|
Thiosulfurous Acid
Thiosulfurous acid is a hypothetical chemical compound with the formula HS−S(=O)−OH or HO−S(=S)−OH. Attempted synthesis leads to polymers. It is a low oxidation state (+1) sulfur acid. It is the Arrhenius acid for disulfur monoxide. Salts derived from thiosulfurous acid, which are also unknown, are named "thiosulfites", "thionosulfites" or "sulfurothioites". The ion is . Structures Other possible isomers are dihydroxydisulfane or hypodithionous acid HOSSOH, a linear chain, and thiothionyl hydroxide (S=S(OH)2) a tautomer where the hydrogen has moved from a sulfur to an oxygen. HOSSOH can have two different rotamers with symmetry C1 and C2. The isomer with one hydrogen on sulfur and one on oxygen is the most stable according to calculations. Dithiosulfurous acid The sulfur analog of thiosulfuric acid (), in which two sulfur atoms branch off of the central sulfur atom of a linear dihydrogen trisulfide structure (tetrathiosulfuric acid, or ) has also been computationally studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemsketch
ACD/ChemSketch is a molecular modeling program used to create and modify images of chemical structures. Also, there is a software that allows molecules and molecular models displayed in two and three dimensions, to understand the structure of chemical bonds and the nature of the functional groups. Features The program offers some advanced features that allows the molecules rotate and apply color to improve visualization. It has several templates with ions and functional groups with the possibility to add text and use other tools to optimize productions created by the software. Applications Using ACD/ChemSketch is primarily for educational use. With this program it is possible to write and perform chemical equations, diagrams laboratories and chemical structures of various entity. See also * ChemDraw * Software design * 3D graphics software * Molecule editor A molecule editor is a computer program for creating and modifying representations of chemical structures. Molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiosulfite
Thiosulfurous acid is a hypothetical chemical compound with the formula HS−S(=O)−OH or HO−S(=S)−OH. Attempted synthesis leads to polymers. It is a low oxidation state (+1) sulfur acid. It is the Arrhenius acid for disulfur monoxide. Salts derived from thiosulfurous acid, which are also unknown, are named "thiosulfites", "thionosulfites" or "sulfurothioites". The ion is . Structures Other possible isomers are dihydroxydisulfane or hypodithionous acid HOSSOH, a linear chain, and thiothionyl hydroxide (S=S(OH)2) a tautomer where the hydrogen has moved from a sulfur to an oxygen. HOSSOH can have two different rotamers with symmetry C1 and C2. The isomer with one hydrogen on sulfur and one on oxygen is the most stable according to calculations. Dithiosulfurous acid The sulfur analog of thiosulfuric acid (), in which two sulfur atoms branch off of the central sulfur atom of a linear dihydrogen trisulfide structure (tetrathiosulfuric acid, or ) has also been computationally s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
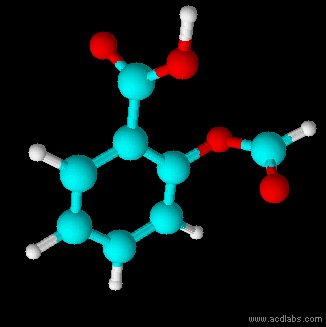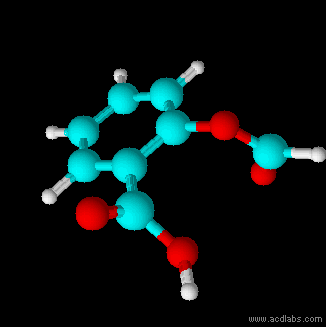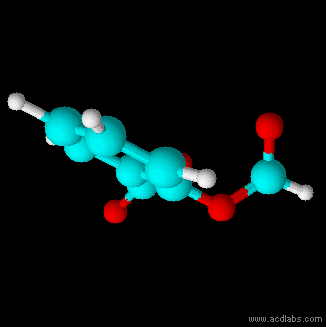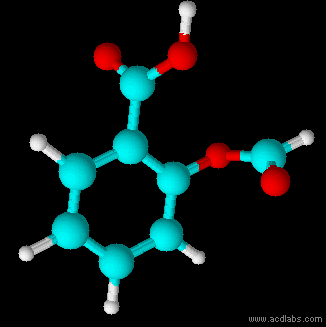
Thiosulfuric Acid
Thiosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It has attracted academic interest as a simple, easily accessed compound that is labile. It has few practical uses. Preparation and degradation The acid cannot be made by acidifying aqueous thiosulfate salt solutions as the acid readily decomposes in water. The decomposition products can include sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid and polythionates, depending on the reaction conditions.. Anhydrous methods of producing the acid were developed by Max Schmidt: : : : The anhydrous acid also decomposes above −5 °C: : Structure The isomer is more stable than the isomer as established by Hartree–Fock/ ab initio calculations with a 6-311 G** basis set and MP2 to MP4 refinements. The theoretically predicted structure conforms with the double bond rule. An isomer of thiosulfuric acid is the adduct An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfur Monoxide
Disulfur monoxide or sulfur suboxide is an inorganic compound with formula S2O, one of the lower sulfur oxides. It is a colourless gas and condenses to give a roughly dark red coloured solid that is unstable at room temperature. occurs rarely in natural atmospheres, but can be made by a variety of laboratory procedures. For this reason, its spectroscopic signature is very well understood. Structure and spectrum Condensed solid S2O absorbs at (roughly indigo) and (roughly lime). These bands have been assigned to decomposition products S3 and S4. In the ultraviolet, S2O has absorption band systems in the ranges 250–340 nm and 190–240 nm. There are bands at 323.5 and 327.8 nm. The band in the 315–340 nm range is due to the transition. Gaseous disulfur monoxide does not absorb in the visible spectrum. The microwave spectrum of S2O has the following rotational parameters: ''A'' = 41915.44 MHz, ''B'' = 5059.07 MHz, and ''C''&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Chemical Compound
A hypothetical chemical compound is a chemical compound that has been conceived of, but is not known to have been synthesized, observed, or isolated (identified or shown to exist). Some hypothetical compounds cannot form at all. Others might turn out to be highly unstable, decomposing, isomerizing, polymerizing, rearranging, or disproportionating. Some are thought to exist only briefly as reactive intermediates, or in vacuum (e.g. helium hydride ion). Some cannot hold together due to steric hindrance (e.g. tetra-''tert''-butylmethane) or bond stress (e.g. tetrahedrane). Some have no known pathway for synthesis (e.g. hypercubane). Some compounds of radioactive elements have never been synthesized due to their radioactive decay and short half-lives (e.g. francium hydroxide) Some "parent compounds" have not been or cannot be isolated, even though stable structural analogs with substituents have been discovered or synthesized (e.g. borole). Hypothetical compounds are often p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius may refer to * Birgit Arrhenius (born 1932), Swedish archaeologist * Carl Axel Arrhenius (1757–1824), Swedish army lieutenant and amateur mineralogist who discovered ytterbite, a mineral that led to the discovery of yttrium by Johan Gadolin * Niklas Arrhenius, Swedish discus thrower * Svante Arrhenius (1859–1927), Swedish physical chemist and 1903 Nobel laureate :* Arrhenius definition, Svante Arrhenius definition of acids and bases :* Arrhenius equation, Svante Arrhenius formula for modeling the temperature dependence of reaction rate constants :* Arrhenius plot :* Arrhenius (lunar crater) Arrhenius is a lunar impact crater that is located just on the far side of the Moon, near the southwest limb. In this location the vicinity of the crater can be viewed during favorable librations, although it is viewed from on edge. To the south- ..., named for Svante Arrhenius :* 5697 Arrhenius, main-belt asteroid, named for Svante Arrhenius :* Arrhenius (Martian crater), named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroxydisulfane
Dihydroxydisulfane or hypodithionous acid is a reduced sulfur oxyacid with sulfur in a formal oxidation state of +1. The structural formula is HOSSOH, with all atoms arranged in a chain. It is an isomer of thiosulfurous acid but is lower in energy. Other isomers include HOS(=O)SH, HOS(=S)OH, and HS(=O)2SH. Disulfur monoxide, S2O, can be considered as the anhydride. Unlike many of these other reduced sulfur acids, dihydroxydisulfane can be formed in a pure state by reacting hydrogen sulfide with sulfur dioxide at −70 °C in dichlorodifluoromethane. :H2S + SO2 → H2S2O2 Dihyroxydisulfane may exist in an equilibrium with thiosulfurous acid. Organic derivatives such as dimethoxydisulfane, diaceto disulfide, and bis(trifluoroaceto) disulfide also exist. The conjugate bases are called disulfanediolate(1−) and disulfanediolate(2−) . Properties Calculations predict that the S−S bond length is 2.013 Å, O−S bond length is 1.645 Å, H−O bond length is 0.943& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypodithionous Acid
Dihydroxydisulfane or hypodithionous acid is a reduced sulfur oxyacid with sulfur in a formal oxidation state of +1. The structural formula is HOSSOH, with all atoms arranged in a chain. It is an isomer of thiosulfurous acid but is lower in energy. Other isomers include HOS(=O)SH, HOS(=S)OH, and HS(=O)2SH. Disulfur monoxide, S2O, can be considered as the anhydride. Unlike many of these other reduced sulfur acids, dihydroxydisulfane can be formed in a pure state by reacting hydrogen sulfide with sulfur dioxide at −70 °C in dichlorodifluoromethane. :H2S + SO2 → H2S2O2 Dihyroxydisulfane may exist in an equilibrium with thiosulfurous acid. Organic derivatives such as dimethoxydisulfane, diaceto disulfide, and bis(trifluoroaceto) disulfide also exist. The conjugate bases are called disulfanediolate(1−) and disulfanediolate(2−) . Properties Calculations predict that the S−S bond length is 2.013 Å, O−S bond length is 1.645 Å, H−O bond length is 0.943& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotamer
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can be referred to as different conformations, conformations that correspond to local minima on the potential energy surface are specifically called conformational isomers or conformers. Conformations that correspond to local maxima on the energy surface are the transition states between the local-minimum conformational isomers. Rotations about single bonds involve overcoming a rotational energy barrier to interconvert one conformer to another. If the energy barrier is low, there is free rotation and a sample of the compound exists as a rapidly equilibrating mixture of multiple conformers; if the energy barrier is high enough then there is restricted rotation, a molecule may exist for a relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysulfane Oxide
A polysulfane is a chemical compound of formula , where ''n'' > 1 (although disulfane () is sometimes excluded). Polysulfanes consist of unbranched chains of sulfur atoms terminated with hydrogen atoms. Compounds containing 2 – 8 concatenated sulfur atoms have been isolated, longer chain compounds have been detected, but only in solution. is colourless, higher members are yellow with the colour increasing with the sulfur content. Even a trace of alkali will cause chemical decomposition, and containers need to be treated with acid to remove any traces of alkali. In the chemical literature the term polysulfanes is sometimes used for compounds containing , e.g. organic polysulfanes . Since sulfur is a chalcogen, polysulfanes can be classed as hydrogen chalcogenides. Chemistry and properties Polysulfanes are thermodynamically unstable with respect to decomposition (disproportionation) to and sulfur: : where is ''cyclo''-octasulfur or cyclooctasulfane, one of the allotropes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polythionic Acid
Polythionic acid is an oxoacid which has a straight chain of sulfur atoms and has the chemical formula Sn(SO3H)2 (''n'' > 2). Trithionic acid (H2S3O6), tetrathionic acid (H2S4O6) are simple examples. They are the conjugate acids of polythionates. The compounds of ''n'' 2− + 2 HCl :: SCl2 + 2 → 3SS3SO3sup>2− + 2 HCl Anhydrous polythionic acids can be formed in diethyl ether solution by the following three general ways: : HSnSO3H + SO3 → H2S''n''+2O6 (''n'' = 1, 2 ... 8) : H2Sn + 2 SO3 → H2S''n''+2O6 (''n'' = 1, 2 ... 8) : 2 HSnSO3H + I2 → H2S2''n''+2O6 + 2 HI (''n'' = 1, 2 ... 6) Polythionic acids with a small number of sulfur atoms in the chain (''n'' = 3, 4, 5, 6) are the most stable. Polythionic acids are stable only in aqueous solutions, and are rapidly destroyed at higher concentrations with the release of sulfur, sulfur dioxide and - sometimes - sulfuric acid. Acid salts of polythionic acids do not exist. Polythionate ions are sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |