|
Synthetic Virology
Synthetic virology is a branch of virology engaged in the study and engineering of synthetic man-made viruses. It is a multidisciplinary research field at the intersection of virology, synthetic biology, computational biology, and DNA nanotechnology, from which it borrows and integrates its concepts and methodologies. There is a wide range of applications for synthetic viral technology such as medical treatments, investigative tools, and reviving organisms. Constructing ''de novo'' synthetic viruses Advances in genome sequencing technology and oligonucleotide synthesis paved the way for construction of synthetic genomes based on previously sequenced genomes. Both RNA and DNA viruses can be made using existing methods. RNA viruses have historically been utilized due to the typically small genome size and existing reverse transcription machinery present. The first man-made infectious viruses generated without any natural template were of the polio virus and the φX174 bacteriophag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virology
Virology is the Scientific method, scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host (biology), host cell (biology), cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy. The identification of the causative agent of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV) as a novel pathogen by Martinus Beijerinck (1898) is now acknowledged as being the history of virology, official beginning of the field of virology as a discipline distinct from bacteriology. He realized the source was neither a bacterial nor a fungal infection, but something completely different. Beijerinck used the word "virus" to describe the mysterious agent in his 'contagium vivum fluidum' ('contagious living fluid'). Rosalind Franklin proposed the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems, or to redesign systems that are already found in nature. It is a branch of science that encompasses a broad range of methodologies from various disciplines, such as biotechnology, biomaterials, material science/engineering, genetic engineering, molecular biology, molecular engineering, systems biology, membrane science, biophysics, chemical and biological engineering, electrical and computer engineering, control engineering and evolutionary biology. Due to more powerful genetic engineering capabilities and decreased DNA synthesis and sequencing costs, the field of synthetic biology is rapidly growing. In 2016, more than 350 companies across 40 countries were actively engaged in synthetic biology applications; all these companies had an estimated net worth of $3.9 billion in the global market. Definition Synthetic biology currently has no gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Biology
Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers. History Bioinformatics, the analysis of informatics processes in biological systems, began in the early 1970s. At this time, research in artificial intelligence was using network models of the human brain in order to generate new algorithms. This use of biological data pushed biological researchers to use computers to evaluate and compare large data sets in their own field. By 1982, researchers shared information via punch cards. The amount of data grew exponentially by the end of the 1980s, requiring new computational methods for quickly interpreting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Nanotechnology
DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, and functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins to determine structures. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated. The conceptual foundation for DNA nanotechnology was first laid out by Nadrian Seeman in the early 1980s, and the field began to attract widespread int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small bits of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by " -mer" (from Greek ''meros'', "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides (nt) is a hexamer, while one of 25 nt wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
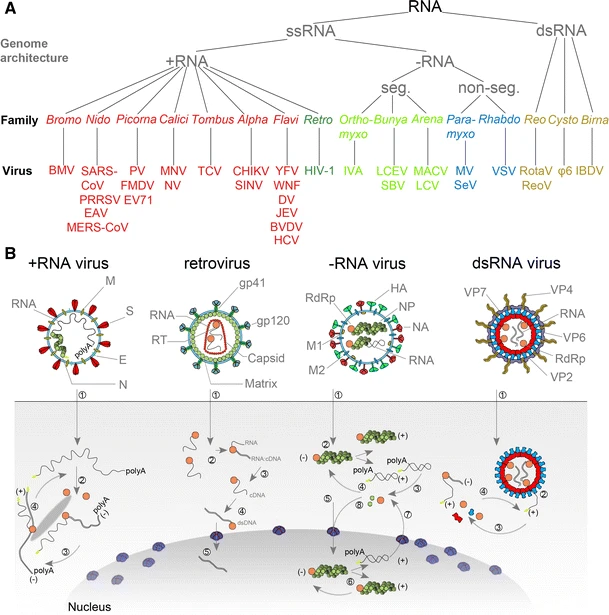
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classifies RNA viruses as those that belong to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Baltimore classification system. This category excludes ''Group VI'', viruses with RNA genetic material but which use DNA intermediates in their life cycle: these are called retroviruses, including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. As of May 2020, all known RNA viruses encoding an RNA-directed RNA polymerase are believed to form a monophyletic group, known as the realm '' Riboviria''. The majority of such RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm '' Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institutes Of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late 1880s and is now part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The majority of NIH facilities are located in Bethesda, Maryland, and other nearby suburbs of the Washington metropolitan area, with other primary facilities in the Research Triangle Park in North Carolina and smaller satellite facilities located around the United States. The NIH conducts its own scientific research through the NIH Intramural Research Program (IRP) and provides major biomedical research funding to non-NIH research facilities through its Extramural Research Program. , the IRP had 1,200 principal investigators and more than 4,000 postdoctoral fellows in basic, translational, and clinical research, being the largest biomedical research instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980, by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990. It is thought to be able to cure many genetic disorders or treat them over time. Between 1989 and December 2018, over 2,900 clinical trials were conducted, with more than half of them in phase I.Gene Therapy Cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioterrorism
Bioterrorism is terrorism involving the intentional release or dissemination of biological agents. These agents are bacteria, viruses, insects, fungi, and/or toxins, and may be in a naturally occurring or a human-modified form, in much the same way as in biological warfare. Further, modern agribusiness is vulnerable to anti-agricultural attacks by terrorists, and such attacks can seriously damage economy as well as consumer confidence. The latter destructive activity is called agrobioterrorism and is a subtype of agro-terrorism. Definition Bioterrorism is the deliberate release of viruses, bacteria, toxins or other harmful agents to cause illness or death in people, animals, or plants. These agents are typically found in nature, but could be mutated or altered to increase their ability to cause disease, make them resistant to current medicines, or to increase their ability to be spread into the environment. Biological agents can be spread through the air, water, or in food. Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)