|
Systemic Capillary Leak Syndrome
Capillary leak syndrome, or vascular leak syndrome, is characterized by the escape of blood plasma through capillary walls, from the blood circulatory system to surrounding tissues, muscle compartments, organs or body cavities. It is a phenomenon most commonly witnessed in sepsis, and less frequently in autoimmune diseases, differentiation syndromeengraftment syndrome hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, viral hemorrhagic fevers, and snakebite and ricin poisoning. Pharmaceuticals, including the chemotherapy medications gemcitabine and denileukin diftitox, as well as certain interleukins and monoclonal antibodies, can also cause capillary leaks. These conditions and factors are sources of secondary capillary leak syndrome. Systemic capillary leak syndrome (SCLS), also called Clarkson's disease, or primary capillary leak syndrome, is a rare, grave and episodic medical condition observed largely in otherwise healthy individuals mostly in middle a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma is separated from the blood by spinning a vessel of fresh blood containing an anticoagulant in a centrifuge until the blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube. The blood plasma is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, binding only to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered, by increasing the therapeutic targets of one monoclonal antibody to two epitopes. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to virtually any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibodies are being used on a clinical level for both the diagnosis and therapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukins
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocyte, as well as through monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and hematopoietic cells. Interleukin receptors on astrocytes in the hippocampus are also known to be involved in the development of spatial memories in mice. History and name The name "interleukin" was chosen in 1979, to replace the various different names used by different research groups to designate interleukin 1 (lymphocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denileukin Diftitox
Denileukin diftitox (trade name Ontak) was an antineoplastic agent, an engineered protein combining interleukin-2 and diphtheria toxin. Denileukin diftitox could bind to interleukin-2 receptors and introduce the diphtheria toxin into cells that express those receptors, killing the cells. In some leukemias and lymphomas, malignant cells express these receptors, so denileukin diftitox can target these. In 1999, Ontak was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). There is some evidence tying it to vision loss, and in 2006 the FDA added a black box warning In the United States, a boxed warning (sometimes "black box warning", colloquially) is a type of warning that appears on the package insert for certain prescription drugs, so called because the U.S. Food and Drug Administration specifies that it ... to the drug's label. In 2014, marketing of Ontak was discontinued in the US. References External links F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by intravenous infusion. It acts against neoplastic growth, and it inhibits the replication of Orthohepevirus A, the causative agent of Hepatitis E, through upregulation of interferon signaling. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, liver and kidney problems, nausea, fever, rash, shortness of breath, mouth sores, diarrhea, neuropathy, and hair loss. Use during pregnancy will likely result in fetal harm. Gemcitabine is in the nucleoside analog family of medication. It works by blocking the creation of new DNA, which results in cell death. Gemcitabine was patented in 1983 and was approved for medical use in 1995. Generic versions were introduced in Europe in 2009 and in the US in 2010. It is on the WHO Model List of Essentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricin
Ricin ( ) is a lectin (a carbohydrate-binding protein) and a highly potent toxin produced in the seeds of the castor oil plant, ''Ricinus communis''. The median lethal dose (LD50) of ricin for mice is around 22 micrograms per kilogram of body weight via intraperitoneal injection. Oral exposure to ricin is far less toxic. An estimated lethal oral dose in humans is approximately 1 milligram per kilogram of body weight. Ricin was first described by Peter Hermann Stillmark, the founder of lectinology. Biochemistry Ricin is classified as a type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP). Whereas type 1 RIPs are composed of a single protein chain that possesses catalytic activity, type 2 RIPs, also known as holotoxins, are composed of two different protein chains that form a heterodimeric complex. Type 2 RIPs consist of an A chain that is functionally equivalent to a type 1 RIP, covalently connected by a single disulfide bond to a B chain that is catalytically inactive, but serves to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
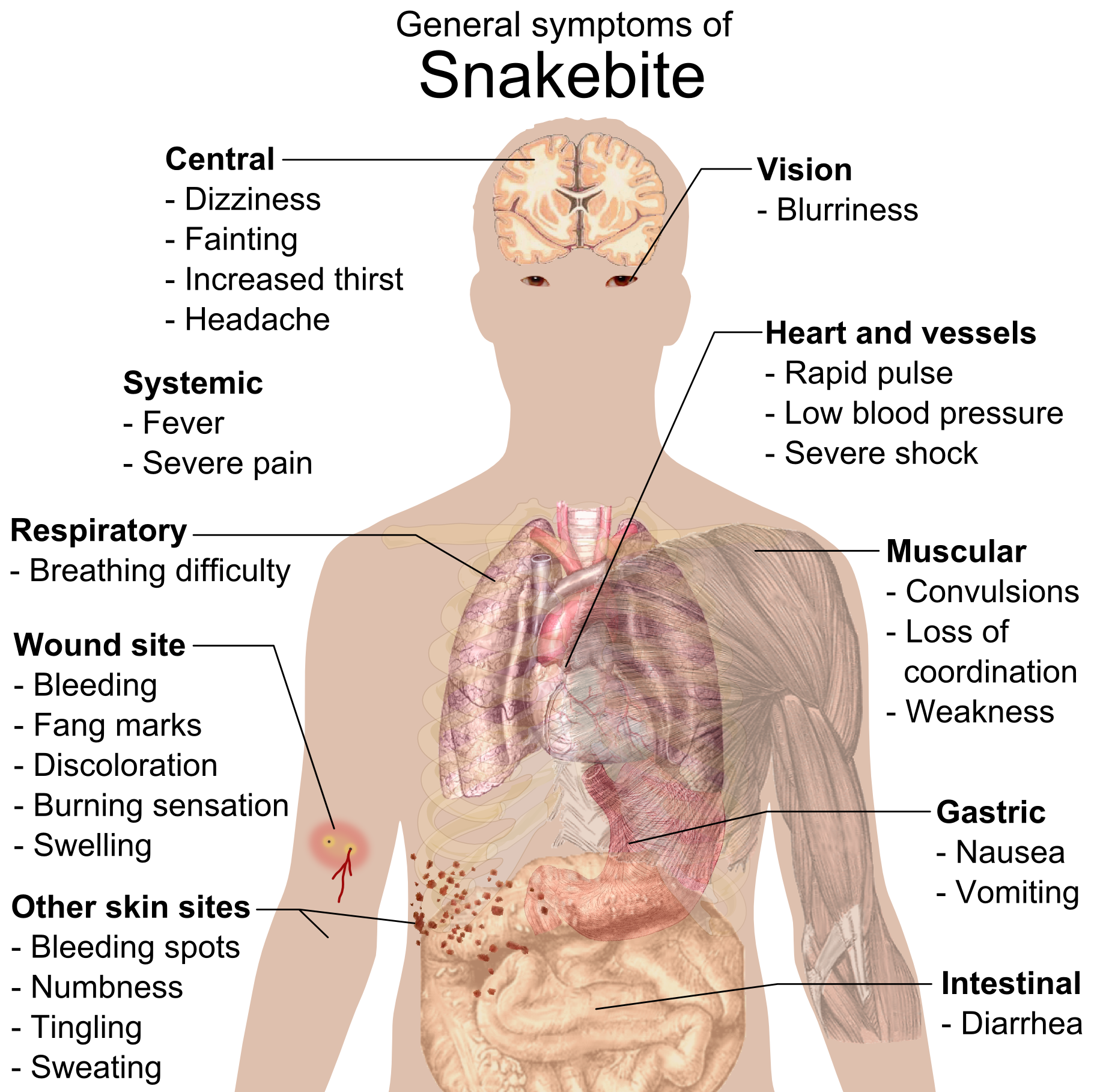
Snakebite
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death. The outcome depends on the type of snake, the area of the body bitten, the amount of snake venom injected, the general health of the person bitten and whether or not anti-venom serum has been administered by a doctor in a ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of animal and human illnesses in which fever and hemorrhage are caused by a viral infection. VHFs may be caused by five distinct families of RNA viruses: the families ''Filoviridae'', ''Flaviviridae'', ''Rhabdoviridae'', and several member families of the ''Bunyavirales'' order such as '' Arenaviridae'', and ''Hantaviridae''. All types of VHF are characterized by fever and bleeding disorders and all can progress to high fever, shock and death in many cases. Some of the VHF agents cause relatively mild illnesses, such as the Scandinavian '' nephropathia epidemica'' (a hantavirus), while others, such as Ebola virus, can cause severe, life-threatening disease. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of VHFs include (by definition) fever and bleeding: * Flushing of the face and chest, small red or purple spots (petechiae), bleeding, swelling caused by edema, low blood pressure (hypotension), and circulatory shock. * Malaise, muscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
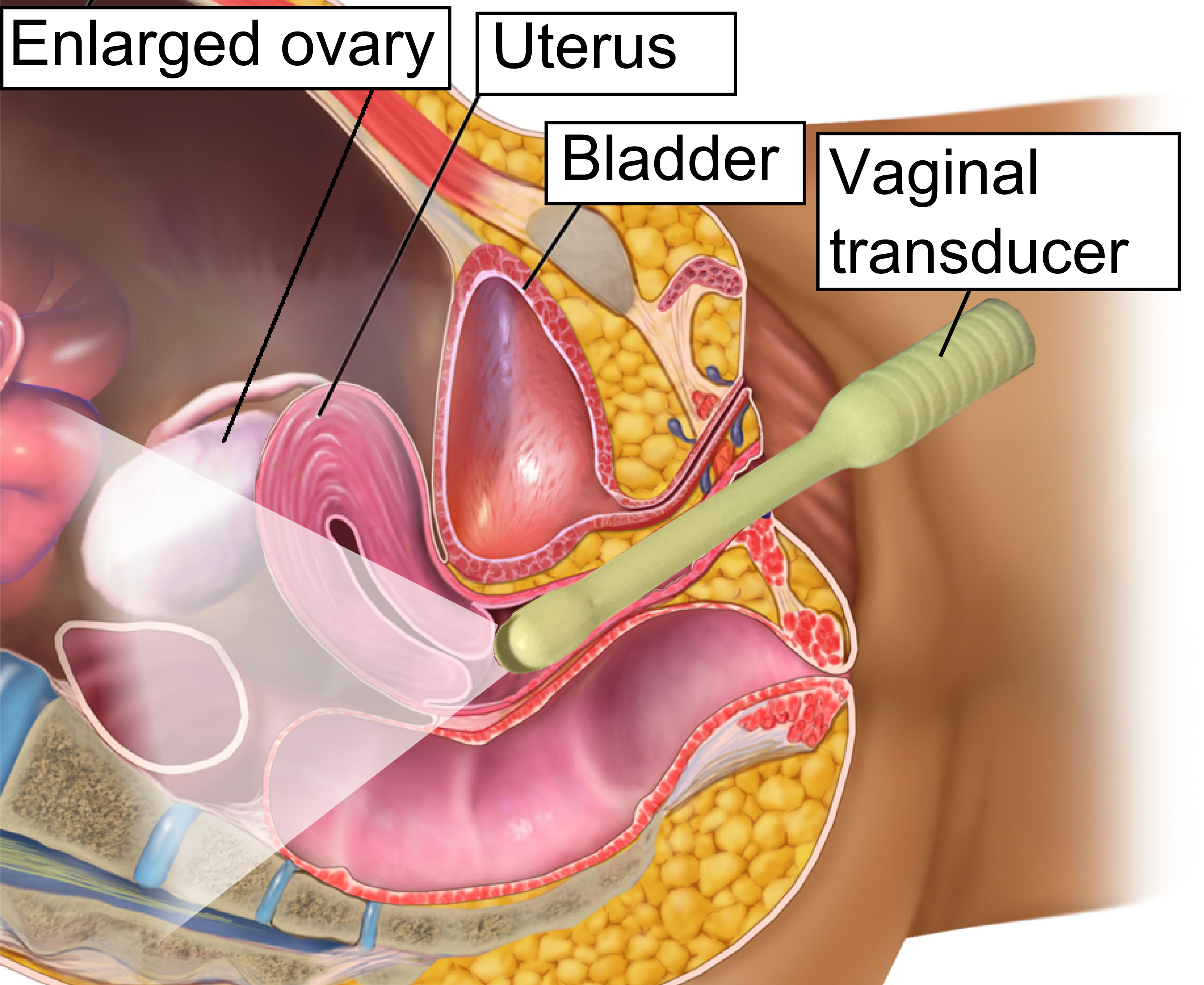
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is a medical condition that can occur in some women who take fertility medication to stimulate egg growth, and in other women in very rare cases. Most cases are mild, but rarely the condition is severe and can lead to serious illness or death. Signs and symptoms Symptoms are set into 3 categories: mild, moderate, and severe. Mild symptoms include abdominal bloating and feeling of fullness, nausea, diarrhea, and slight weight gain. Moderate symptoms include excessive weight gain (weight gain of greater than 2 pounds per day), increased abdominal girth, vomiting, diarrhea, darker urine, decreased urine output, excessive thirst, and skin and/or hair feeling dry (in addition to mild symptoms). Severe symptoms are fullness/bloating above the waist, shortness of breath, pleural effusion, urination significantly darker or has ceased, calf and chest pains, marked abdominal bloating or distention, and lower abdominal pains (in addition to mild and mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), also known as haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (British spelling), and hemophagocytic or haemophagocytic syndrome, is an uncommon hematologic disorder seen more often in children than in adults. It is a life-threatening disease of severe hyperinflammation caused by uncontrolled proliferation of activated lymphocytes and macrophages, characterised by proliferation of morphologically benign lymphocytes and macrophages that secrete high amounts of inflammatory cytokines. It is classified as one of the cytokine storm syndromes. There are inherited and non-inherited (acquired) causes of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Signs and symptoms The onset of HLH occurs before the age of one year in approximately 70 percent of cases. Familial HLH should be suspected if siblings are diagnosed with HLH or if symptoms recur when therapy has been stopped. Familial HLH is an autosomal recessive disease, hence each sibling of a child with familial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiation Syndrome
Retinoic acid syndrome (RAS) is a potentially life-threatening complication observed in people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML) and first thought to be specifically associated with Tretinoin, all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA) (also known as tretinoin) treatment. Subsequently, so-called RAS was recognized in APML patients who had been treated with another highly efficacious drug, arsenic trioxide, and yet did not appear in patients treated with tretinoin for other disorders. These facts and others support the notion that RAS depends on the presence of the malignant promyelocytes. This has led to the growing deprecation of the term 'retinoic acid syndrome' and to an increasing use of the term differentiation syndrome to signify this APML treatment complication. Signs and symptoms The syndrome is characterized by dyspnea, fever, weight gain, hypotension, and pulmonary infiltrates. This is effectively treated by giving dexamethasone and withholding ATRA (or arsenic trioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |