|
Telecommunications In Thailand
Modern telecommunications in Thailand began in 1875 with the deployment of the first telegraph service. Historically, the development of telecommunication networks in Thailand were in the hands of the public sector. Government organisations were established to provide telegraph, telephone, radio, and television services, and other government agencies, especially the military, still control a large estate of radio and television spectra. Private telecommunication operators initially acquired concession agreements with state enterprises. For mobile phone services, all the concessions have been amended by successive government to last 25 years have gradually ended in 2015. For other services, the concession terms and conditions vary, ranging from one to fifteen years. Nearly all of the concessions are build-operate-transfer (BTO) contracts. The private investor has to build all the required facilities and transfer them to the state before they can operate or offer services to public. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prayut Chan-o-cha
Prayut Chan-o-cha (sometimes spelled Prayuth Chan-ocha; th, ประยุทธ์ จันทร์โอชา, ; born 21 March 1954) is a Thai politician and retired Royal Thai Army, army officer who has served as the Prime Minister of Thailand since he seized power in a military coup in 2014. He is concurrently the List of Defence Ministers of Thailand, Minister of Defence, a position he has held in his own government since 2019. Prayut served as List of commanders-in-chief of the Royal Thai Army, Commander in Chief of Royal Thai Army from 2010 to 2014 and led the 2014 Thai coup d'état which installed the National Council for Peace and Order (NCPO), the military junta which governed Thailand between 22 May 2014 and 10 July 2019. After his appointment as army chief in 2010, Prayut was characterised as a royalist and an opponent of former prime minister Thaksin Shinawatra. Considered a hardliner within the military, he was one of the leading proponents of military crackdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (Thailand)
The Ministry of Defence ( Abrv: MOD; th, กระทรวงกลาโหม, ), is a cabinet-level government department of the Kingdom of Thailand. The ministry controls and manages the Royal Thai Armed Forces to maintain national security, territorial integrity, and national Defence. The armed forces of Thailand are composed of three branches: the Royal Thai Army, Royal Thai Navy, and Royal Thai Air Force. Although the King of Thailand is the Head of the Royal Thai Armed Forces ( th, จอมทัพไทย), his position is only nominal. The ministry and the forces are administered by an appointed politician, the Minister of Defence, a member of the Cabinet of Thailand. The post of minister of Defence has been held by General Prayut Chan-o-cha, who is also prime minister, since 10 July 2019. History Initially, the Ministry was called ''Krom Kalahom'' ( th, กรมกลาโหม) and its head was called ''Samuha Kalahom'' ( th, สมุหกลาโหม), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landline
A landline (land line, land-line, main line, home phone, fixed-line, and wireline) is a telephone connection that uses metal wires or optical fiber telephone line for transmission, as distinguished from a mobile cellular network, which uses radio waves for signal transmission. Characteristics A corded landline telephone made by Siemens from c. 1997 Landline service is typically provided through the outside plant of a telephone company's central office, or wire center. The outside plant comprises tiers of cabling between distribution points in the exchange area, so that a single pair of copper wire, or an optical fiber, reaches each subscriber location, such as a home or office, at the network interface. Customer premises wiring extends from the network interface to the location of one or more telephones inside the premises. The telephone connected to a landline can be hard-wired or cordless and typically refers to the operation of wireless devices or systems in fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Telecom Public Company Limited
National Telecom Public Company Limited (NT) (บริษัท โทรคมนาคมแห่งชาติ จำกัด (มหาชน)) is a Thai state-owned telecommunications company. Established and corporatized in 2021 by resulting from the merger of CAT Telecom and TOT Public Company Limited. NT's main line of business is fixed line telephony, mobile telephony, international telecommunications infrastructure, including its international gateways, satellite, and submarine cable networks connections. Early history On 1 September 2020, the Cabinet passed a resolution acknowledging the progress of the merger and the use of the new company name resulting from the merger is National Telecom Public Company Limited; NT PCL. Later, on 18 December 2020, Puttipong Punnakanta, Minister of Digital Economy and Society talked to employees and state enterprise labor unions of both TOT and CAT Telecom to communicate the organization's driving in the same direction. This in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Terrestrial Television
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV or DTT, or DTTB with "broadcasting") is a technology for terrestrial television in which land-based (terrestrial) television stations broadcast television content by radio waves to televisions in consumers' residences in a digital format. DTTV is a major technological advance over the previous analog television, and has largely replaced analog which had been in common use since the middle of the 20th century. Test broadcasts began in 1998 with the changeover to DTTV (aka Analog Switchoff (ASO), or Digital Switchover (DSO)) beginning in 2006 and is now complete in many countries. The advantages of ''digital'' terrestrial television are similar to those obtained by digitising platforms such as cable TV, satellite, and telecommunications: more efficient use of limited radio spectrum bandwidth, provision of more television channels than analog, better quality images, and potentially lower operating costs for broadcasters (after the initial up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
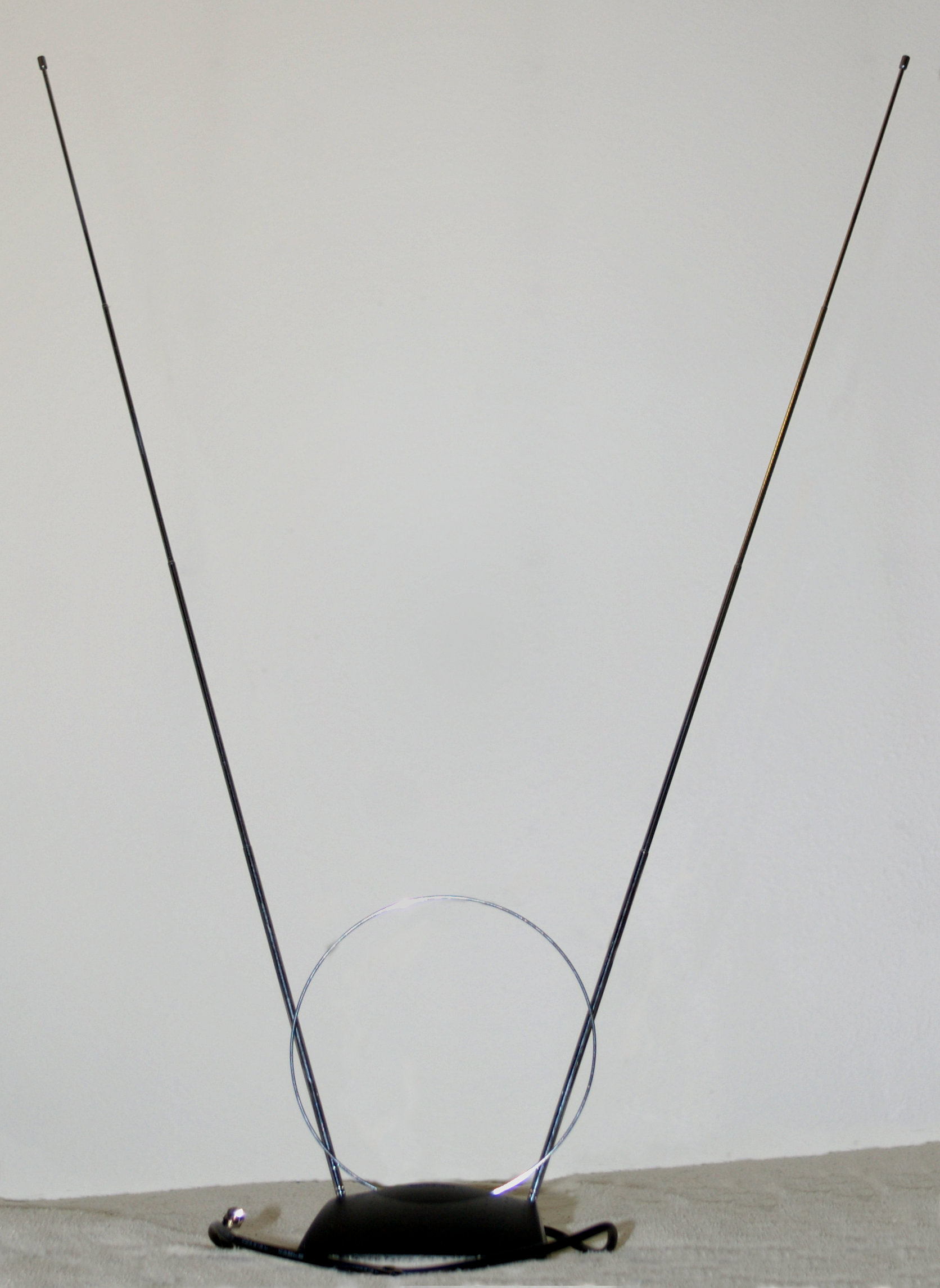
Terrestrial Television
Terrestrial television or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the signal transmission occurs via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a TV station to a TV receiver having an antenna. The term ''terrestrial'' is more common in Europe and Latin America, while in Canada and the United States it is called ''over-the-air'' or simply ''broadcast''. This type of TV broadcast is distinguished from newer technologies, such as satellite television (direct broadcast satellite or DBS television), in which the signal is transmitted to the receiver from an overhead satellite; cable television, in which the signal is carried to the receiver through a cable; and Internet Protocol television, in which the signal is received over an Internet stream or on a network utilizing the Internet Protocol. Terrestrial television stations broadcast on television channels with frequencies between about 52 and 600 MHz in the VHF and U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogue Television
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, phase and frequency of an analog signal. Analog signals vary over a continuous range of possible values which means that electronic noise and interference may be introduced. Thus with analog, a moderately weak signal becomes snowy and subject to interference. In contrast, picture quality from a digital television (DTV) signal remains good until the signal level drops below a threshold where reception is no longer possible or becomes intermittent. Analog television may be wireless (terrestrial television and satellite television) or can be distributed over a cable network as cable television. All broadcast television systems used analog signals before the arrival of DTV. Motivated by the lower bandwidth requirements of compressed digital signals, beginning in the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTE (telecommunication)
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported. The standard is developed by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and is specified in its Release 8 document series, with minor enhancements described in Release 9. LTE is also called 3.95G and has been marketed as "4G LTE" and "Advanced 4G"; but it does not meet the technical criteria of a 4G wireless service, as specified in the 3GPP Release 8 and 9 document series for LTE Advanced. The requirements were set forth by the ITU-R organisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators. UMTS specifies a complete network system, which includes the radio access network (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, or UTRAN), the core network (Mobile Application Part, or MAP) and the authentication of users via SIM (subscriber identity module) cards. The technology described in UMTS is sometimes also referred to as Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA) or 3GSM. Unlike EDGE (IMT Single-Carrier, based on GSM) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |