low-profile life and rarely speaks to the media. He was thought to be a contender for the Nobel Prize in Literature, and was also a nominee for other awards. He was awarded the 1985 Jerusalem Prize, in 1987 the Austrian State Prize for European Literature, and the 2000 Herder Prize. In 2021, he received the Golden Order of Merit from the president of Slovenia, Borut Pahor. Biography Kundera was born in 1929 at Purkyňova 6 (6 Purkyně Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiří Weil
Jiří Weil (; 6 August 1900, Praskolesy – 13 December 1959, Prague) was a Czech writer of Jewish origin and Holocaust survivor. His noted works include the two novels '' Life with a Star'' (''Život s hvězdou''), and ''Mendelssohn Is on the Roof'' (''Na střeše je Mendelssohn''), as well as many short stories, and other novels. Biography Weil was born in Praskolesy, a village about 40 kilometres from Prague, on 6 August 1900. He was the second son born to upper-middle-class Orthodox Jewish parents. Weil graduated from secondary school in 1919. As a student he had already begun writing mainly verses, but had also begun planning his three-part novel, ''Město'', which he planned to publish under the pseudonym, Jiří Wilde. Upon graduation, Weil was accepted to Charles University in Prague where he entered the Department of Philosophy and also studied Slavic philology and comparative literature. He was a favourite student of F. X. Šalda. He completed his doctoral dissertati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Schulz
Bruno Schulz (12 July 1892 – 19 November 1942) was a Polish writer, fine artist, literary critic and art teacher. He is regarded as one of the great Polish-language prose stylists of the 20th century. In 1938, he was awarded the Polish Academy of Literature's prestigious Golden Laurel award. Several of Schulz's works were lost in the Holocaust The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ..., including short stories from the early 1940s and his final, unfinished novel ''The Messiah''. Schulz was shot and killed by a German Nazi, a Gestapo officer, in 1942 while walking back home toward Drohobycz Ghetto with a loaf of bread. Biography Schulz was born in Drohobych, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, Austrian Galicia, historically part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danilo Kiš
Danilo Kiš (; born Dániel Kiss; 22 February 1935 – 15 October 1989) was a Yugoslav novelist, short story writer, essayist and translator. His best known works include ''Hourglass'', ''A Tomb for Boris Davidovich'' and ''The Encyclopedia of the Dead''. Life and work Early life Kiš was born in Subotica, Danube Banovina, Kingdom of Yugoslavia (now Serbia). Kiš was the son of Eduard Kiš ( hu, Kis Ede), a Hungarian-speaking Jewish railway inspector and Milica (née Dragićević), a Serbian Orthodox Christian from Cetinje. His father was born in Austria-Hungary with the surname Kohn, but changed it to Kiš as part of Magyarization, a widely implemented practice at the time. Kiš's parents met in 1930 in Subotica and married the following year. Milica gave birth to a daughter, Danica, in Zagreb in 1932 before the family relocated to Subotica. Kiš's father was an unsteady and often absent figure in Danilo's childhood. Eduard Kiš spent time in a psychiatric hospital in Belg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Roth
Philip Milton Roth (March 19, 1933 – May 22, 2018) was an American novelist and short story writer. Roth's fiction—often set in his birthplace of Newark, New Jersey—is known for its intensely autobiographical character, for philosophically and formally blurring the distinction between reality and fiction, for its "sensual, ingenious style" and for its provocative explorations of American identity. He first gained attention with the 1959 novella '' Goodbye, Columbus''; the collection so titled received the U.S. National Book Award for Fiction.Brauner (2005), pp. 43–47 He became one of the most awarded American writers of his generation. His books twice received the National Book Award and the National Book Critics Circle award, and three times the PEN/Faulkner Award. He received a Pulitzer Prize for his 1997 novel ''American Pastoral'', which featured one of his best-known characters, Nathan Zuckerman. '' The Human Stain'' (2000), another Zuckerman novel, was awarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


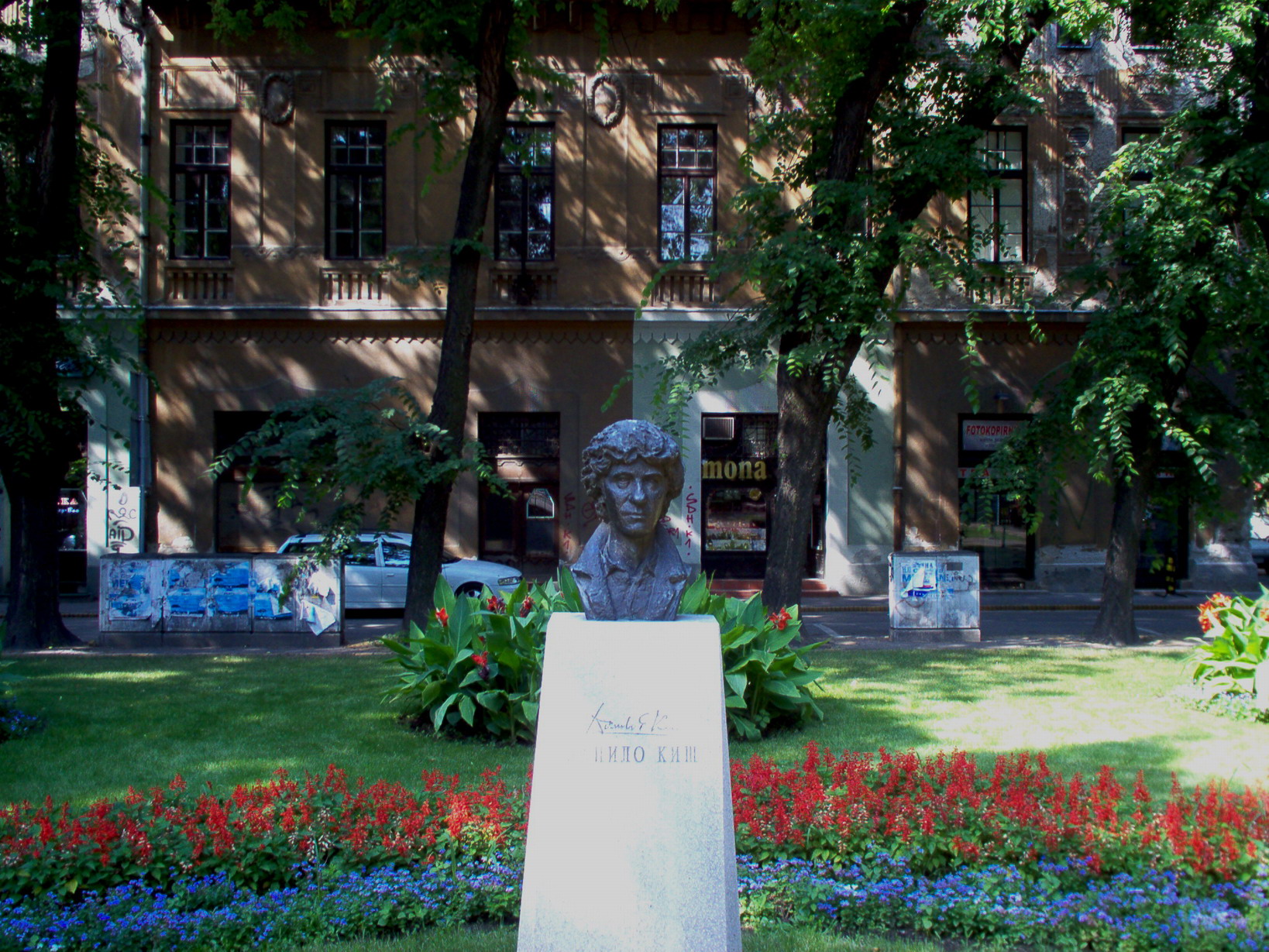
.jpg)