|
Systolic Heart Murmur
Systolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during systole, i.e. they begin and end between S1 and S2. Many involve stenosis of the semilunar valves or regurgitation of the atrioventricular valves. Types * Mid-systolic ejection murmurs are due to blood flow through the semilunar valves. They occur at the start of blood ejection — which starts after S1 — and ends with the cessation of the blood flow — which is before S2. Therefore, the onset of a midsystolic ejection murmur is separated from S1 by the isovolumic contraction phase; the cessation of the murmur and the S2 interval is the aortic or pulmonary hangout time. The resultant configuration of this murmur is a crescendo-decrescendo murmur. Causes of midsystolic ejection murmurs include outflow obstruction, increased flow through normal semilunar valves, dilation of aortic root or pulmonary trunk, or structural changes in the semilunar valves without obstruction. * Late systolic murmurs start after S1 and, if left s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonocardiograms From Normal And Abnormal Heart Sounds
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (heart and breath sounds), as well as the alimentary canal. The term was introduced by René Laennec. The act of listening to body sounds for diagnostic purposes has its origin further back in history, possibly as early as Ancient Egypt. (Auscultation and palpation go together in physical examination and are alike in that both have ancient roots, both require skill, and both are still important today.) Laënnec's contributions were refining the procedure, linking sounds with specific pathological changes in the chest, and inventing a suitable instrument (the stethoscope) to mediate between the patient's body and the clinician's ear. Auscultation is a skill that requires substantial clinical experience, a fine stethoscope and good listening sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An '' embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term ''fetus'' is used until birth. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Septal Defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the atrioventricular node, is most commonly affected in adults and older children in the United States. It is also the type that will most commonly require surgical intervention, comprising over 80% of cases. Membranous ventricular septal defects are more common than muscular ventricular septal defects, and are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly. Signs and symptoms Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a few weeks after birth. VSD is an acyanotic congenital heart defect, aka a lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood.Mitral valve regurgitation at Mount Sinai Hospital It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards – regurgitation from the , through the mitral valve, into the |
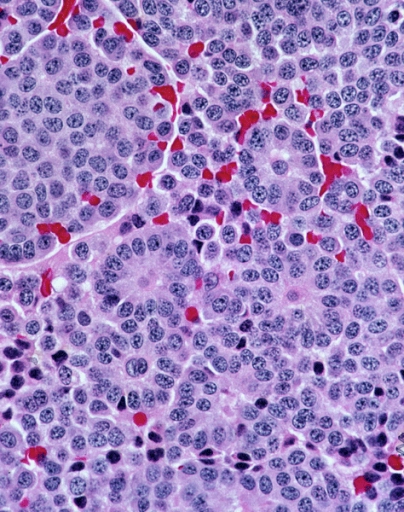
Carcinoid Disease
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebstein's Anomaly
Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital heart defect in which the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced towards the apex of the right ventricle of the heart. It is classified as a critical congenital heart defect accounting for less than 1% of all congenital heart defects presenting in around per 200,000 live births. Ebstein anomaly is the congenital heart lesion most commonly associated with supraventricular tachycardia. Signs and symptoms The annulus of the valve is still in the normal position. The valve leaflets, however, are to a varying degree, attached to the walls and septum of the right ventricle. A subsequent "atrialization" of a portion of the morphologic right ventricle (which is then contiguous with the right atrium) is seen. This causes the right atrium to be large and the anatomic right ventricle to be small in size. * S3 heart sound * S4 heart sound * Triple or quadruple gallop due to widely split S1 and S2 sounds plus a loud S3 and/or S4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IV Drug Use
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or subcutaneous location). Intravenous therapy, a form of drug injection, is universally practiced in modernized medical care. , there were 13.2 million people worldwide who self-administered injection drugs outside of medical supervision, of which 22% are from developed countries. A wide variety of drugs are injected, often opioids: these may include legally prescribed medicines and medication such as morphine, as well as stronger compounds often favored in recreational drug use, which are often illegal. Although there are various methods of taking drugs, injection is favoured by some people as the full effects of the drug are experienced very quickly, typically in five to ten seconds. It also bypasses first-pass metabolism in the liver, resulting in higher bioavailability and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the surfaces of intracardiac devices. Endocarditis is characterized by lesions, known as '' vegetations'', which is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies of microorganisms, and scant inflammatory cells. In the subacute form of infective endocarditis, the vegetation may also include a center of granulomatous tissue, which may fibrose or calcify. There are several ways to classify endocarditis. The simplest classification is based on cause: either ''infective'' or ''non-infective'', depending on whether a microorganism is the source of the inflammation or not. Regardless, the diagnosis of endocarditis is based on clinical features, investigations such as an echocardiogram, and blood cultures demonstrating the presence of endocarditis-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carvallo's Sign
Carvallo's sign is a clinical sign found in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. The pansystolic murmur found in this condition becomes louder during inspiration; this sign enables it to be distinguished from mitral regurgitation. Pathophysiology During inspiration, the venous blood flow into the right atrium and ventricle are increased, which increases the stroke volume of the right ventricle during systole. As a result, the leak of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium is larger during inspiration, causing the murmur to become louder. During expiration, the leak of blood backwards through the tricuspid valve is lessened, making the murmur more quiet. Conversely, the murmur of mitral regurgitation becomes louder during expiration due to the increase in venous return from the pulmonary vein The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air out as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be used either in medical examination as a test of cardiac function and autonomic nervous control of the heart, or to clear the ears and sinuses (that is, to equalize pressure between them) when ambient pressure changes, as in scuba diving, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or air travel. A modified version is done by expiring against a closed glottis. This will elicit the cardiovascular responses described below but will not force air into the Eustachian tubes. History The technique is named after Antonio Maria Valsalva, a 17th-century physician and anatomist from Bologna whose principal scientific interest was the human ear. He described the Eustachian tube and the maneuver to test its patency (openness). He also described the use of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. It is the primary form of myxomatous degeneration of the valve. There are various types of MVP, broadly classified as classic and nonclassic. In severe cases of classic MVP, complications include mitral regurgitation, infective endocarditis, congestive heart failure, and, in rare circumstances, cardiac arrest. The diagnosis of MVP depends upon echocardiography, which uses ultrasound to visualize the mitral valve. MVP is the most common valvular abnormality and is estimated to affect 2–3% of the population and 1 in 40 people might have it. The condition was first described by John Brereton Barlow in 1966. It was subsequently termed ''mitral valve prolapse'' by J. Michael Criley. Although mid-systolic click (sound of prolapsing mitral leaflet) and systolic murmur have been noticed earlier with stethoscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |