|
Technical Rate Of Substitution
In microeconomic Microeconomics is a branch of mainstream economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics fo ... theory, the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS)—or technical rate of substitution (TRS)—is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced (-\Delta x_2) when one extra unit of another input is used (\Delta x_1 = 1), so that output remains constant (y = \bar). MRTS(x_1,x_2) =-\frac = \frac where MP_1 and MP_2 are the marginal products of input 1 and input 2, respectively. Along an isoquant, the MRTS shows the rate at which one input (e.g. capital or labor) may be substituted for another, while maintaining the same level of output. Thus the MRTS is the absolute value of the slope of an isoquant at the point in question. When relative input usages are optimal, the marginal rate of te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
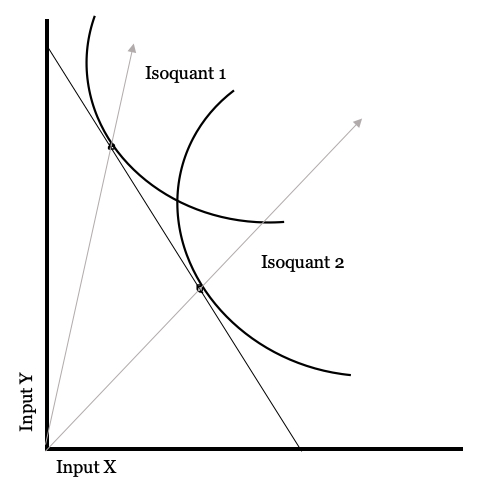
Isoquant Map
An isoquant (derived from quantity and the Greek word iso, meaning equal), in microeconomics, is a contour line drawn through the set of points at which the same quantity of output is produced while changing the quantities of two or more inputs. The x and y axis on an isoquant represent two relevant inputs, which are usually a factor of production such as labour, capital, land, or organisation. An isoquant may also be known as an “Iso-Product Curve”, or an “Equal Product Curve”. Isoquant vs. Indifference Curve While an indifference curve mapping helps to solve the utility-maximizing problem of consumers, the isoquant mapping deals with the cost-minimization and profit and output maximisation problem of producers. Indifference curves further differ to isoquants, in that they cannot offer a precise measurement of utility, only how it is relevant to a baseline. Whereas, from an isoquant, the product can be measured accurately in physical units, and it is known by exactly how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of mainstream economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the national economy as whole, which is studied in macroeconomics. One goal of microeconomics is to analyze the market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocate limited resources among alternative uses. Microeconomics shows conditions under which free markets lead to desirable allocations. It also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce efficient results. While microeconomics focuses on firms and individuals, macroeconomics focuses on the sum total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation, and unemployment and with national policies relating to these issues. Microeconomics also d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
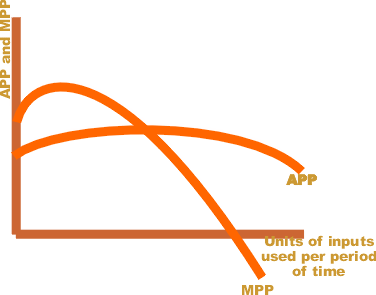
Marginal Product
In economics and in particular neoclassical economics, the marginal product or marginal physical productivity of an input (factor of production) is the change in output resulting from employing one more unit of a particular input (for instance, the change in output when a firm's labor is increased from five to six units), assuming that the quantities of other inputs are kept constant. The marginal product of a given input can be expressed as: :MP = \frac where \Delta X is the change in the firm's use of the input (conventionally a one-unit change) and \Delta Y is the change in quantity of output produced (resulting from the change in the input). Note that the quantity Y of the "product" is typically defined ignoring external costs and benefits. If the output and the input are infinitely divisible, so the marginal "units" are infinitesimal, the marginal product is the mathematical derivative of the production function with respect to that input. Suppose a firm's output ''Y'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoquant
An isoquant (derived from quantity and the Greek word iso, meaning equal), in microeconomics, is a contour line drawn through the set of points at which the same quantity of output is produced while changing the quantities of two or more inputs. The x and y axis on an isoquant represent two relevant inputs, which are usually a factor of production such as labour, capital, land, or organisation. An isoquant may also be known as an “Iso-Product Curve”, or an “Equal Product Curve”. Isoquant vs. Indifference Curve While an indifference curve mapping helps to solve the utility-maximizing problem of consumers, the isoquant mapping deals with the cost-minimization and profit and output maximisation problem of producers. Indifference curves further differ to isoquants, in that they cannot offer a precise measurement of utility, only how it is relevant to a baseline. Whereas, from an isoquant, the product can be measured accurately in physical units, and it is known by exactly ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
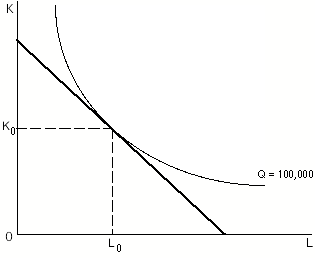
Isocost
In economics, an isocost line shows all combinations of inputs which cost the same total amount.Chiang, Alpha C., ''Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics'', third edition, McGraw-Hill, 1984. Although similar to the budget constraint in consumer theory, the use of the isocost line pertains to cost-minimization in production, as opposed to utility-maximization. For the two production inputs labour and capital, with fixed unit costs of the inputs, the equation of the isocost line is :rK+wL = C\, where w represents the wage rate of labour, r represents the rental rate of capital, K is the amount of capital used, L is the amount of labour used, and C is the total cost of acquiring those quantities of the two inputs. The absolute value of the slope of the isocost line, with capital plotted vertically and labour plotted horizontally, equals the ratio of unit costs of labour and capital. The slope is: :-w/r. \, The isocost line is combined with the isoquant map to determine t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Factor Demands
In economics, a conditional factor demand is the cost-minimizing level of an input (factor of production) such as labor or capital, required to produce a given level of output, for given unit input costs ( wage rate and cost of capital) of the input factors. A conditional factor demand function expresses the conditional factor demand as a function of the output level and the input costs.Varian, Hal., 1992, ''Microeconomic Analysis'' 3rd Ed., W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. New York. The conditional portion of this phrase refers to the fact that this function is conditional on a given level of output, so output is one argument of the function. Typically this concept arises in a long run context in which both labor and capital usage are choosable by the firm, so a single optimization gives rise to conditional factor demands for each of labor and capital. Since the optimal mix of input levels depends on the wage and rental rates, these rates are also arguments of the conditional demand fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Rate Of Substitution
In economics, the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the rate at which a consumer can give up some amount of one good in exchange for another good while maintaining the same level of utility. At equilibrium consumption levels (assuming no externalities), marginal rates of substitution are identical. The marginal rate of substitution is one of the three factors from marginal productivity, the others being marginal rates of transformation and marginal productivity of a factor. As the slope of indifference curve Under the standard assumption of neoclassical economics that goods and services are continuously divisible, the marginal rates of substitution will be the same regardless of the direction of exchange, and will correspond to the slope of an indifference curve (more precisely, to the slope multiplied by −1) passing through the consumption bundle in question, at that point: mathematically, it is the implicit derivative. MRS of X for Y is the amount of Y which a consumer can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production–possibility Frontier
A production–possibility frontier (PPF), production possibility curve (PPC), or production possibility boundary (PPB), or transformation curve/boundary/frontier is a curve which shows various combinations of the amounts of two goods which can be produced within the given resources and technology/a graphical representation showing all the possible options of output for two products that can be produced using all factors of production, where the given resources are fully and efficiently utilized per unit time. A PPF illustrates several economic concepts, such as allocative efficiency, economies of scale, opportunity cost (or marginal rate of transformation), productive efficiency, and scarcity of resources (the fundamental economic problem that all societies face). This tradeoff is usually considered for an economy, but also applies to each individual, household, and economic organization. One good can only be produced by diverting resources from other goods, and so by produci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production Economics
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental production factors. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they are byproducts of land, labour and capital. Delving further, primary facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Concepts
In economics, marginal concepts are associated with a ''specific change'' in the quantity used of a good or service, as opposed to some notion of the over-all significance of that class of good or service, or of some total quantity thereof.{{citation needed, date=February 2012 Marginality Constraints are conceptualized as a ''border'' or ''margin''. Wicksteed, Philip Henry; ''The Common Sense of Political Economy'' (1910), Bk I Ch 2 and elsewhere. The location of the margin for any individual corresponds to his or her ''endowment'', broadly conceived to include opportunities. This endowment is determined by many things including physical laws (which constrain how forms of energy and matter may be transformed), accidents of nature (which determine the presence of natural resources), and the outcomes of past decisions made both by others and by the individual himself or herself. A value that holds true given particular constraints is a ''marginal'' value. A change that would be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |