|
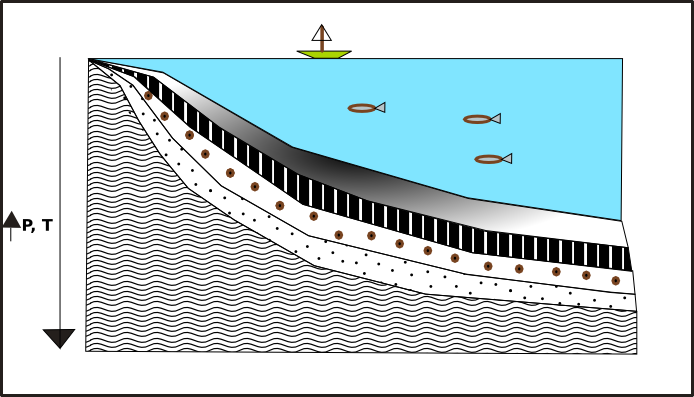
Tectonic Burial
Tectonic Burial is the deformation of rocks caused by extreme pressure over millions of years. It often causes temperature evolutions and deep burials. Tectonic burial is usually the result of continental collisions or subduction in a region. An increase in burial depth leads to a weakened basin and basement but creates better preservation structure within the basement. Geologic Processes Sedimentary Burial Sedimentary burial is more typical when thinking of burial processes. Sedimentary burial is the deposition of sediments on and area of interest such as a sedimentary basin, oceans, or other locations typically leading to Diagenesis. Tectonic Burial Tectonic Burial specifically refers to burial of material on a area of interest as a result of tectonic processes such as a Thrust fault or other processes of crustal thickening. Tectonic burial is common in orogenic systems such as mountain belts or collisional zones. This is a critical part of the rock cycle and can lead to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagenesis
Diagenesis () is the process that describes physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a role as sediments become buried much deeper in the Earth's crust. In the early stages, the transformation of poorly consolidated sediments into sedimentary rock (lithification) is simply accompanied by a reduction in porosity and water expulsion (clay sediments), while their main mineralogical assemblages remain unaltered. As the rock is carried deeper by further deposition above, its organic content is progressively transformed into kerogens and bitumens. The process of diagenesis excludes surface alteration (weathering) and deep metamorphism. There is no sharp boundary between diagenesis and metamorphism, but the latter occurs at higher temperatures and pressures. Hydrothermal solutions, meteoric groundwater, rock porosity, permeability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular ''klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. The use of radiometric dating was first published in 1907 by Bertram Boltwood and is now the principal source of information about the absolute age of rocks and other geological features, including the age of fossilized life forms or the age of Earth itself, and can also be used to date a wide range of natural and man-made materials. Together with stratigraphic principles, radiometric dating methods are used in geochronology to establish the geologic time scale. Among the best-known techniques are radiocarbon dating, potassium–argon dating and uranium–lead dating. By al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermochronology
Thermochronology is the study of the thermal evolution of a region of a planet. Thermochronologists use radiometric dating along with the closure temperatures that represent the temperature of the mineral being studied at the time given by the date recorded to understand the thermal history of a specific rock, mineral, or geologic unit. It is a subfield within geology, and is closely associated with geochronology. A typical thermochronological study will involve the dates of a number of rock samples from different areas in a region, often from a vertical transect along a steep canyon, cliff face, or slope. These samples are then dated. With some knowledge of the subsurface thermal structure, these dates are translated into depths and times at which that particular sample was at the mineral's closure temperature. If the rock is today at the surface, this process gives the exhumation rate of the rock. Common isotopic systems used for thermochronology include fission track dating in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closure Temperature
In radiometric dating, closure temperature or blocking temperature refers to the temperature of a system, such as a mineral, at the time given by its radiometric date. In physical terms, the closure temperature is the temperature at which a system has cooled so that there is no longer any significant diffusion of the parent or daughter isotopes out of the system and into the external environment. The concept's initial mathematical formulation was presented in a seminal paper by Martin H. Dodson, "Closure temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems" in the journal ''Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology'', 1973, with refinements to a usable experimental formulation by other scientists in later years. This temperature varies broadly among different minerals and also differs depending on the parent and daughter atoms being considered.''Earth: a Portrait of a Planet'Glossary W.W. Norton & Company It is specific to a particular material and isotopic system.Rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitrinite
Vitrinite is one of the primary components of coals and most sedimentary kerogens. Vitrinite is a type of maceral, where "macerals" are organic components of coal analogous to the "minerals" of rocks. Vitrinite has a shiny appearance resembling glass (vitreous). It is derived from the cell-wall material or woody tissue of the plants from which coal was formed. Chemically, it is composed of polymers, cellulose and lignin. The vitrinite group, which consists of various individual vitrinite ''macerals'', is the most common component of coals. It is also abundant in kerogens that are derived from the same biogenic precursors as coals, namely land plants and humic peats. Vitrinite forms diagenetically by the thermal alteration of lignin and cellulose in plant cell walls. It is therefore common in sedimentary rocks that are rich in organic matter, such as shales and marls with a terrigenous origin, or some terrigenous content. Conversely, carbonates, evaporites and well-sorted sandstone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |