|
Thermal Diode
The term "thermal diode" is sometimes used for a (possibly non-electrical) device which allows heat to flow preferentially in one direction. Or, the term may be used to describe an electrical (semiconductor) diode in reference to a thermal effect or function. Or the term may be used to describe both situations, where an electrical diode is used as a heat pump or thermoelectric cooler. One-way heat-flow A thermal diode in this sense is a device whose thermal resistance is different for heat flow in one direction than for heat flow in the other direction. I.e., when the thermal diode's first terminal is hotter than the second, heat will flow easily from the first to the second, but when the second terminal is hotter than the first, little heat will flow from the second to the first. Such an effect was first observed in a copper–Cuprous oxide, cuprous-oxide interface by Chauncey Starr in the 1930s. Beginning in 2002, theoretical models were proposed to explain this effect. In 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pipe
A heat pipe is a heat-transfer device that employs phase transition to transfer heat between two solid interfaces. At the hot interface of a heat pipe, a volatile liquid in contact with a thermally conductive solid surface turns into a vapor by absorbing heat from that surface. The vapor then travels along the heat pipe to the cold interface and condenses back into a liquid, releasing the latent heat. The liquid then returns to the hot interface through either capillary action, centrifugal force, or gravity and the cycle repeats. Due to the very high heat transfer coefficients for boiling and condensation, heat pipes are highly effective thermal conductors. The effective thermal conductivity varies with heat pipe length, and can approach for long heat pipes, in comparison with approximately for copper. Structure, design and construction A typical heat pipe consists of a sealed pipe or tube made of a material that is compatible with the working fluid such as copper f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Heat Pipe
A loop heat pipe (LHP) is a two-phase heat transfer device that uses capillary action to remove heat from a source and passively move it to a Condenser (heat transfer), condenser or radiator. LHPs are similar to heat pipes but have the advantage of being able to provide reliable operation over long distance and the ability to operate against gravity. They can transport a large heat load over a long distance with a small temperature difference. Different designs of LHPs ranging from powerful, large size LHPs to miniature LHPs (micro loop heat pipe) have been developed and successfully employed in a wide sphere of applications both ground and space-based applications. Construction The most common coolants used in LHPs are anhydrous ammonia and propylene. LHPs are made by controlling the volumes of the reservoir carefully, condenser and vapor and liquid lines so that liquid is always available to the wick. The reservoir volume and fluid charge are set so that there is always fluid in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Bird
Drinking birds, also known as insatiable birdies, dunking birds, drinky birds, water birds, dipping birds, and “Sippy Chickens” are toy heat engines that mimic the motions of a bird drinking from a water source. They are sometimes incorrectly considered examples of a perpetual motion device. Construction and materials A drinking bird consists of two glass bulbs joined by a glass tube (the bird's neck). The tube extends nearly all the way into the bottom bulb, and attaches to the top bulb but does not extend into it. The space inside the bird contains a fluid, usually colored to make the liquid more visible. The dye might fade when exposed to light, with the rate depending on the dye/color. The fluid is typically dichloromethane (DCM), also known as methylene chloride. Earlier versions contained trichlorofluoromethane. Miles V. Sullivan's 1945 patent suggested ether, alcohol, carbon tetrachloride, or chloroform. Air is removed from the apparatus during manufacture, so the spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltier Device
Thermoelectric cooling uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a solid-state active heat pump which transfers heat from one side of the device to the other, with consumption of electrical energy, depending on the direction of the current. Such an instrument is also called a Peltier device, Peltier heat pump, solid state refrigerator, or thermoelectric cooler (TEC) and occasionally a thermoelectric battery. It can be used either for heating or for cooling, although in practice the main application is cooling. It can also be used as a temperature controller that either heats or cools. This technology is far less commonly applied to refrigeration than vapor-compression refrigeration is. The primary advantages of a Peltier cooler compared to a vapor-compression refrigerator are its lack of moving parts or circulating liquid, very long life, invulnerability to leaks, smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerator
A refrigerator, colloquially fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermal insulation, thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so that its inside is cooled to a temperature below the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential Food preservation, food storage technique around the world. The lower temperature lowers the reproduction rate of bacteria, so the refrigerator reduces the rate of Food spoilage, spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. The optimal temperature range for perishable food storage is .Keep your fridge-freezer clean and ice-free ''BBC''. 30 April 2008 A similar device that maintains a temperature below the freezing point of water is called a freezer. The refrigerator replaced the icebox, which had been a common household appliance for almost a century and a half. The United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
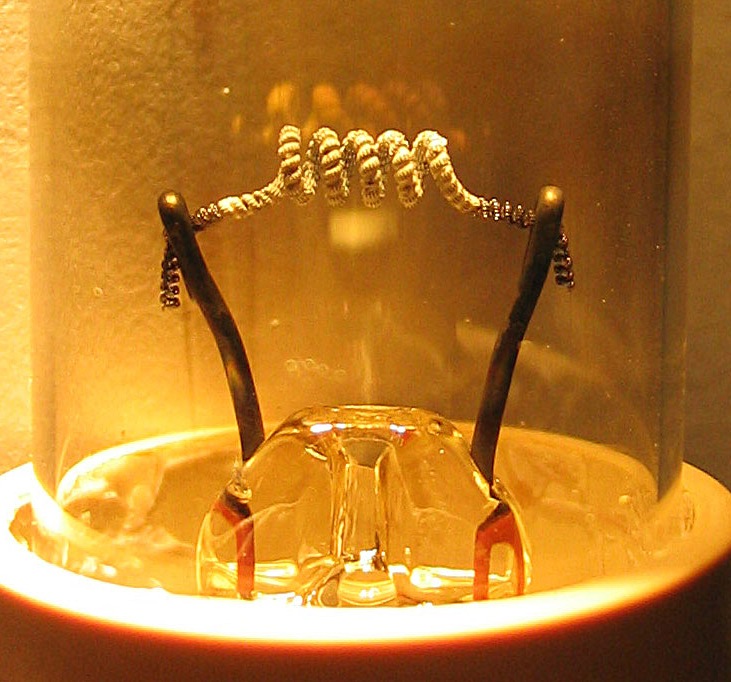
Thermionic Emission
Thermionic emission is the liberation of electrons from an electrode by virtue of its temperature (releasing of energy supplied by heat). This occurs because the thermal energy given to the charge carrier overcomes the work function of the material. The charge carriers can be electrons or ions, and in older literature are sometimes referred to as thermions. After emission, a charge that is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the total charge emitted is initially left behind in the emitting region. But if the emitter is connected to a battery, the charge left behind is neutralized by charge supplied by the battery as the emitted charge carriers move away from the emitter, and finally the emitter will be in the same state as it was before emission. The classical example of thermionic emission is that of electrons from a hot cathode into a vacuum (also known as thermal electron emission or the Edison effect) in a vacuum tube. The hot cathode can be a metal filament, a coate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltier-Seebeck Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical process; textbooks may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermocouple
A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of the Seebeck effect, and this voltage can be interpreted to measure temperature. Thermocouples are widely used as temperature sensors. Commercial thermocouples are inexpensive, interchangeable, are supplied with standard connectors, and can measure a wide range of temperatures. In contrast to most other methods of temperature measurement, thermocouples are self powered and require no external form of excitation. The main limitation with thermocouples is accuracy; system errors of less than one degree Celsius (°C) can be difficult to achieve. Thermocouples are widely used in science and industry. Applications include temperature measurement for kilns, gas turbine exhaust, diesel engines, and other industrial processes. Thermocouples are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
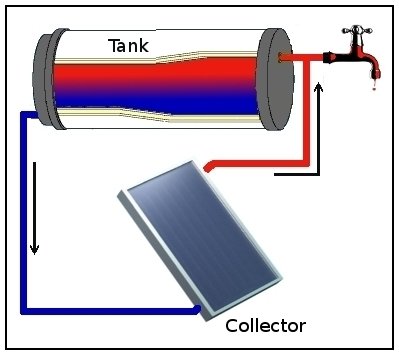
Thermosiphon
Thermosiphon (or thermosyphon) is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney. This circulation can either be open-loop, as when the substance in a holding tank is passed in one direction via a heated transfer tube mounted at the bottom of the tank to a distribution point—even one mounted above the originating tank—or it can be a vertical closed-loop circuit with return to the original container. Its purpose is to simplify the transfer of liquid or gas while avoiding the cost and complexity of a conventional pump. Simple thermosiphon Natural convection of the liquid starts when heat transfer to the liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two- terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Nanotechnology
''Nature Nanotechnology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Publishing Group. It was established in October 2006. The editor-in-chief is Fabio Pulizzi. It covers all aspects of nanoscience and nanotechnology. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: List of databases published by Thomson Reuters that index this journal. Journals referenced in the NCBI databases * Chemical Abstracts Service * Science Citation Index * Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * Current Contents/Engineering, Computing & Technology * Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 39.213. References Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |