|
Terbium Gallium Garnet
Terbium gallium garnet (TGG) is a kind of synthetic garnet, with the chemical composition . This is a Faraday rotator material with excellent transparency properties and is very resistant to laser damage. TGG can be used in optical isolators for laser systems, in optical circulators for fiber optic systems, in optical modulators, and in current and magnetic field sensors. TGG has a high Verdet constant which results in the Faraday effect. The Verdet constant increases substantially as the mineral approaches cryogenic temperatures. The highest Verdet constants are found in terbium doped dense flint glasses or in crystals of TGG. The Faraday effect is chromatic (i.e. it depends on wavelength) and therefore the Verdet constant is quite a strong function of wavelength. At 632 nm, the Verdet constant for TGG is reported to be , whereas at 1064 nm it falls to . This behavior means that the devices manufactured with a certain degree of rotation at one wavelength, will produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Rotator
A Faraday rotator is a polarization rotator based on the Faraday effect, a magneto-optic effect involving transmission of light through a material when a longitudinal static magnetic field is present. The state of polarization (such as the axis of linear polarization or the orientation of elliptical polarization) is rotated as the wave traverses the device, which is explained by a slight difference in the phase velocity between the left and right circular polarizations. Thus it is an example of ''circular birefringence'', as is optical activity, but involves a material only having this property in the presence of a magnetic field. Circular birefringence, involving a difference in propagation between opposite ''circular'' polarizations, is distinct from ''linear birefringence'' (or simply birefringence, when the term is not further specified) which also transforms a wave's polarization but not through a simple rotation. The polarization state is rotated in proportion to the appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint Glass
Flint glass is optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number (high dispersion). Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45 and 2.00. A concave lens of flint glass is commonly combined with a convex lens of crown glass to produce an achromatic doublet lens because of their compensating optical properties, which reduces chromatic aberration (colour defects). With respect to glass, the term ''flint'' derives from the flint nodules found in the chalk deposits of southeast England that were used as a source of high purity silica by George Ravenscroft, c. 1662, to produce a potash lead glass that was the precursor to English lead crystal. Traditionally, flint glasses were lead glasses containing around 4–60% lead(II) oxide; however, the manufacture and disposal of these glasses were sources of pollution. In many modern flint gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terbium Compounds
Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states. The trivalent terbium ion is generally colorless in aqueous solution, and when it is irradiated by certain wavelengths of ultraviolet light (such as 254 nm or 365 nm) in solution or crystal form, it will emit green fluorescence. This property has given rise to applications in fields such as optics. Properties of terbium compounds Chalcogenides Oxides Terbium has a variety of oxides. The most easily obtained is terbium(III,IV) oxide, which can be produced by the decomposition of terbium compounds such as the hydroxide,Chen Shouchun. Important Inorganic Chemical Reactions. Shanghai Science and Technology Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxides
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of a equation or reaction) Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Minerals
Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to: Science * Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis * Synthetic organic compounds synthetic chemical compounds based on carbon (organic compounds). * Synthetic peptide * Synthetic biology * Synthetic elements, chemical elements that are not naturally found on Earth and therefore have to be created in experiments Industry * Synthetic fuel * Synthetic oil * Synthetic marijuana * Synthetic diamond * Synthetic fibers, cloth or other material made from other substances than natural (animal, plant) materials Other * Synthetic position, a concept in finance * Synthetic-aperture radar, a type or radar * Analytic–synthetic distinction, in philosophy * Synthetic language in linguistics, inflected or agglutinative languages * Synthetic intelligence a term emphasizing that true intelligence expressed by comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium Aluminium Garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG, Y3 Al5 O12) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group. It is a cubic yttrium aluminium oxide phase, with other examples being YAlO3 (YAP) in a hexagonal or an orthorhombic, perovskite-like form, and the monoclinic Y4Al2O9 (YAM). Due to its broad optical transparency, low internal stress, high hardness, chemical and heat resistance, YAG is used for a variety of optics. Its lack of birefringence (unlike sapphire) makes it an interesting material for high-energy/high-power laser systems. Laser damage levels of YAG ranged from 1.1 to 2.2 kJ/cm² (1064 nm, 10 ns). YAG, like garnet and sapphire, has no uses as a laser medium when pure. However, after being doped with an appropriate ion, YAG is commonly used as a host material in various solid-state lasers. Rare earth elements such as neodymium and erbium can be doped into YAG as active laser ions, yielding Nd:YAG and Er:YAG lasers, respectively. Cerium-doped YAG (Ce:YA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium Iron Garnet
Yttrium iron garnet (YIG) is a kind of synthetic garnet, with chemical composition , or Y3Fe5O12. It is a ferrimagnetic material with a Curie temperature of 560 K. YIG may also be known as yttrium ferrite garnet, or as iron yttrium oxide or yttrium iron oxide, the latter two names usually associated with powdered forms. In YIG, the five iron(III) ions occupy two octahedral and three tetrahedral sites, with the yttrium(III) ions coordinated by eight oxygen ions in an irregular cube. The iron ions in the two coordination sites exhibit different spins, resulting in magnetic behavior. By substituting specific sites with rare-earth elements, for example, interesting magnetic properties can be obtained. YIG has a high Verdet constant which results in the Faraday effect, high Q factor in microwave frequencies, low absorption of infrared wavelengths down to 1200 nm, and very small linewidth in electron spin resonance. These properties make it useful for MOI (magneto optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadolinium Gallium Garnet
Gadolinium Gallium Garnet (GGG, ) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group, with good mechanical, thermal, and optical properties. It is typically colorless. It has a cubic lattice, a density of 7.08 g/cm3 and its Mohs hardness is variously noted as 6.5 and 7.5. Its crystals are produced with the Czochralski method. During production, various dopants can be added for colour modification. The material is also used in fabrication of various optical components and as a substrate material for magneto–optical films (magnetic bubble memory Bubble memory is a type of non-volatile computer memory that uses a thin film of a magnetic material to hold small magnetized areas, known as ''bubbles'' or ''domains'', each storing one bit of data. The material is arranged to form a series of ...).J. F. Greber "Gallium and Gallium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It also finds use in jewelry as a diamond simulant. GGG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
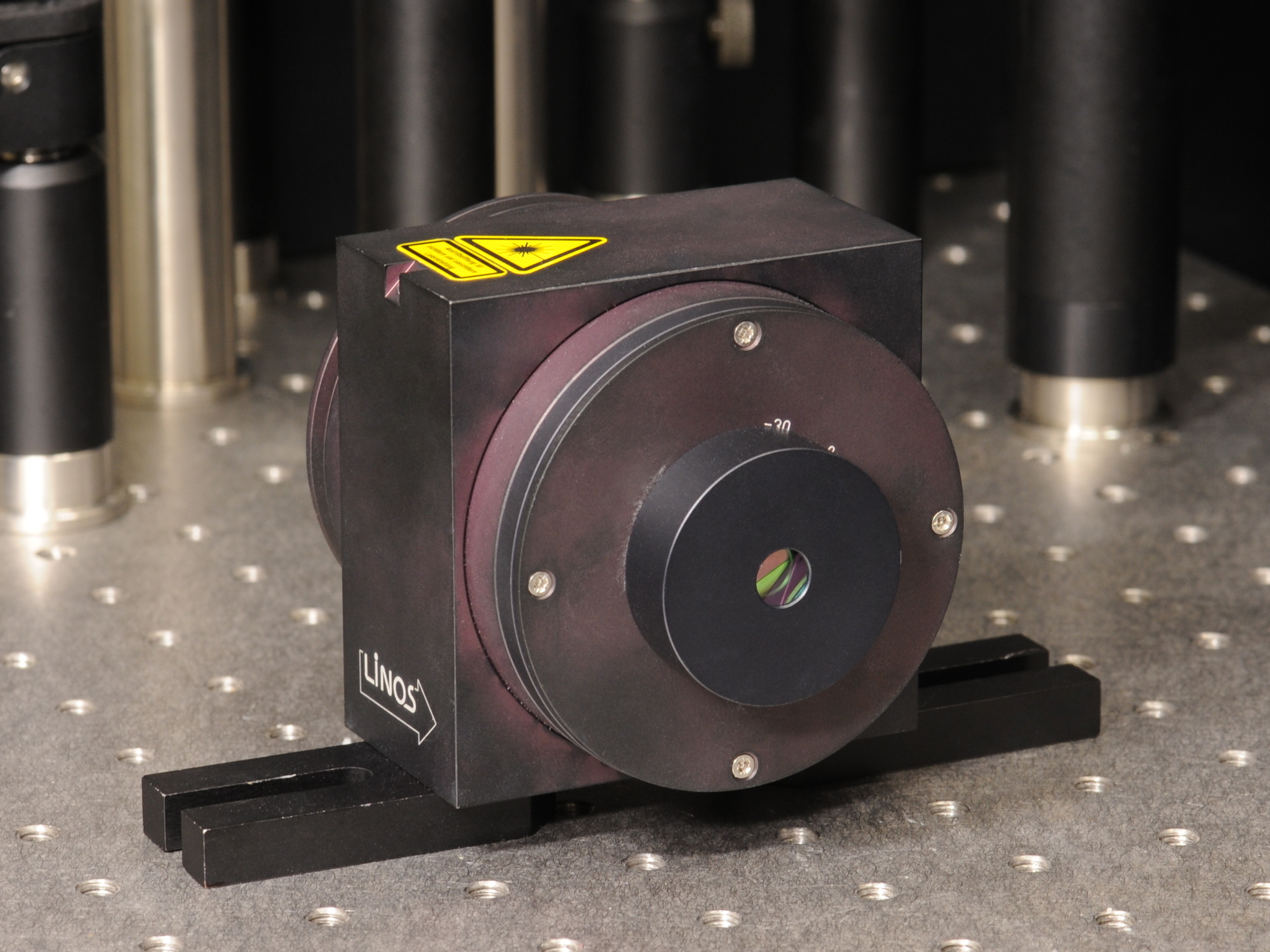
Faraday Isolator
An optical isolator, or optical diode, is an optical component which allows the transmission of light in only one direction. It is typically used to prevent unwanted feedback into an optical oscillator, such as a laser cavity. The operation of ome ofthe devices depends on the Faraday effect (which in turn is produced by magneto-optic effect), which is used in the main component, the Faraday rotator. Theory The main component of the optical isolator is the Faraday rotator. The magnetic field, B, applied to the Faraday rotator causes a rotation in the polarization of the light due to the Faraday effect. The angle of rotation, \beta, is given by, :\beta=\nu B d\,, where, \nu is the Verdet constant of the material (amorphous or crystalline solid, or liquid, or crystalline liquid, or vaprous, or gaseous) of which the rotator is made, and d is the length of the rotator. This is shown in Figure 2. Specifically for an optical isolator, the values are chosen to give a rotation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic (other)
Chromatic, a word ultimately derived from the Greek noun χρῶμα (''khrṓma''), which means "complexion" or "color", and then from the Greek adjective χρωματικός (''khrōmatikós''; "colored"), may refer to: In music *Chromatic scale, the western-tempered twelve-tone scale *Chromatic chord, chords built from tones chromatically altered from the native scale of the musical composition *Chromaticism, the use of chromatic scales, chords, and modulations *Total chromatic, the use of all twelve pitches of the chromatic scale in tonal music *Chromatic fantasia, a specific form of fantasia originating in sixteenth century Europe *The Chromatic button accordion *The chromatic harmonica *Chromatic genus, a genus of divisions of the tetrachord characterized by an upper interval of a minor third *Diatonic and chromatic, as a property of several structures, genres, and other features in music, often contrasted with ''diatonic'' *Chromatics (band), an American electronic music ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Temperature
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cryogenic” by accepting a threshold of 120 K (or –153 °C) to distinguish these terms from the conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120K while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120K. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology considers the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below -153 Celsius (120K; -243.4 Fahrenheit) Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low cost metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, diamagnetic materials are repelled by magnetic fields and form induced magnetic fields in the direction opposite to that of the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials include most chemical elements and some compounds; they have a relative magnetic permeability slightly greater than 1 (i.e., a small positive magnetic susceptibility) and hence are attracted to magnetic fields. The magnetic moment induced by the applied field is linear in the field strength and rather weak. It typically requires a sensitive analytical balance to detect the effect and modern measurements on paramagnetic materials are often conducted with a SQUID magnetometer. Paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in the material, so most atoms w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |