|
The Case Against Education
''The Case Against Education: Why the Education System Is a Waste of Time and Money'' is a book written by libertarian economist Bryan Caplan and published in 2018 by Princeton University Press. Drawing on the economic concept of job market signaling and research in educational psychology, the book argues that much of higher education is very inefficient and has only a small effect in improving human capital, contrary to the conventional consensus in labor economics. Caplan argues that the primary function of education is not to enhance students' skills but to certify their intelligence, conscientiousness, and conformity—attributes that are valued by employers. He ultimately estimates that approximately 80% of individuals' return to education is the result of signaling, with the remainder due to human capital accumulation. Summary Human capital model The foundation of the drive to increase educational attainment across the board is the human capital model of education, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryan Caplan
Bryan Douglas Caplan (born April 8, 1971) is an American economist and author. Caplan is a professor of economics at George Mason University, research fellow at the Mercatus Center, adjunct scholar at the Cato Institute, and former contributor to the ''Freakonomics'' blog and EconLog. He currently publishes his own blog, ''Bet on It''. Caplan is a self-described "economic libertarian". The bulk of Caplan's academic work is in behavioral economics and public economics, especially public choice theory. Education Caplan holds a B.A. in economics from the University of California, Berkeley (1993) and a Ph.D. in economics from Princeton University (1997). Writings ''The Myth of the Rational Voter'' ''The Myth of the Rational Voter: Why Democracies Choose Bad Policies'', published in 2007, further develops the "rational irrationality" concept from Caplan's earlier academic writing. It draws heavily from the ''Survey of Americans and Economists on the Economy'' in making the argume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean of a large number of independently selected outcomes of a random variable. The expected value of a random variable with a finite number of outcomes is a weighted average of all possible outcomes. In the case of a continuum of possible outcomes, the expectation is defined by integration. In the axiomatic foundation for probability provided by measure theory, the expectation is given by Lebesgue integration. The expected value of a random variable is often denoted by , , or , with also often stylized as or \mathbb. History The idea of the expected value originated in the middle of the 17th century from the study of the so-called problem of points, which seeks to divide the stakes ''in a fair way'' between two players, who have to end th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austerity
Austerity is a set of political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. There are three primary types of austerity measures: higher taxes to fund spending, raising taxes while cutting spending, and lower taxes and lower government spending. Austerity measures are often used by governments that find it difficult to borrow or meet their existing obligations to pay back loans. The measures are meant to reduce the budget deficit by bringing government revenues closer to expenditures. Proponents of these measures state that this reduces the amount of borrowing required and may also demonstrate a government's fiscal discipline to creditors and credit rating agencies and make borrowing easier and cheaper as a result. In most macroeconomic models, austerity policies which reduce government spending lead to increased unemployment in the short term. These reductions in employment usually occur di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocational Education
Vocational education is education that prepares people to work as a technician or to take up employment in a skilled craft or trade as a tradesperson or artisan. Vocational Education can also be seen as that type of education given to an individual to prepare that individual to be gainfully employed or self employed with requisite skill. Vocational education is known by a variety of names, depending on the country concerned, including career and technical education, or acronyms such as TVET (technical and vocational education and training) and TAFE (technical and further education). A vocational school is a type of educational institution specifically designed to provide vocational education. Vocational education can take place at the post-secondary, further education, or higher education level and can interact with the apprenticeship system. At the post-secondary level, vocational education is often provided by highly specialized trade schools, technical schools, community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Student Loans In The United States
Student loans in the United States are a form of financial aid intended to help students access higher education. In 2018, 70 percent of higher education graduates had used loans to cover some or all of their expenses. With notable exceptions, student loans must be repaid, in contrast to other forms of financial aid such as scholarships, which are not repaid, and grants, which rarely have to be repaid. Student loans may be discharged through bankruptcy, but this is difficult. Student loan debt has proliferated since 2006, totaling $1.73 trillion by July 2021. In 2019, students who borrowed to complete a bachelor's degree had about $30,000 of debt upon graduation. Almost half of all loans are for graduate school, typically in much higher amounts. Loan amounts vary widely based on race, social class, age, institution type, and degree sought. As of 2017, student debt constituted the largest non-mortgage liability for US households. Research indicates that increasing borrowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
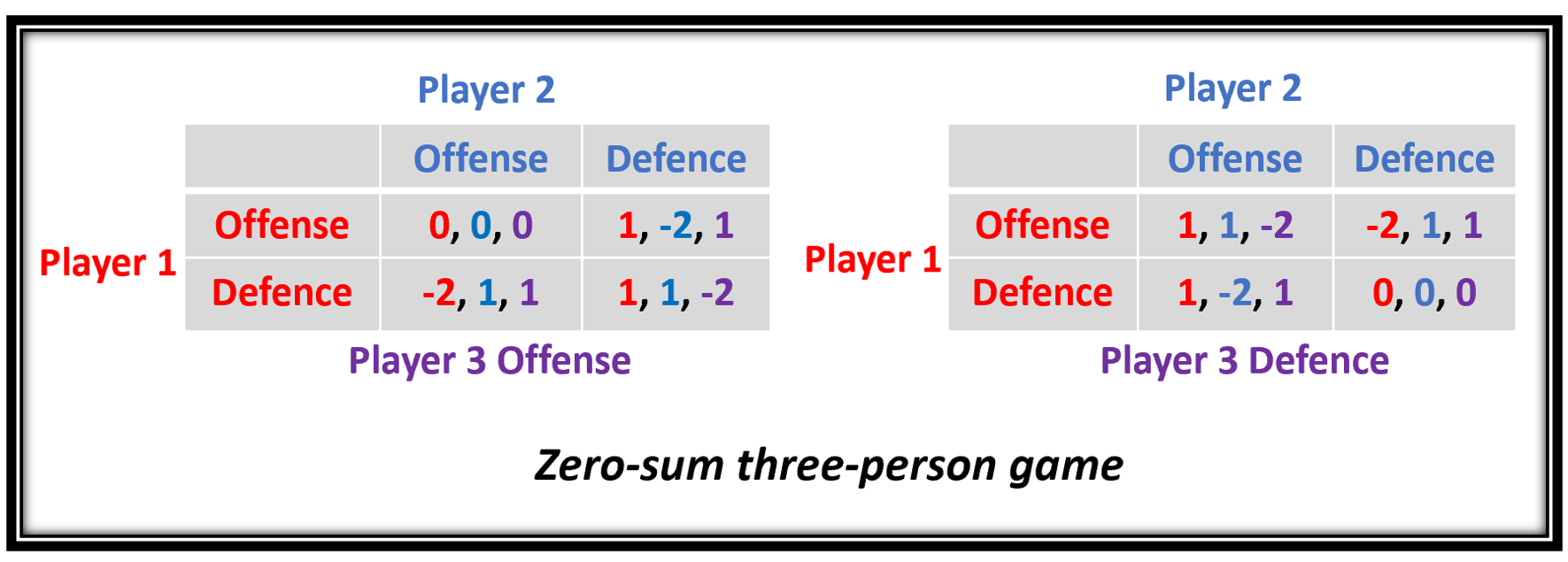
Zero-sum Game
Zero-sum game is a mathematical representation in game theory and economic theory of a situation which involves two sides, where the result is an advantage for one side and an equivalent loss for the other. In other words, player one's gain is equivalent to player two's loss, therefore the net improvement in benefit of the game is zero. If the total gains of the participants are added up, and the total losses are subtracted, they will sum to zero. Thus, cutting a cake, where taking a more significant piece reduces the amount of cake available for others as much as it increases the amount available for that taker, is a zero-sum game if all participants value each unit of cake equally. Other examples of zero-sum games in daily life include games like poker, chess, and bridge where one person gains and another person loses, which results in a zero-net benefit for every player. In the markets and financial instruments, futures contracts and options are zero-sum games as well. In c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Externality
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either consumer or producer market transactions. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport to the rest of society. Water pollution from mills and factories is another example. All consumers are all made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. A positive externality is when an individual's consumption in a market increases the well-being of others, but the individual does not charge the third party for the benefit. The third party is essentially getting a free product. An example of this might be the apartment above a bakery receiving the benefit of enjoyment from smelling fresh pastries every mornin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Return On Investment
Social return on investment (SROI) is a principles-based method for measuring extra-financial value (such as environmental or social value not currently reflected or involved in conventional financial accounts). It can be used by any entity to evaluate impact on stakeholders, identify ways to improve performance, and enhance the performance of investments. The SROI method as it has been standardized by Social Value UK provides a consistent quantitative approach to understanding and managing the impacts of a project, business, organisation, fund or policy. It accounts for stakeholders' views of impact, and puts financial 'proxy' values on all those impacts identified by stakeholders which do not typically have market values. The aim is to include the values of people that are often excluded from markets in the same terms as used in markets, that is money, in order to give people a voice in resource allocation decisions. Some SROI users employ a version of the method that does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return On Investment
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is a ratio between net income (over a period) and investment (costs resulting from an investment of some resources at a point in time). A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably to its cost. As a performance measure, ROI is used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiencies of several different investments.Return On Investment – ROI , Investopedia as accessed 8 January 2013 In economic terms, it is one way of relating profits to capital invested. Purpose In business, the pur ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Of Learning
Transfer of learning occurs when people apply information, strategies, and skills they have learned to a new situation or context. Transfer is not a discrete activity, but is rather an integral part of the learning process. Researchers attempt to identify when and how transfer occurs and to offer strategies to improve transfer. Overview The ''formal discipline'' (or ''mental discipline'') approach to learning believed that specific mental faculties could be strengthened by particular courses of training and that these strengthened faculties transferred to other situations, based on faculty psychology which viewed the mind as a collection of separate modules or faculties assigned to various mental tasks. This approach resulted in school curricula that required students to study subjects such as mathematics and Latin in order to strengthen reasoning and memory faculties. Disputing formal discipline, Edward Thorndike and Robert S. Woodworth in 1901 postulated that the transfer of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheepskin Effect
The sheepskin effect (named for the vellum on which diplomas were traditionally written) is a phenomenon in applied economics observing that people possessing a completed academic degree earn a greater income than people who have an equivalent amount of studying without possessing an academic degree. There are many applied economics papers which investigate the signaling effect of possession of such an academic degree. For example, if Student A is one credit short of a Bachelor's degree, while Student B has earned their Bachelor's degree, then the two students have essentially the same amount of education. However, according to the sheepskin effect, Student B will earn a greater income than Student A. Research into the sheepskin effect can be divided into studies of explicit degree effects and, because many of the useful data sets don't explicitly report degrees, studies with no explicit degree measures. The latter typically use 12 years of education as a proxy for a high sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade Inflation
Grade inflation (also known as grading leniency) is the awarding of higher grades than students deserve, which yields a higher average grade given to students. The term is also used to describe the tendency to award progressively higher academic grades for work that would have received lower grades in the past. However, higher average grades in themselves do not prove grade inflation. For this to be grade inflation, it is necessary to demonstrate that the quality of work does not deserve the high grade. Grade inflation is frequently discussed in relation to education in the United States, and to GCSEs and A levels in England and Wales. It is also an issue in many other nations, such as Canada, Australia, New Zealand, France, Germany, South Korea and India. In the United States At the secondary level Data from the ACT show that, since 2016, and particularly during the COVID-19 restrictions, grade inflation in secondary schools has sharply accelerated. Most students taking the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |