|
Talha Ibn Ubaidullah
Ṭalḥa ibn ʿUbayd Allāh al-Taymī ( ar, طَلْحَة بن عُبَيْد اللّه التَّيمي, ) was a Companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Sunni Islam, he is mostly known for being among ('the ten to whom Paradise was promised'). He played an important role in the Battle of Uhud and the Battle of the Camel, in which he died. According to Sunnis, he was given the title "The Generous" by Muhammad.سير أعلام النبلاء، لشمس الدين الذهبي، ترجمة طلحة بن عبيد الله، الجزء الأول، صـ 24: 40 Biography Talha was born c.594,Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al- ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calligraphic
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "the art of giving form to signs in an expressive, harmonious, and skillful manner". Modern calligraphy ranges from functional inscriptions and designs to fine-art pieces where the letters may or may not be readable. Classical calligraphy differs from type design and non-classical hand-lettering, though a calligrapher may practice both. CD-ROM Calligraphy continues to flourish in the forms of wedding invitations and event invitations, font design and typography, original hand-lettered logo design, religious art, announcements, graphic design and commissioned calligraphic art, cut stone inscriptions, and memorial documents. It is also used for props and moving images for film and television, and also for testimonials, birth and death c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musa Ibn Talha
Musa may refer to: Places *Mūša, a river in Lithuania and Latvia * Musa, Azerbaijan, a village in Yardymli Rayon * Musa, Iran, a village in Ilam Province *Musa, Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, Iran *Musa, Kerman, Iran * Musa, Bukan, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran *Musa, Maku, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Musa, Pakistan, a village in Chhachh, Attock, Punjab, Pakistan * Musa (crater), an impact crater on Saturn's moon Enceladus *Musa (Tanzanian ward), a ward in Tanzania *Abu Musa, an island in the Persian Gulf *Musa Dagh a mountain peak in Turkey *Jebel Musa (Morocco), a mountain known as one of the pillars of Hercules * Jabal Musa, or Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Desert believed to be a possible location of the Biblical Mount Sinai * Muza Emporion, an ancient port city near present day Mocha, Yemen People * Musa (name), including a list of people with the surname and given name * Moses in Islam * Musa I of Mali, emperor of the Mali Empire 1312–37 * Musa of Parthia, queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
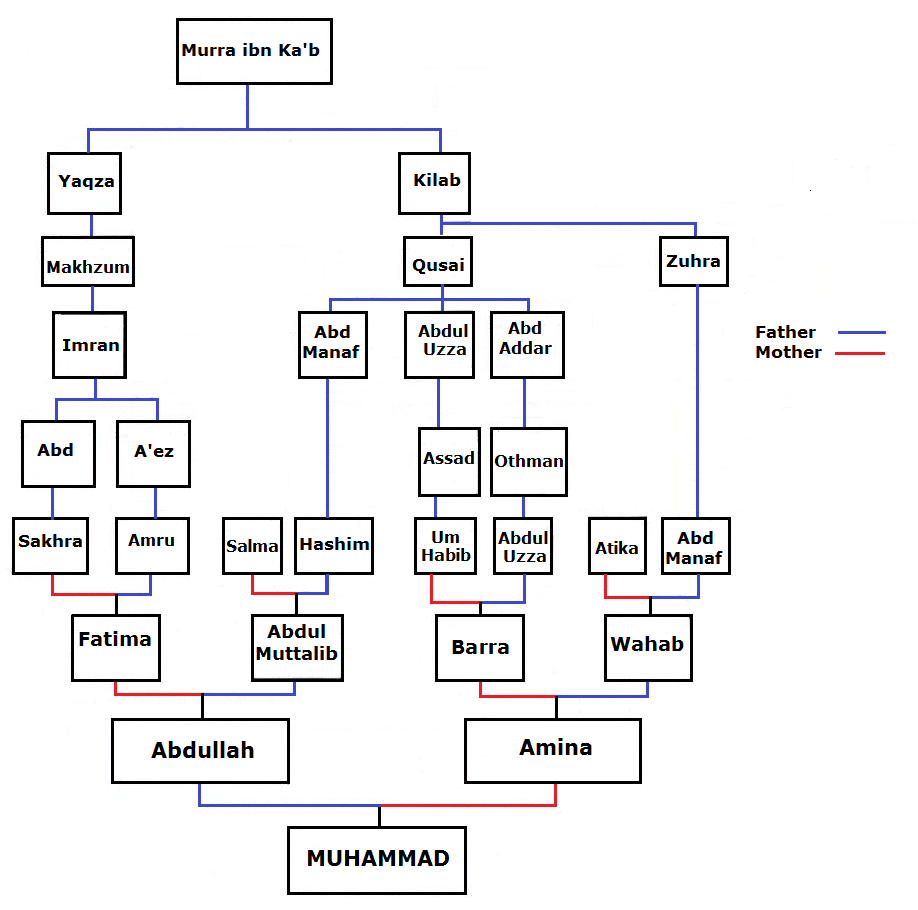
Murra Ibn Ka'b
) , image = , alt = , caption = , birth_name = , birth_date = , birth_place = , death_date = , death_place = , nationality = , other_names = , occupation = , known_for = Ancestor of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and numerous branches of the Quraish tribe , spouse = Hind bint Surayr Asma bint Adiy , children = Kilab ibn Murrah, Taym ibn Murrah, Yaqazah ibn Murrah , parents = Ka'b ibn Lu'ayy Wahshiya bint Shaiban , relatives = Adiy ibn Ka'b, Husays ibn Ka'b (brothers) Murrah ibn Ka'b ( ar, مُرَّة ٱبْن كَعْب) ibn Luay ibn Ghalib ibn Fihr ibn Malik was a man from Quraysh tribe, supposed to have lived in the 4th century. He was the sixth-in-line of Muhammad's grandfathers. He is the common ancestor of all four of Muhammad's grandparents. He is also the common ancestor of six of Muhammad's eight great-grandparents. He is also the common ancestor of Muhammad and his friend Abu Bakr. Descendants *Abdul M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Camel
The Battle of the Camel, also known as the Battle of Jamel or the Battle of Basra, took place outside of Basra, Iraq, in 36 AH (656 CE). The battle was fought between the army of the fourth caliph Ali, on one side, and the rebel army led by Aisha, Talha and Zubayr, on the other side. Ali was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, while Aisha was a widow of Muhammad, and Talha and Zubayr were both prominent companions of Muhammad. Ali emerged victorious from this battle, Talha and Zubayr were both killed, and Aisha was sent back to Hejaz afterward. The triumvirate had revolted against Ali ostensibly to avenge the assassination of the third caliph Uthman, though the leading roles of Aisha and Talha in inciting against Uthman are well-cited. The three also called for the removal of Ali and the appointment of his replacement by a Qurayshite council (''shura'') which was to include Talha and Zubayr. Background Opposition to Uthman Ali and other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Uhud
The Battle of Uhud ( ar, غَزْوَة أُحُد, ) was fought on Saturday, 23 March 625 AD (7 Shawwal, 3 AH), in the valley north of Mount Uhud.Watt (1974) p. 136. The Qurayshi Meccans, led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, commanded an army of 3,000 men toward Muhammad's stronghold in Medina. The battle was the only battle throughout the Muslim–Quraysh War in which the Muslims did not manage to defeat their enemy and it came just a year after the Battle of Badr. Abu Sufyan became the ''de facto'' leader of the Quraish after the death of Amr ibn Hishām at Badr nine months prior. Wanting to avenge the Meccan's losses at the Battle of Badr, he marched upon Medina from Makkah on 10 December 624 AD with a force three times stronger than that of the Meccans at Badr. Another reason for the battle was to protect the trade route of Abu Sufyan's caravans. The Battle of Uhud was the second military encounter between the Meccans and the Muslims and the first one in which the Muslims were on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ten To Whom Paradise Was Promised
The ten to whom Paradise was promised (Arabic: ar, العشرة المبشرون, translit=al-ʿashara al-mubashsharūn, label=none or ar, العشرة المبشرة, translit=al-ʿashara al-mubashshara, label=none) were ten early Muslims to whom, according to Sunni Islamic tradition, the Islamic prophet Muhammad () had promised Paradise. Several different lists of names exist, but most of them contain the four Rashidun caliphs Abu Bakr (), Umar (), Uthman (), and Ali (), as well as the members of the committee ( ) that elected Uthman as caliph, i.e., Talha (), Zubayr (born , died 656), Abd al-Rahman ibn Awf (), and Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas (born , died ). The version that became canonical from the 9th century on also lists Sa'id ibn Zayd () and Abu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah (). However, the earliest known version of the list, which may date to , contains the name of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya (). Mu'awiya's place was occupied in later versions by Abu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad and subsequently acquired broader political significance, as well as theological and juridical dimensions. According to Sunni traditions, Muhammad left no successor and the participants of the Saqifah event appointed Abu Bakr as the next-in-line (the first caliph). This contrasts with the Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed his son-in-law and cousin Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor. The adherents of Sunni Islam are referred to in Arabic as ("the people of the Sunnah and the community") or for short. In English, its doctrines and practices are sometimes called ''Sunnism'', while adherents are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis, Sunnites and Ahlus Sunnah. Sunni Islam is sometimes referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridda Wars
The Ridda Wars ( ar, حُرُوْبُ الرِّدَّةِ, lit=Apostasy Wars) were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 632 and concluded the next year, with all battles won by the Rashidun Caliphate.Laura V. Vaglieri in The Cambridge History of Islam, p.58 These wars secured the caliphate's control over Arabia and restored its nascent prestige. During Muhammad's lifetime, many Arab rebels declared themselves prophets. After Muhammad died in June 632, Abu Bakr was elected as the caliph of the Muslim community at Saqifah. The next day, he launched a successful expedition into the Byzantine Syria. Meanwhile in Arabia, the self-proclaimed prophets started to cause mischief and arranged rebellions against Abu Bakr. The first attack on the caliphate was done by Tulayha, who prepared an army in an attempt to capture Medina, the capital of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim–Quraysh War
The Muslim–Quraysh War was the six-year-long military and religious conflict in the Arabian Peninsula between the early Muslims led by Muhammad, and the Arab pagan Quraysh tribe. The conflict started in March 623 with the Battle of Badr, and concluded with the fall of the Quraysh tribe and the Conquest of Mecca. Muslims believe Muhammad began receiving revelation around 610. He preached Islam in secret for three years, before openly preaching the religion. Subsequently, the early Muslims of Mecca faced persecution at the hands of the Quraysh. After being threatened with murder by the Quraysh, Muhammad received pledges of protection from the Ansar of Yathrib. He then allowed his followers to emigrate to the city, before leaving for Yathrib in 624 himself. Following his migration, Muhammad took to intercepting the caravans of the Quraysh as a means of retaliation and compensation for the wealth lost by his Meccan companions. The Battle of Badr took place in March 624, when M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aisha Bint Abu Bakr
Aisha ( ar, , translit=ʿĀʾisha bint Abī Bakr; , also , ; ) was Muhammad's third and youngest wife. In Islamic writings, her name is thus often prefixed by the title "Mother of the Believers" ( ar, links=no, , ʾumm al- muʾminīn), referring to the description of Muhammad's wives in the Qur'an. Little is known about the early life of Aisha. A preponderance of classical sources converge on Aisha being six or seven years old at the time of her marriage, and nine at the consummation; her age has become a source of ideological friction in modern times. Aisha had an important role in early Islamic history, both during Muhammad's life and after his death. In Sunni tradition, Aisha is portrayed as scholarly and inquisitive. She contributed to the spread of Muhammad's message and served the Muslim community for 44 years after his death. She is also known for narrating 2,210 hadiths, not just on matters related to Muhammad's private life, but also on topics such as inheritance, pil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabian Peninsula, Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishaq Ibn Talha
Isḥāq ibn Ṭalḥa ibn ʿUbayd Allāh (died 675 or 676) was a member of the Muslim elite settled in Iraq under Umayyad rule and a transmitter of Muslim tradition. The caliph Mu'awiya I appointed time oversee fiscal affairs in the vast province of Khurasan in 675 or 676, but he died on his way there. He was son of Talha ibn Ubaydallah and his sons and grandsons were transmitters of Muslim tradition in Medina and Kufa. Life Ishaq was a son of Talha ibn Ubaydallah, a prominent companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and Umm Aban bint Utbah ibn Rabi'ah, the daughter of a Qurayshite aristocrat who died fighting the Muslims at the Battle of Badr in 624. Talha died in the Battle of the Camel in 656 fighting against the forces of Caliph Ali () near Basra. Along with his full brothers Isma'il and Yahya, Ishaq settled in Kufa and enjoyed the favor of the Umayyad caliphs who came to rule Iraq from 661. He and Isma'il were among those who testified against a prominent advocate of Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |