|
T. L. Venkatarama Iyer
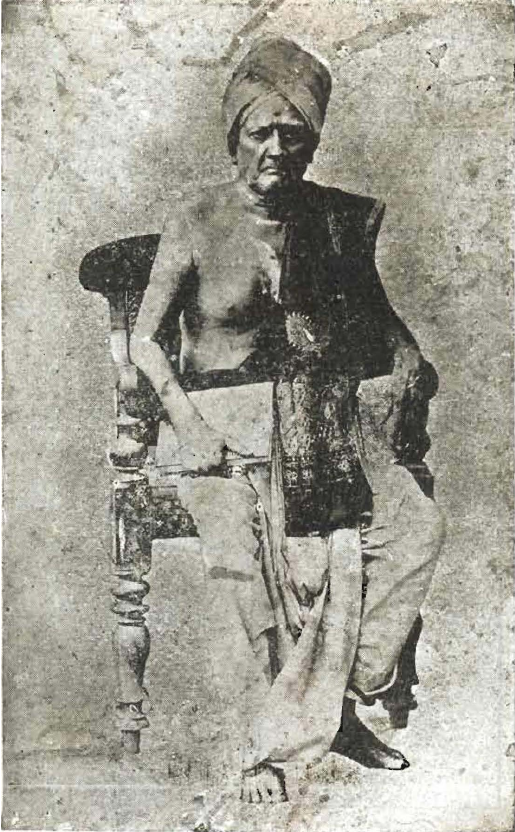
T. L. Venkatarama Iyer (25 November 1893 - 2 January 1971) was a Judge of the Supreme Court of India, a Carnatic musician and a musicologist. Early life T. L. Venkatarama Iyer hails from Harikesanallur, Tirunelveli district, Tamilnadu. He born in a family with a tradition in music and research. His father, M. Lakshmanasuri was a Sanskrit scholar and was instrumental in bringing up his son to the level he achieved later in life. Venkatarama Iyer was a close relative of Harikesanallur Muthiah Bhagavatar (a recipient of Sangeet Kalanidhi award in 1930), and was a disciple of Ambi Dikshitar (a grand-nephew of Muthuswami Dikshitar). Law T. L. Venkatarama Iyer graduated from Madras Christian law College in 1916. After doing apprenticeship under Sir Alladi Krishnaswamy Iyer, he started practicing in the Madras High Court from 1917. He became a Judge of the Madras High Court in 1951 and continued to serve till November 1953. Thereafter he served as a Judge of the Supreme Court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of India
The Supreme Court of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme judicial authority of India and is the highest court of the Republic of India under the constitution. It is the most senior constitutional court, has the final decision in all legal matters except for personal laws and interstate river disputes, and also has the power of judicial review. The Chief Justice of India is the Head and Chief Judge of the Supreme Court, which consists of a maximum of 34 judges, and has extensive powers in the form of original, appellate and advisory jurisdictions. New judges here are uniquely nominated by existing judges and other branches of government have neglible say as the court follows collegium system for appointments. As the apex and most powerful constitutional court in India, it takes up appeals primarily against verdicts of the High Courts of various states of the Union and other courts and tribunals. It is required to safeguard the fundamental rights of citizens and settles dispute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musicologist
Musicology (from Greek μουσική ''mousikē'' 'music' and -λογια ''-logia'', 'domain of study') is the scholarly analysis and research-based study of music. Musicology departments traditionally belong to the humanities, although some music research is scientific in focus (psychological, sociological, acoustical, neurological, computational). Some geographers and anthropologists have an interest in musicology so the social sciences also have an academic interest. A scholar who participates in musical research is a musicologist. Musicology traditionally is divided in three main branches: historical musicology, systematic musicology and ethnomusicology. Historical musicologists mostly study the history of the western classical music tradition, though the study of music history need not be limited to that. Ethnomusicologists draw from anthropology (particularly field research) to understand how and why people make music. Systematic musicology includes music theory, aesthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hindu
''The Hindu'' is an Indian English-language daily newspaper owned by The Hindu Group, headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu. It began as a weekly in 1878 and became a daily in 1889. It is one of the Indian newspapers of record and the second most circulated English-language newspaper in India, after '' The Times of India''. , ''The Hindu'' is published from 21 locations across 11 states of India. ''The Hindu'' has been a family-owned newspaper since 1905, when it was purchased by S. Kasturi Ranga Iyengar from the original founders. It is now jointly owned by Iyengar's descendants, referred to as the "Kasturi family", who serve as the directors of the holding company. The current chairperson of the group is Malini Parthasarathy, a great-granddaughter of Iyengar. Except for a period of about two years, when S. Varadarajan held the editorship of the newspaper, the editorial positions of the paper were always held by members of the family or held under their direction. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arikesavanallur
Arikesavanallur is a village in Ambasamuthiram Taluk, Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu, India. This village derives its name from the King Nindraseer Nedumaran who was also called as Harikesa. This village is known for the Temple of Lord Shiva, Ariyanadaswamy Temple. This temple is more than 1100 years old. References Notable people * Muthiah Bhagavatar Harikesanallur Muthiah Bhagavatar (15 November 1877 – 30 June 1945), commonly known as Muthiah Bhagavatar, is one of Carnatic classical music's famous twentieth-century composers. He also created about 20 '' ragas''. Early life Muthiah was bo ... Carnatic music composer * Harikesanallur Venkataraman, Astrologer * Rasulmansur MOHAMMED, Automotive Expert * T. L. Venkatarama Iyer, Carnatic music musicologist, Supreme Court Judge External links Shiva Temple, Harikesanallur Villages in Tirunelveli district {{Tirunelveli-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muthiah Bhagavatar
Harikesanallur Muthiah Bhagavatar (15 November 1877 – 30 June 1945), commonly known as Muthiah Bhagavatar, is one of Carnatic classical music's famous twentieth-century composers. He also created about 20 '' ragas''. Early life Muthiah was born on 15 November 1877, in Harikesanallur, a small village in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu in India, into an affluent Brahmin Tamil family. He was exposed to music from a very early age, as his father was a patron of musicians. He lost his father at the young age of six years, and his maternal uncle M. Lakshmana Suri took over the responsibility for his education, initiating Muthiah into Sanskrit and Vedic studies. However, the love of music that had been implanted in him led Muthiah to leave his hometown of Harikesanallur, Tamil Nadu when he was only ten years in search of a teacher. He found the gifted teacher Padinaindumandapa Sambasiva Iyer at Tiruvarur, who recognised Muthiah's talent for music. Sambasiva Iyer was the father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muthuswami Dikshitar
Muthuswami Dikshitar (Mudduswamy Dikshitar)(, 24 March 1776 – 21 October 1835), mononymously Dikshitar, was a South Indian poet, singer and veena player, and a legendary composer of Indian classical music, who is considered one of the musical trinity of Carnatic music. Muthuswami Dikshitar was born on 24 March 1775 in Tiruvarur near Thanjavur, in what is now the state of Tamil Nadu in India, to a family that is traditionally traced back to Virinichipuram in the northern boundaries of the state. His compositions, of which around 500 are commonly known, are noted for their elaborate and poetic descriptions of Hindu gods and temples and for capturing the essence of the raga forms through the vainika (veena) style that emphasises gamakas. They are typically in a slower speed (chowka kala). He is also known by his signature name of Guruguha which is also his mudra (and can be found in each of his songs). His compositions are widely sung and played in classical concerts of Carnatic mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alladi Krishnaswamy Iyer
Dewan Bahadur Sir Alladi Krishnaswamy Iyer (14 May 1883 – 3 October 1953) was an Indian lawyer and member of the Constituent Assembly of India, which was responsible for framing the Constitution of India. He also served as the advocate general of Madras State from 1929 to 1944. Neuroscientist Vilayanur S. Ramachandran is his grandson. Alladi Ramakrishnan, an Indian physicist and the founder of the Institute of Mathematical Sciences was his son. Early life Krishnaswamy Iyer was born in 1883 to a Tamil family in the small village of Pudur in Madras State (present day Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh). His father, Ekamra Sastry, was a priest. Krishnaswamy passed his matriculation examination in 1899 and joined the Madras Christian College to study history. He used his spare time to attend classes in law and passed the B.L. exam and became one of the leading members of the bar. He was made a Dewan Bahadur in 1930 and was knighted in the 1932 New Year Honours list. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras High Court
The Madras High Court is a High Court in India. It has appellate jurisdiction over the state of Tamil Nadu and the union territory of Puducherry. It is located in Chennai, and is the third oldest high court of India after the Calcutta High Court in Kolkata and Bombay High Court in Mumbai. The Madras High Court is one of three high courts of colonial India established in the three Presidency Towns of Madras, Bombay and Calcutta by letters patent granted by Queen Victoria, dated 26 June 1862. It exercises original jurisdiction over the city of Chennai, as well as extraordinary original jurisdiction, civil and criminal, under the letters patent and special original jurisdiction for the issue of writs under the Constitution of India. Covering 107 acres, the court complex is one of the largest in the world, second only to the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. The High Court consists of 74 judges and a chief justice. History From 1817 to 1862, the Supreme Court of Madras was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras Music Academy
Madras Music Academy is one of the earliest established music academies in South India. Before the concept of infrastructure was introduced to India in the early 1920s, it was a gathering for elite musicians simply called (and is still more commonly referred to as) Music Academy () It plays an important role in encouraging and promoting primarily the Carnatic Music Indian art form. It played a vital role in the revival of the Indian classical dance form of Bharatnatyam in the 1930s when it faced near extinction due to a negative connotation caused by conservative societal standards. They also run a music school called the Teachers college of Carnatic Music which has many eminent musicians on its faculty. Musicians such as Tiger Varadachariar, Appa Iyer, Valadi Krishnaiyer and Mudicondan Venkatarama Iyer adorned the chair of Principal of the Teacher's College. History In 1927, the Indian National Congress held the All India Music Conference in Madras. At the end of the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangita Kalanidhi
Sangeetha Kalanidhi or Sangeeta Kalanidhi (Tamil: சங்கீத கலாநிதி, Sanskrit : संगीत-कला-निधि) (''sangeetha'' = music, ''kala'' = art, ''nidhi'' = treasure or ocean) is the title awarded yearly to a Carnatic musician by the Madras Music Academy. From 1929 to 1941, the award did not exist. The idea of the award was conceived in 1942 by the then Academy President KV Krishnaswami Iyer; and on 1 January 1943, all musicians who had presided over the annual conferences between 1929 and 1942 were awarded the title. This included 2 or 3 past presidents - Palamarneri Swaminatha Iyer (1931), probably Umayalpuram Swaminatha Iyer (1936) and Mangudi Chidambara Bhagavatar (1937) - who were no more, but no posthumous award has been presented since then. Some sources cite 1946 as the year of death for Umayalpuram Swaminatha Iyer, in which case he might have received Sangeet Kalanighi award in his lifetime only. Sangeetha Kalanidhis Source(s): ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship
The Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship, also known as Akademi Ratna Sadasyata, is an Indian honour for the performing arts presented by Sangeet Natak Academy. It is "the most prestigious and rare honour" conferred by the Academy and is "restricted to 40 individuals at any given time". Background In 1945, The Asiatic Society of Bengal submitted a proposal to establish a National Cultural Trust consisting of three academies: an Academy of Music, Dance, and Drama, an Academy of Letters, and an Academy of Art and Architecture. The proposal was reconsidered in the Conference on Art held in Kolkata in 1949, and two conferences, the Conference on Letters, and the Conference on Dance, Drama, and Music, were held in New Delhi in 1951. All three conferences were organized by the Government of India and recommended the establishment of three national academies: an Academy of Music, Dance, and Drama (Sangeet Natak Akademi), an Academy of Letters ( Sahitya Akademi), and an Academy of Art ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)