|
Theory Of Pashtun Descent From Israelites
Historically, there have been multiple claims and theories conceived that concern the origin of the Pashtun people, who are classified as an Iranic ethnic group native to Central and South Asia. The most prominent theories of Pashtun origin are: # The traditional legend of descent from the Ten Lost Tribes of the ancient Israelites through Saul, the first king of Israel. # Descent from the Hephthalites (also known as the White Huns), a late-antiquity nomadic confederation in Central Asia. # Descent from the Saka, a group of nomadic Iranic peoples who historically inhabited the Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin. # Descent from the Pakthas, an ancient people referenced in Sanskrit and Greek sources who inhabited what is today southeastern Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. # Descent from the ancient Greeks and Rajputs (see Ancient Greece–Ancient India relations). Prior to DNA studies, it was generally acknowledged that their origins were obscure; modern schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically referred to as Afghans () or xbc, αβγανο () until the 1970s, when the term's meaning officially evolved into that of a demonym for all residents of Afghanistan, including those outside of the Pashtun ethnicity. The group's native language is Pashto, an Iranian language in the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family. Additionally, Dari Persian serves as the second language of Pashtuns in Afghanistan while those in the Indian subcontinent speak Urdu and Hindi (see Hindustani language) as their second language. Pashtuns are the 26th-largest ethnic group in the world, and the largest segmentary lineage society; there are an estimated 350–400 Pashtun tribes and clans with a variety of origin theories. The total popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RV 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to ''Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are additionally credited to Kumara Agneya. It is one of the "family books" (mandalas 2-7), the oldest core of the Rigveda, which were composed in early vedic period(1500-1000 BCE). The hymns are dedicated to Agni, Indra, the Visvadevas, the Maruts, Mitra-Varuna, the Asvins, Ushas (Dawn), Indra-Varuna, Varuna, Vayu (Wind), two each to Sarasvati, Rudra, the Waters, the Adityas, Vishnu, Vastospati, Brhaspati, one each to the Apris, to Vashista, Savitar, Bhaga, the Dadhikras, the Rbhus, Dyaus and Prthivi (Heaven and Earth), Parjanya (Rain) and Indra-Soma. 7.103 is dedicated to the frogs. The rivers mentioned in the 7th Mandala are the Sarasvati, Asikni, Parusni and possibly the Yamuna (in 7.18.19 the name of a helper of Indra, maybe also the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. The sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted since the 2nd millennium BCE. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the bulk of the ''Rigveda'' Samhita was composed in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent (see) Rigvedic rivers), most likely between 1500 and 1000 BCE, although a wider approximation of 19001200 BCE has also been given. The text is layered, consisting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasarajna
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, दाशराज्ञ युद्ध, translit=Dāśarājñá yuddhá) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Bharatas and subsequent formation of the Kuru polity. Background In Book 3, the Bharatas are noted to have crossed Beas and Sutlej, in their progress towards Kurukshetra where they came across a nascent (and temporary) inter-tribal alliance. This led to the battle, which is described in the 18th hymn (verses 5-21) of Book 7; the exact motivations are doubtful — Michael Witzel argues that it might have been a product of intratribal resentment or intrigues of an ousted family-priest while Ranabir Chakravarti argues that the battle was probably fought for controlling the rivers, which were a lifeline for irrigation. The hymns also mention of the tribes seeking to steal cows from the Bharatas. Battle Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudas
Sudās Paijavana ( sa, सुदास्) was an Indo-Aryan tribal king of the Bharatas, during the main or middle Rigvedic period (c. 14th century BCE). He led his tribe to victory in the Battle of the Ten Kings near the Paruṣṇī (modern Ravi River) in Punjab, defeating an alliance of the powerful Puru tribe with other tribes, for which he was eulogised by his purohita Vashistha in a hymn of the Rigveda. His victory established the ascendency of the Bhārata clan, allowing them to move eastwards and settle in Kurukshetra, paving the way for the emergence of the Kuru "super-tribe" or tribal union, which dominated northern India in the subsequent period. Family Sudās' ancestors include Pijavana, Divodāsa Atithigva, and Devavant, although scholars disagree regarding the order of these ancestors chronologically. According to Witzel, Divodāsa was the father of Sudās, but he includes Pijavana on the grid of Bharata descent as a possible ancestor between Divodāsa an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rigvedic Tribes
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions. From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent – Indus Valley (roughly today's Punjab), Western India, Northern India, Central India, and also in areas of the southern part like Sri Lanka and the Maldives through and after a complex process of migration, assimilation of other peoples and language shift.Mallory, J.P.; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. . Ancestors *Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers) **Proto-Indo-Iranians (common ancestors of the Iranian, Nuristani and Indo-Aryan peoples) ( Proto-Indo-Iranian speakers) ***Proto-Indo-Aryans (Proto-Indo-Aryan speakers) Vedic tribes * Alina people (RV 7.18.7) * Andhras * Anu (RV 1.108.8, RV 8.10.5) * Āyu * Bhajerath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
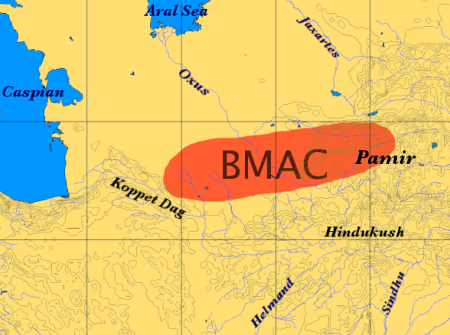
Afghanistan Region During 500 BC
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. , its population is 40.2 million (officially estimated to be 32.9 million), composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital. Human habitation in Afghanistan dates back to the Middle Paleolithic era, and the country's strategic location along the historic Silk Road has led it to being described, picturesquely, as the ‘ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC. In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age. The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era: The first half of the millennium is dominated by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and Babylonia. The alphabet develops. At the center of the millennium, a new order emerges with Mycenaean Greek dominance of the Aegean and the rise of the Hittite Empire. The end of the millennium sees the Bronze Age collapse and the transition to the Iron Age. Other regions of the world are still in the prehistoric period. In Europe, the Beaker culture introduces the Bronze Age, presumably associated with Indo-European expansion. The Indo-Iranian expansion reaches the Iranian plateau and onto the Indian subcontinent (Vedic India), propagating the use of the chariot. Mesoamerica enters the Pre-Classic (Olmec) period. North America is in the late Archaic stage. In Maritime Southeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. or Amazonia is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses , of which are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations and 3,344 formally acknowledged Indigenous territory (Brazil), indigenous territories. The majority of the forest is contained Amazônia Legal, within Brazil, with 60% of the rainforest, followed by Peruvian Amazonia, Peru with 13%, Amazon natural region, Colombia with 10%, and with minor amounts in Bolivia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela. Four nations have "Amazonas (other), Amazonas" as the name of one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashtun Tribes
The Pashtun tribes ( ps, پښتانه قبايل), historically also known as Afghan tribes, are the tribes of the Pashtun people, a large Eastern Iranian ethnic group who use the Pashto language and follow Pashtunwali code of conduct. They are found primarily in Afghanistan and Pakistan and form the world's largest tribal society, comprising over 49 million people and between 350 and 400 tribes and clans. They are traditionally divided into four tribal confederacies: the Sarbani (), the Bettani (), the Gharghashti () and the Karlani (). Folkloric genealogies trace the descendants of the Pashtuns to Qais Abdur Rashid and his three sons ''Saṛban'' (), ''Bēṭ'' (), and ''Gharghax̌t'' () as well as an adopted son, not directly adopted by Qais Abdul Rashid, therefore, the identity of Karlan himself and the man who adopted him, according to some books written on the history of the Pashtuns, is either unclear or controversial, the Karlani confederacy Ormur Baraki, who became t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)