|
Tayloria Acuminata
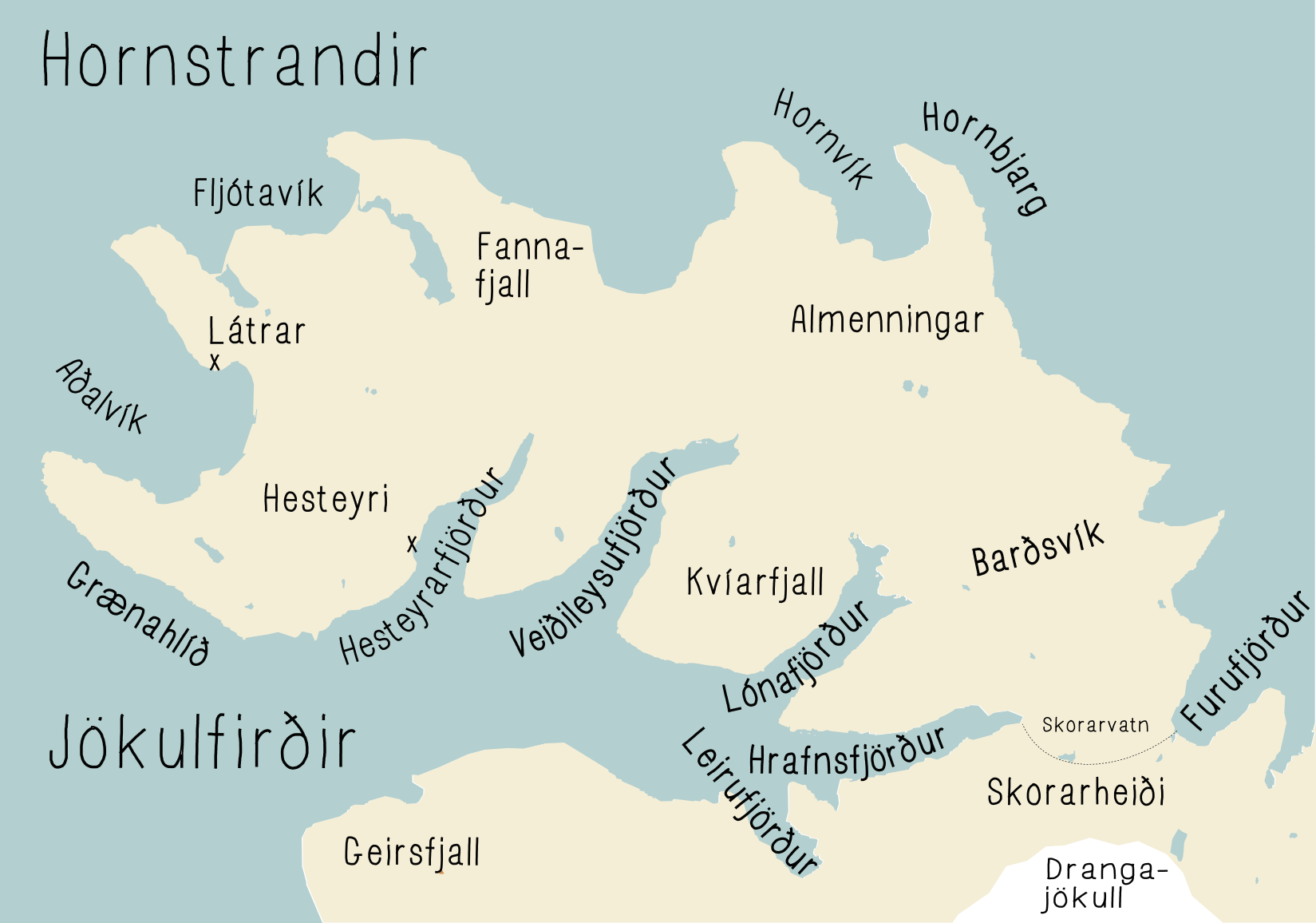
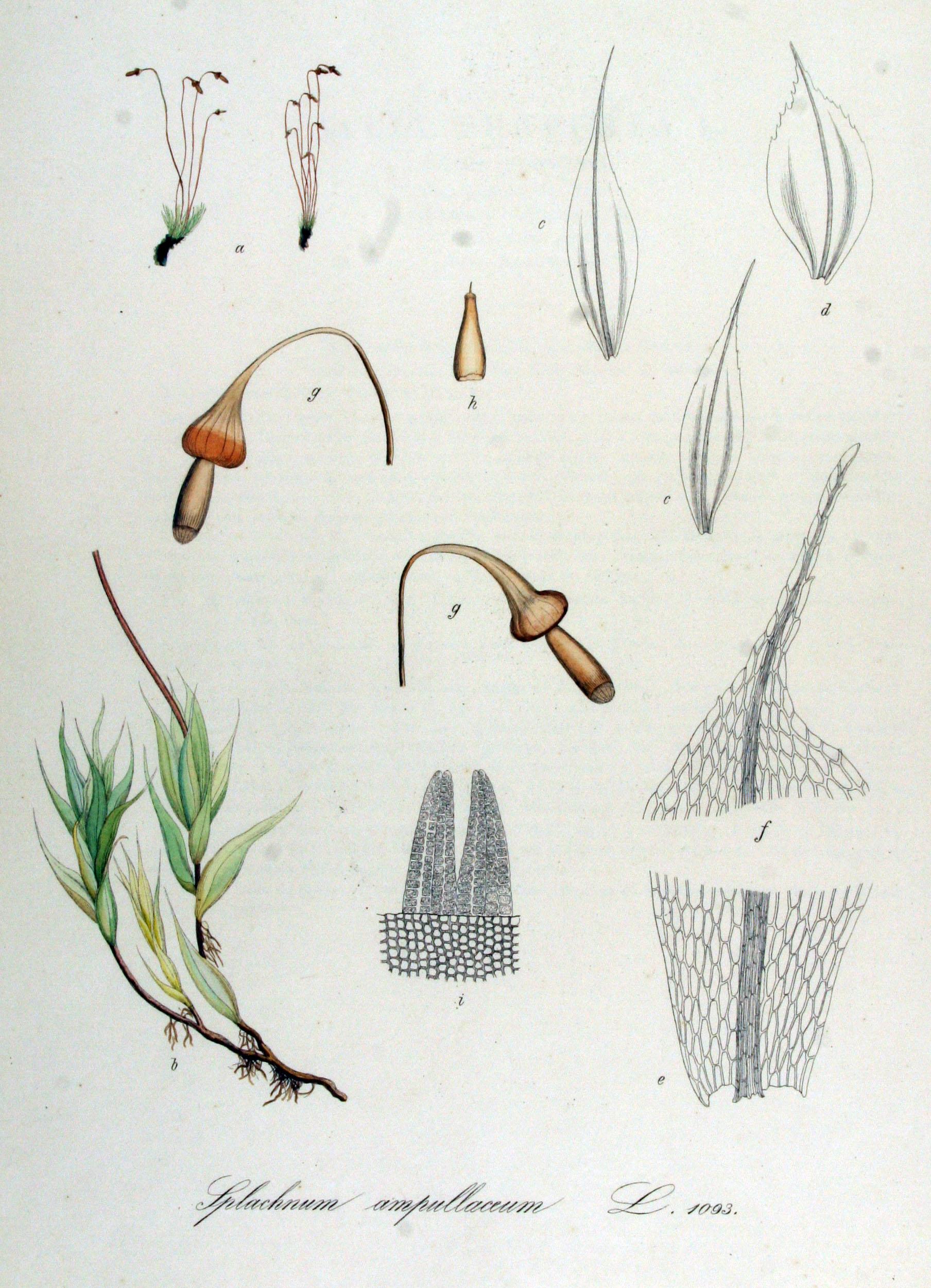
''Tayloria acuminata'', commonly known as acuminate dung moss and acuminate trumpet moss, is a bright-green dung moss species with violet radicles that age to a dark red. It is native to North America and Iceland, where it is found in bird cliffs in Hornstrandir.Náttúrufræðistofnun Íslands celandic Institute of Natural History(1996). Válisti 1: Plöntur.' (in Icelandic) Reykjavík: Náttúrufræðistofnun Íslands. In Iceland it has the conservation status of a vulnerable species A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, ... (VU). References Bryophyta of North America Splachnaceae {{bryidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Friedrich Hornschuch
Christian Friedrich Hornschuch (21 August 1793 – 24 December 1850) was a German botanist born in Rodach, Bavaria. In 1808 he started his career as an apprentice at a pharmacy in Hildburghausen. In 1813 he moved to Regensburg as an assistant to botanist David Heinrich Hoppe (1760–1846), and afterwards worked as an assistant to Heinrich Christian Funck (1771–1839) in Gefrees, where he performed research of mosses (Bryopsida) native to the Fichtelgebirge. In 1816 he accompanied Hoppe on a botanical expedition to the Adriatic coast, then returned to Coburg to arrange his diaries, and in April 1817 continued his research with Hoppe in Tyrol and Carinthia. Later he worked as a "botanical demonstrator" at the University of Greifswald, and for a period of time studied with Carl Adolph Agardh (1785–1859) from the University of Lund. In 1820 he was appointed associate professor of natural history and botany, and director of the botanical gardens at the University of Greifsw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Plant List
The Plant List was a list of botanical names of species of plants created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and the Missouri Botanical Garden and launched in 2010. It was intended to be a comprehensive record of all known names of plant species over time, and was produced in response to Target 1 of the 2002-2010 Global Strategy for Plant Conservation (GSP C), to produce "An online flora of all known plants.” It has not been updated since 2013, and has been superseded by World Flora Online. World Flora Online In October 2012, the follow-up project World Flora Online was launched with the aim to publish an online flora of all known plants by 2020. This is a project of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity, with the aim of halting the loss of plant species worldwide by 2020. It is developed by a collaborative group of institutions around the world response to the 2011-2020 GSPC's updated Target 1. This aims to achieve an online Flora of all known plants by 2020. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splachnaceae
Splachnaceae is a family of mosses, containing around 70 species in 6 genera. Around half of those species are entomophilous, using insects to disperse their spores, a characteristic found in no other seedless land plants. Many species in this family are coprophilous, growing exclusively on animal faeces or carrion. For this reason, certain genera such as ''Splachnum'' Hedw. are often referred to as dung mosses. Description Gametophyte Mosses in this family are predominantly dioicous (archegonia and antheridia on separate individuals); although exceptions are known such as ''S.'' ''pensylvanicum'' which is monoicous. The gametophyte is always acrocarpous (standing up), with green-yellow to reddish leaves/stems, and most often under 5 cm in height. Stems stand vertically and when cross-sectioned, can be seen to have a well-defined central strand. Large parenchymatous cells surround the central strand with thin, red to orange cell walls. Cortex (botany), Cortical cells a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicle
In botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling (a growing plant embryo) to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil (the shoot emerges from the plumule). Above the radicle is the embryonic stem or hypocotyl, supporting the cotyledon(s). It is the embryonic root inside the seed. It is the first thing to emerge from a seed and down into the ground to allow the seed to suck up water and send out its leaves so that it can start photosynthesizing. The radicle emerges from a seed through the micropyle. Radicles in seedlings are classified into two main types. Those pointing away from the seed coat scar or hilum are classified as ''antitropous'', and those pointing towards the hilum are ''syntropous''. If the radicle begins to decay, the seedling undergoes pre-emergence damping off. This disease appears on the radicle as darkened spots. Eventually, it causes death of the seedling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fields of literary and cultural studies, history, social work, sociology, religion, film, and international studies. History Founded in May 1893, In 1933 the first four volumes of the ''History of the State of New York'' were published. In early 1940s revenues rises, partially thanks to the ''Encyclopedia'' and the government's purchase of 12,500 copies for use by the military. Columbia University Press is notable for publishing reference works, such as ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'' (1935–present), ''The Columbia Granger's Index to Poetry'' (online as ''The Columbia World of Poetry Online'') and ''The Columbia Gazetteer of the World'' (also online) and for publishing music. First among American university presses to publish in electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Life
The ''Encyclopedia of Life'' (''EOL'') is a free, online encyclopedia intended to document all of the 1.9 million living species known to science. It is compiled from existing trusted databases curated by experts and with the assistance of non-experts throughout the world. It aims to build one "infinitely expandable" page for each species, including video, sound, images, graphics, as well as text. In addition, the Encyclopedia incorporates content from the Biodiversity Heritage Library, which digitizes millions of pages of printed literature from the world's major natural history libraries. The project was initially backed by a US$50 million funding commitment, led by the MacArthur Foundation and the Sloan Foundation, who provided US$20 million and US$5 million, respectively. The additional US$25 million came from five cornerstone institutions—the Field Museum, Harvard University, the Marine Biological Laboratory, the Missouri Botanical Garden, and the Smithsonian Institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornstrandir
Hornstrandir () is Iceland's northernmost peninsula, covering at the northern end of the Westfjords, to the north of the Jökulfirðir and to the northwest of Drangajökull glacier. Ecosystem The area covers of tundra, fjord, glacier and alpine land with rich but fragile vegetation, and protected as Hornstrandir Nature Reserve since 1975, under some of the strictest preservation rules in Iceland. The area's nature thrived as very few people resided there. In the 1950s also the handful of its residents who were based on agricultural livelihood left. However, decades later some of their descendants returned and rebuilt their old houses, and much of the land is privately owned. Jökulfirðir The ''Jökulfirðir'' (, "glacier fjords") form a system of five fjords in Westfjords, Iceland, situated north of Ísafjarðardjúp and south of the Hornstrandir peninsula. They are named for '' Drangajökull'', a glacier situated to the south ..., meaning Glacier Fjords, is the formatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulnerable Species
A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, threatening its survival and reproduction improve. Vulnerability is mainly caused by habitat loss or destruction of the species' home. Vulnerable habitat or species are monitored and can become increasingly threatened. Some species listed as "vulnerable" may be common in captivity (animal), captivity, an example being the military macaw. There are currently 5196 animals and 6789 plants classified as Vulnerable, compared with 1998 levels of 2815 and 3222, respectively. Practices such as cryoconservation of animal genetic resources have been enforced in efforts to conserve vulnerable breeds of livestock specifically. Criteria The International Union for Conservation of Nature uses several criteria to enter species in this category. A tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryophyta Of North America )
{{Disambiguation ...
Bryophyta may refer to: * Mosses – Bryophyta in the strict sense; a specific group of leafy nonvascular plants, now regarded as Division Bryophyta * Bryophytes – Bryophyta in the broad sense; a group of plants regarded as a single division by some, but further split into: ** mosses (Bryophyta) ** hornworts (Anthocerotophyta) **liverworts (Marchantiophyta The Marchantiophyta () are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)