|
Telecommunications In The People's Republic Of China
The People's Republic of China possesses a diversified communications system that links all parts of the country by Internet, telephone, telegraph, radio, and television. The country is served by an extensive system of automatic telephone exchanges connected by modern networks of fiber-optic cable, coaxial cable, microwave radio relay, and a domestic satellite system; cellular telephone service is widely available, expanding rapidly, and includes roaming service to foreign countries. Fiber to the x infrastructure has been expanded rapidly in recent years. History When the People's Republic was founded in 1949, the telecommunication systems and facilities in China first established by the Qing and Republican ITA and Ministry of Posts and Communications had been seriously damaged from over thirty years of on and off war between warlords, Japan, and the two sides of the Chinese Civil War. What little remained was largely outdated and rudimentary and limited to the eastern coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Soviet Relations
SinoSoviet relations (; russian: Советско-китайские отношения, ''Sovetsko-kitayskiye otnosheniya''), or China–Soviet Union relations, refers to the diplomatic relationship between China (both the Chinese Republic of 1912–49 and its successor, the People's Republic of China) and the various forms of Soviet Power which emerged from the Russian Revolution of 1917 to 1991, when the Soviet Union ceased to exist. Country comparison Russian Civil War and Mongolia The Beiyang government in north China joined the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War, sending forces to Siberia and North Russia beginning in 1918. Mongolia and Tuva became contested territories. After being occupied by the Chinese General Xu Shuzheng in 1919, they came under the sway of the Russian White Guard General turned independent warlord, Ungern von Sternberg in 1920. Soviet troops, with support from Mongolian guerrillas led by Damdin Sükhbaatar, defeated the White warlord a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
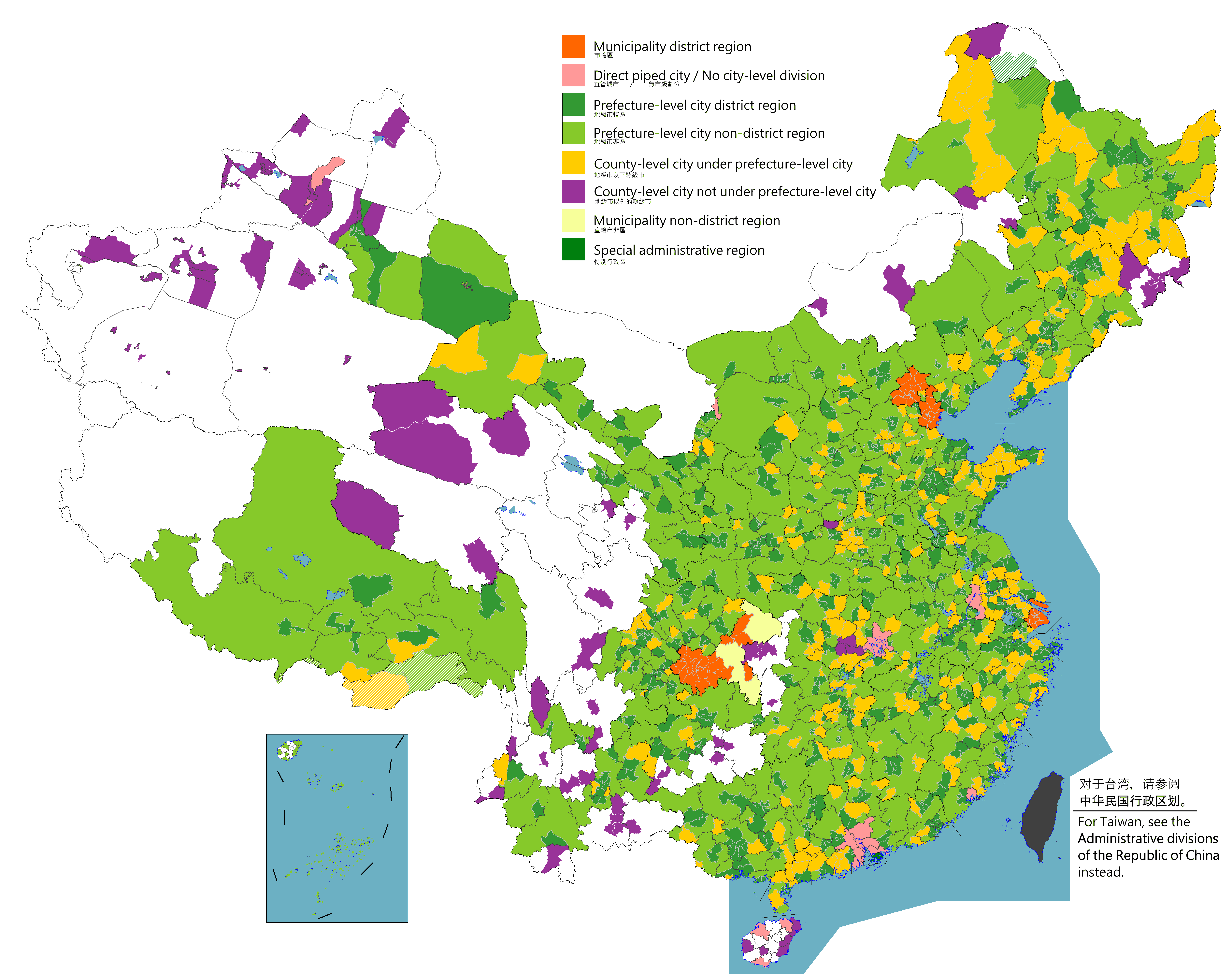
List Of Cities In The People's Republic Of China
According to the administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China there are three levels of cities, namely provincial-level (consists of municipalities ), prefecture-level cities, and county-level cities. As of June 2020 the PRC has a total of 687 cities: 4 municipalities, 2 SARs, 293 prefectural-level cities (including the 15 sub-provincial cities) and 388 county-level cities (including the 38 sub-prefectural cities and 10 XXPC cities). This list does not include any cities in the disputed Taiwan Province and portions of Fujian Province (see the List of cities in Taiwan), as these are controlled by the Republic of China and claimed by the PRC under the One-China policy. Four cities are centrally administered municipalities, which include dense urban areas, suburbs, and large rural areas: Chongqing (28.84 million), Shanghai (23.01 million), Beijing (19.61 million), and Tianjin (12.93 million). According to 2017 research from the Demographia research group, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Areas Of China
Chinese autonomous administrative divisions are associated with one or more ethnic minorities that are designated as autonomous within the People's Republic of China. These areas are recognized in the Constitution of the People's Republic of China and are nominally given a number of rights not accorded to other administrative divisions of China. For example, Tibetan minorities in autonomous regions are granted rights and support not given to the Han Chinese, such as fiscal and medical subsidies. Autonomous administrative divisions The PRC's autonomous administrative divisions may be found in the first (or top) to third levels of its national administrative divisions thus: Ethnic area Although not named as autonomous areas, some third-level settlements and areas that are identified as county-level cities and county-level districts enjoy the same autonomy as autonomous areas. At the fourth ("township") level, 1 ethnic sum (the Evenk Ethnic Sum) and over 270 ethnic townships a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Current And Former Capitals Of Subnational Entities Of China
This is a list of the current and former capitals of the country subdivisions of China. The history of China and its administrative divisions is long and convoluted; hence, this chart will cover only capitals after the completion of the Mongol conquest of China in 1279, because the modern province ( ) was first created during the Mongol Yuan dynasty. A selection of country subdivisions and their capitals before 1279 can be found in the article History of the political divisions of China. Years may not line up perfectly during periods of turmoil (e.g. at the end of each dynasty). The list includes current and former provinces, as well as other first-level units that have been used over the course of China's recent history, such as autonomous regions, military command zones during the Qing dynasty, and so forth. Unless otherwise specified, a given administrative unit can be assumed to be a province with its present name. Historical names of provinces and entities that are not prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward (Second Five Year Plan) of the People's Republic of China (PRC) was an economic and social campaign led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1958 to 1962. CCP Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to reconstruct the country from an agrarian economy into a communist society through the formation of people's communes. Mao decreed that efforts to multiply grain yields and bring industry to the countryside should be increased. Local officials were fearful of Anti-Rightist Campaigns and they competed to fulfill or over-fulfill quotas which were based on Mao's exaggerated claims, collecting non-existent "surpluses" and leaving farmers to starve to death. Higher officials did not dare to report the economic disaster which was being caused by these policies, and national officials, blaming bad weather for the decline in food output, took little or no action. Millions of people died in China during the Great Leap, with estimates ranging from 15 to 55 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution (business), distribution of sound, audio or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, all forms of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
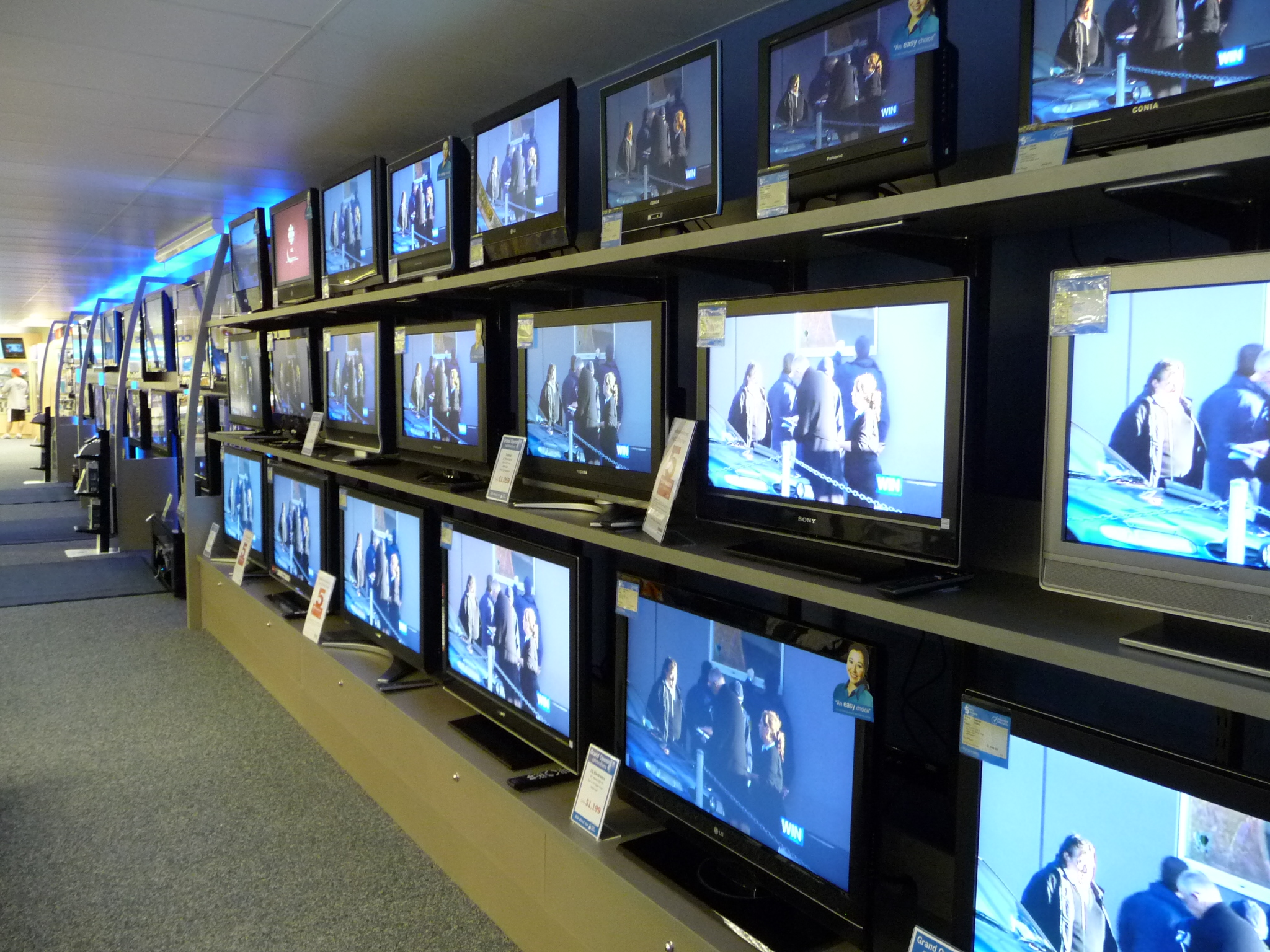
Television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initially they were used in telegraphy, which developed in the late 1830s and 1840s as the first use of electrical engineering, though teleprinters were not used for telegraphy until 1887 at the earliest. The machines were adapted to provide a user interface to early mainframe computers and minicomputers, sending typed data to the computer and printing the response. Some models could also be used to create punched tape for data storage (either from typed input or from data received from a remote source) and to read back such tape for local printing or transmission. Teleprinters could use a variety of different communication media. These included a simple pair of wires; dedicated non-switched telephone circuits (leased lines); switched network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegraphic
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined and such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the optical telegraph of Claude Chappe, invented in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid to railway signalling. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications System
A communications system or communication system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. The components of a communications system serve a common purpose, are technically compatible, use common procedures, respond to controls, and operate in union. Telecommunications is a method of communication (e.g., for sports broadcasting, mass media, journalism, etc.). Communication is the act of conveying intended meanings from one entity or group to another through the use of mutually understood signs and semiotic rules. Types By media An optical communication system is any form of telecommunication that uses light as the transmission medium. Equipment consists of a transmitter, which encodes a ''message'' into an optical ''signal'', a ''communication channel'', which carries the signal to its dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |