|
Talamanca Languages
The Talamanca languages are a well-defined branch of Chibchan languages spoken in central–southern Costa Rica and northern Panama. They are: : Huetar (Güetar), Bribri The Bribri are an Indigenous people in eastern Costa Rica and northern Panama. Today, most Bribri people speak the Bribri language or Spanish. There are varying estimates from government officials of the group's population. Estimates of the t ... (Talamanca), Cabécar (Talamanca), Chánguena, Teribe (Quequexque, Naso), and maybe Movere (Move). References {{authority control Chibchan languages Indigenous languages of Central America Languages of Costa Rica Languages of Panama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chibchan
The Chibchan languages (also Chibchan, Chibchano) make up a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of these countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. The name is derived from the name of an extinct language called ''Chibcha'' or ''Muysccubun'', once spoken by the people who lived on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense of which the city of Bogotá was the southern capital at the time of the Spanish Conquista. However, genetic and linguistic data now indicate that the original heart of Chibchan languages and Chibchan-speaking peoples might not have been in Colombia, but in the area of the Costa Rica-Panama border, where the greatest variety of Chibchan languages has been identified. External relations A larger family called ''Macro-Chibchan'', which would contain the Misumalpan languages, Xinca, and Lenca, was found convincing by Kaufman (1990). Pache (2018) suggests a distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chibchan Languages
The Chibchan languages (also Chibchan, Chibchano) make up a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of these countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. The name is derived from the name of an extinct language called ''Chibcha'' or ''Muysccubun'', once spoken by the people who lived on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense of which the city of Bogotá was the southern capital at the time of the Spanish Conquista. However, genetic and linguistic data now indicate that the original heart of Chibchan languages and Chibchan-speaking peoples might not have been in Colombia, but in the area of the Costa Rica-Panama border, where the greatest variety of Chibchan languages has been identified. External relations A larger family called ''Macro-Chibchan'', which would contain the Misumalpan languages, Xinca, and Lenca, was found convincing by Kaufman (1990). Pache (2018) suggests a dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
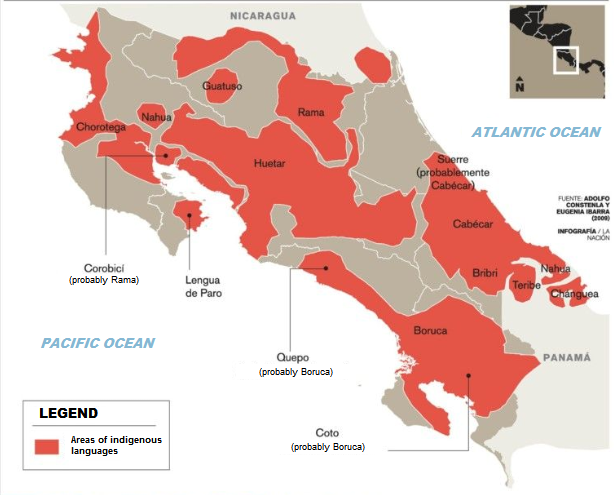
Huetar Language
Huetar (Güetar) is an extinct Chibchan language of Costa Rica that was spoken by the Huetar people. It served as the '' lingua franca'' for precolonial peoples in central Costa Rica, and went extinct in the 17th century. Only a few words in the language are currently known, preserved mainly in the names of various Costa Rican places, such as Aserrí, Barva, Curridabat, Turrialba, Tucurrique, and Ujarrás Ujarrás is a village and historical site in the Orosí Valley of Cartago Province in central Costa Rica, southeast of the provincial capital of Cartago. It lies near the northeastern bank of the man-made Lake Cachí, created by the damming o .... The main source of studies regarding the language is the Costa Rican linguist Miguel Ángel Quesada Pacheco. Bibliography * Chibchan languages Extinct languages of North America {{IndigenousAmerican-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bribri Language
Bribri, also known as Bri-bri, Bribriwak, and Bribri-wak, is a Chibchan language, from a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of those countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. As of 2002, there were about 11,000 speakers left. An estimate by the National Census of Costa Rica in 2011 found that Bribri is currently spoken by 54.7% of the 12,785 Bribri people, about 7,000 individuals. It is a tonal language whose word order is subject–object–verb. There are three traditional dialects of Bribri: Coroma (in the western region of the Talamanca mountain range), Amubre (in the eastern region of the Talamanca mountain range) and Salitre (in the South Pacific area). ''Bribri'' is a tribal name, deriving from a word for "mountainous" in their own language. The Bribri language is also referred to as ''Su Uhtuk'', which means "our language." Bribri is reportedly most sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabécar Language
The Cabécar language is an indigenous American language of the Chibchan language family spoken by the Cabécar people in the inland Turrialba Region, Cartago Province, Costa Rica. As of 2007, 2,000 speakers were monolingual. It is the only indigenous language in Costa Rica with monolingual adults. The language is also known by its dialect names Chirripó, Estrella, Telire, and Ujarrás. History Cabécar is considered to be one of a few "Chibcha-speaking tribes", categorized by similarities in the languages that they speak. Other Chibcha speaking tribes include the Bribri and the Boruca, also of Costa Rica. It is believed that the languages of the Chibcha speaking tribes shared a common ancestor around 8,000 years ago. However, differences in the languages are thought to have come about from the influence of outside people, including influences from Mesoamerica. Geographic distribution Cabécar is an endangered language spoken in Costa Rica. It is spoken by the Cabécar peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chánguena Language
Dorasque, which has the dialects Chumulu, Changuena (Changuina), and Gualaca, is an extinct Chibchan language of Panama Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co .... References * Alphonse Louis Pinart, ''Vocabulario Castellano-dorasque, Dialectos Chumulu, Gualaca y Changuina'', 1890 Languages of Panama Chibchan languages {{na-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teribe Language
Teribe is a language spoken by the Naso or Teribe Indians; it is used primarily in the Bocas del Toro Province of northwestern Panama and in the southern part of Costa Rica's Puntarenas Province, but is almost extinct in the latter. It is part of the Chibchan language family, in the Talamanca branch. There are currently about 3,000 speakers, nearly all of whom speak Spanish as well. The language is of the OVS type. Its ISO 639 ISO 639 is a set of standards by the International Organization for Standardization that is concerned with representation of names for languages and language groups. It was also the name of the original standard, approved in 1967 (as ''ISO 639/R ...-3 code is tfr. Writing system Teribe also uses the ll with diaeresis centered over the letters.http://software.sil.org/doulos/wp-content/uploads/sites/18/2015/11/DoulosSIL-features5.000.pdf References External links Teribe phonology Languages of Panama Languages of Costa Rica Chibchan langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movere Language
The Mové, also called Movere, Western Guaymi, or Ngäbere, are a Chibchan (Dorasque-Guaymi) speaking people in Panama (150,000) and Costa Rica (4,300). This tribe, like the Murire (Eastern Guaymi), is a division of the Guaymi. They are further subdivided into the Valiente. The Mové live in the rainforest as hunters and gatherers of wild plants. Among their crafts are basket weaving Basket weaving (also basketry or basket making) is the process of weaving or sewing pliable materials into three-dimensional artifacts, such as baskets, mats, mesh bags or even furniture. Craftspeople and artists specialized in making baskets ... and pottery. References *1971 Ngawbe: Tradition and Change Among the Western Guaymi of Panama. Illinois Studies in Anthropology No. 7. Urbana: U. of Illinois Press. *1968 The Ngawbe: An Analysis of the Economy and Social Structure of the Western Guaymi of Panama. Doctoral Dissertation, Department of Anthropology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Languages Of Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Central America consists of eight countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from northern Guatemala to central Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage. In the pre-Columbian era, Central America was inhabited by the indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica to the north and west and the Isthmo-Colombian peoples to the south and east. Following the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' voyages to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Costa Rica
Costa Rica's official and predominant language is Spanish. The variety spoken there, Costa Rican Spanish, is a form of Central American Spanish. Costa Rica is a linguistically diverse country and home to at least five living local indigenous languages spoken by the descendants of pre-Columbian peoples: Maléku, Cabécar, Bribri, Guaymí, and Buglere. Immigration has also brought people and languages from various countries around the world. Along the Atlantic Ocean in Limón Province, inhabited primarily by Afro-Caribs, an English-based creole language called Mekatelyu or Patua is spoken to varying degrees, as is English; many older Limonenses speak English as their native language. The Quakers community, who settled in Monteverde in the early 1950s, speaks an older dialect of English, using ''thou'' instead of ''you''. Costa Rican Sign Language is also spoken by the deaf community, and Costa Rican Spanish slang is known as "pachuco". Since 2015 Costa Rica is officially know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |