|
Sânpetru
Sânpetru (German: ''Petersberg''; Hungarian: ''Barcaszentpéter'') is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania, located just north of the county seat, Brașov. It is composed of a single village, Sânpetru. The commune is located in the Burzenland ethnographic area, in the eastern part of the county, at the foot of the Carpathian Mountains. This area was home to many Transylvanian Saxons, although after the Romanian Revolution of 1989 much of this community emigrated to Germany. The center of the village was built by this group and shows the influence of German architecture. Separate from this there is a Romanian-built area featuring a small church and houses dating at least to the early 19th century. A new center was built closer to Brașov during the communist era to house migrating workers for the tractor and bus factories in the city. Since 1989, new, more luxurious houses have been built on the outskirts of the village, slowly linking it with Brașov. Demogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhold Batschi
Reinhold Batschi OAM (born 20 August 1942 in Sânpetru, Brașov County, Romania) is a former Romanian rower and leading Australian rowing coach. He was the inaugural Head Coach of the Australian Institute of Sport's rowing program and Head Coach of the Australian Olympic rowing teams from 1980 to 2000. Rowing career Batschi became involved in rowing as a result of Romania's compulsory national service. Representing Romania as a rower, Batschi won a bronze medal in the men's coxed fours at the 1967 European Rowing Championships. At the 1968 Mexico Olympics, his crew the men's coxed four finished seventh. He retired from competitive rowing in 1969. Coaching career Batschi competed a sports studies degree at the National Academy of Physical Education and Sport in Bucharest, Romania. In 1970, he became at coach at his rowing club in Bucharest. Batschi them moved to West Germany to become Head Coach at the City of West Berlin Rowing Centre. He coached the West German team to me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brașov County
Brașov County () is a county ( județ) of Romania, in Transylvania. Its capital city is Brașov. The county incorporates within its boundaries most of the Medieval "lands" (''țări'') Burzenland and Făgăraș. Name In Hungarian, it is known as ''Brassó megye'', and in German as ''Kreis Kronstadt''. Under Austria-Hungary, a county with an identical name (Brassó County, ro, Comitatul Brașov) was created in 1876, covering a smaller area. Demographics On 20 October 2011, the county had a population of 549,217 and the population density was . * Romanians – 87.4% * Hungarians – 7.77% * Romas – 3.5% * Germans (Transylvanian Saxons) – 0.65% Traditionally the Romanian population was concentrated in the west and southwest of the county, the Hungarians in the east part of the county, and the Germans in the north and around Brașov city. Geography The county has a total area of . The south side comprises the Carpathian Mountains (Southern Carpathians and Eastern Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
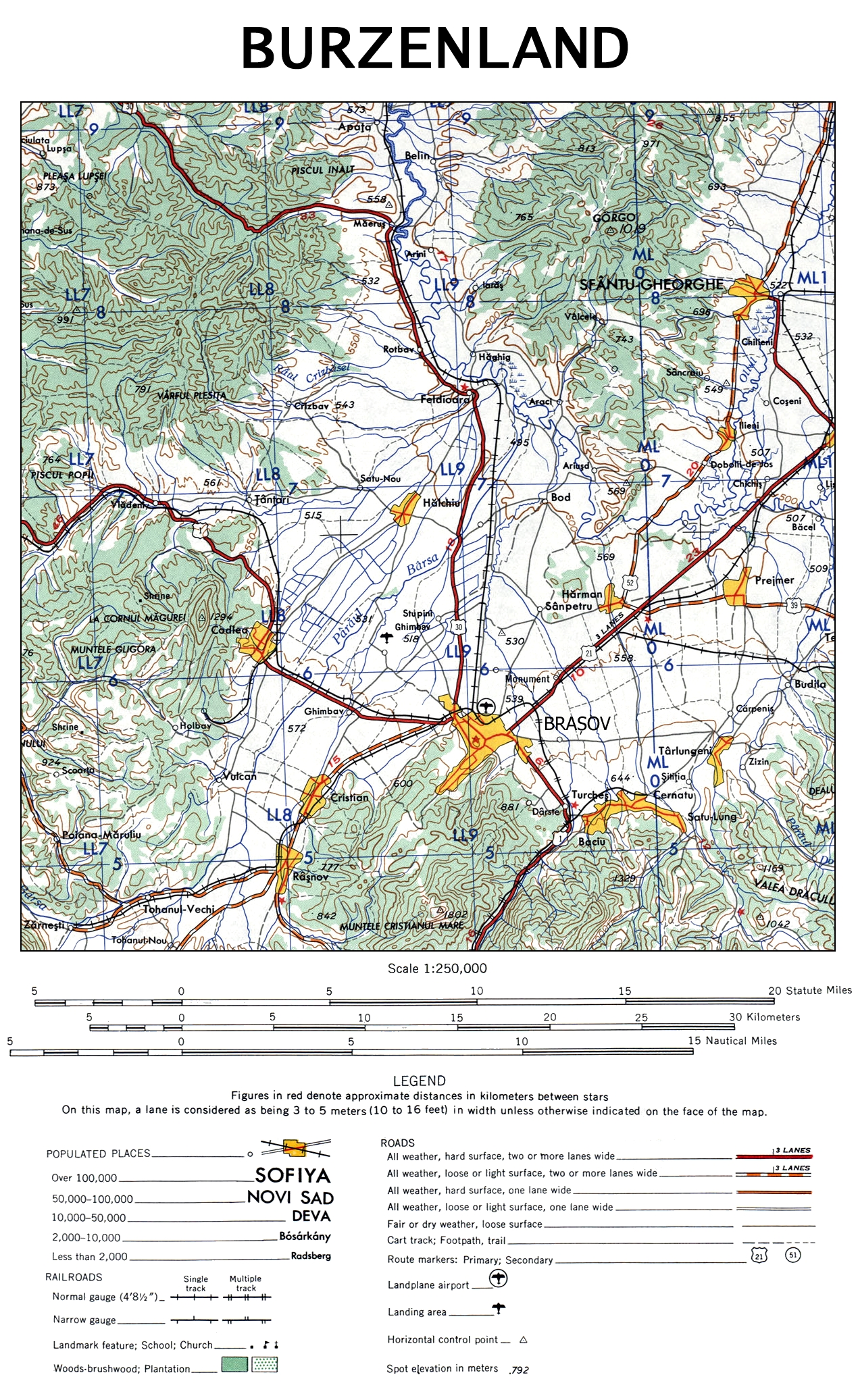
Burzenland
Țara Bârsei, Burzenland () or Barcaság is a historic and ethnographic area in southeastern Transylvania, Romania with a mixed population of Romanians, Germans, and Hungarians. Geography The Burzenland lies within the Southern Carpathians mountains ranges, bordered approximately by Apața in the north, Bran in the southwest and Prejmer in the east. Its most important city is Brașov. Burzenland is named after the stream Bârsa (''Barca'', ''Burzen'', 1231: ''Borza''), which flows into the Olt river. The Romanian word ''bârsă'' is supposedly of Dacian origin (''see List of Romanian words of possible Dacian origin''). History Middle Ages Based on archaeological evidence, it seems German colonization of the region started in the middle of the 12th century during the reign of King Géza II of Hungary. The German colonists from this region are attested in documents as early as 1192 when ''terra Bozza'' is mentioned as being settled by Germans (''Theutonici''). In 1211 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaharia Bârsan
Zaharia Bârsan ( – December 13, 1948) was an Austro-Hungarian-born Romanian playwright, poet and actor. He was born in Sânpetru, Brassó County, in what was then the Transylvania region of Austria-Hungary. His parents were Zaharie Bârsan, a small landowner, and his wife Maria (''née'' Vlădăreanu). After completing a gymnasium in his native city in 1895, Bârsan went to the Romanian Old Kingdom. Settling in its capital Bucharest, he earned a degree from Gheorghe Lazăr High School.Justin Ceuca, ''Zaharia Bârsan: monografie'', p. 8. Editura Dacia, Bucharest, 1978. He subsequently enrolled in the Dramatic Arts Conservatory, studying under Constantin Nottara and graduating in 1901. An employee of the National Theatre Bucharest from that point, he also participated in numerous traveling shows; between 1903 and 1913, he was a central figure of theatrical life in Transylvania. Following the province's 1918 union with Romania, Bârsan became the first director of the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal occupied by the Roman magistrates. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also built in private residences an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Cistercians
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly-influential Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Saint Bernard himself, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of the "cuculla" or cowl (choir robe) worn by the Cistercians over their habits, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098, with the goal of following more closely the Rule of Saint Benedict. The best known of them were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and the English monk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; in fact, humans and many animals have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language usage, "fruit" normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet or sour and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term "fruit" also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is consumed in large quantities, either fresh or in such prepared foods as jam, juice, pies, ice cream, milkshakes, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavorings and aromas are also widely used in products such as candy, soap, lip gloss, perfume, and many others. The garden strawberry was first bred in Brittany, France, in the 1750s via a cross of ''Fragaria virginiana'' from eastern North America and ''Fragaria chiloensis'', which was brought from Chile by Amédée-François Frézier in 1714. Cultivars of ''Fragaria'' × ''ananassa'' have replaced, in commercial production, the woodland strawberry ('' Fragaria vesca''), which was the first straw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches from the far eastern Czech Republic (3%) and Austria (1%) in the northwest through Slovakia (21%), Poland (10%), Ukraine (10%), Romania (50%) to Serbia (5%) in the south. "The Carpathians" European Travel Commission, in The Official Travel Portal of Europe, Retrieved 15 November 2016 The Carpathian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raspberry
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with woody stems. World production of raspberries in 2020 was 895,771 tonnes, led by Russia with 20% of the total. Description A raspberry is an aggregate fruit, developing from the numerous distinct carpels of a single flower. What distinguishes the raspberry from its blackberry relatives is whether or not the torus ( receptacle or stem) "picks with" (i.e., stays with) the fruit. When picking a blackberry fruit, the torus stays with the fruit. With a raspberry, the torus remains on the plant, leaving a hollow core in the raspberry fruit. Raspberries are grown for the fresh fruit market and for commercial processing into individually quick frozen (IQF) fruit, purée, juice, or as dried fruit used in a variety of grocery products such as raspb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
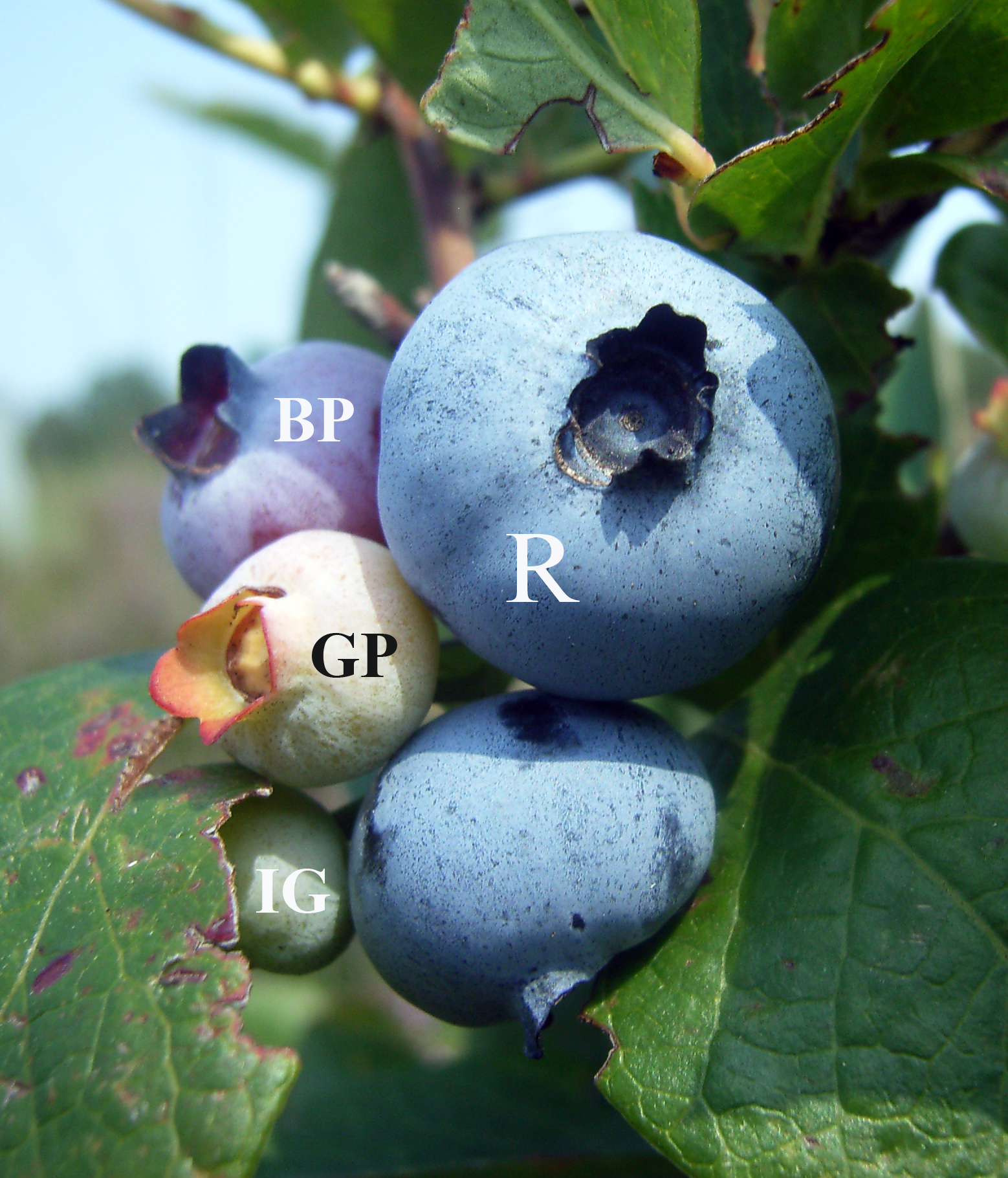
Blueberry
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)