|
Synthesis Of Bioglass
Bioactive glasses have been synthesized through methods such as conventional melting, quenching, the sol–gel process, flame synthesis, and microwave irradiation. The synthesis of bioglass has been reviewed by various groups, with sol-gel synthesis being one of the most frequently used methods for producing bioglass composites, particularly for tissue engineering applications. Other methods of bioglass synthesis have been developed, such as flame and microwave synthesis, though they are less prevalent in research. History and methodology Melt quench synthesis The first bioactive glass, developed by Larry Hench in 1969, was produced by melting a mixture of related oxide precursors at relatively high temperatures. This original bioactive glass, named Bioglass, was melt-derived with a composition of 46.1 mol% SiO2, 24.4 mol% Na2O, 26.9 mol% CaO, and 2.6 mol% P2O5. The selection of glass composition for specific applications is often based on a comprehensive understanding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioactive Glass
Bioactive glasses are a group of surface reactive glass-ceramic biomaterials and include the original bioactive glass, Bioglass®. The biocompatibility and bioactivity of these glasses has led them to be used as implant devices in the human body to repair and replace diseased or damaged bones. Most bioactive glasses are silicate based glasses that are degradable in body fluids and can act as a vehicle for delivering ions beneficial for healing. Bioactive glass is differentiated from other synthetic bone grafting biomaterials (eg. hydroxyapatite, biphasic calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate), in that it is the only one with anti-infective and angiogenic properties. History Discovery and development Larry Hench and colleagues at the University of Florida first developed these materials in 1969 and they have been further developed by his research team at the Imperial College London and other researchers worldwide. Hench began development by submitting a proposal hypothesis to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CaF2
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white insoluble solid. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities. Chemical structure The compound crystallizes in a cubic motif called the fluorite structure. Ca2+ centres are eight-coordinate, being centered in a cube of eight F− centres. Each F− centre is coordinated to four Ca2+ centres in the shape of a tetrahedron. Although perfectly packed crystalline samples are colorless, the mineral is often deeply colored due to the presence of F-centers. The same crystal structure is found in numerous ionic compounds with formula AB2, such as CeO2, cubic ZrO2, UO2, ThO2, and PuO2. In the corresponding anti-structure, called the antifluorite structure, anions and cations are swapped, such as Be2C. Gas phase The gas phase is noteworthy for failing the predictions of VSEPR theory; the molecule is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a derivative o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation. Crystallization occurs in two major steps. The first is nucleation, the appearance of a crystalline phase from either a supercooled liquid or a supersaturated solvent. The second step is known as crystal growth, which is the increase in the size of particles and leads to a crystal state. An important feature of this step is that loose particles form layers at the crystal's surface and lodge themselves into open inconsistencies such as pores, cracks, etc. The majority of minerals and organic molecules crystallize easily, and the resulting crystals are g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Treatment
Thermal treatment is any waste treatment technology that involves high temperatures in the processing of the waste feedstock. Commonly this involves the combustion of waste materials. Systems that are generally considered to be thermal treatment include: *Cement kiln *Gasification *Incineration *Mechanical heat treatment *Pyrolysis *Thermal depolymerization *Waste autoclaves See also *Anaerobic digestion *List of solid waste treatment technologies *Mechanical biological treatment *Waste-to-energy *Pyrolysis The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ... Weblinks * Germany and thermal treatment – an exemplary German companyREMEX Mineralstoff GmbH* Recycling solutions for tar contaminated stratification material – thermal treatment ants.verwertungin Germany {{Waste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Salen Complex
A metal salen complex is a coordination compound between a metal cation and a ligand derived from ''N'',''N''′-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine, commonly called salen. The classical example is salcomine, the complex with divalent cobalt , usually denoted as Co(salen). These complexes are widely investigated as catalysts and enzyme mimics. The metal-free salen compound (H2salen or salenH2) has two phenolic hydroxyl groups. The salen ligand is usually its conjugate base (salen2−), resulting from the loss of protons from those hydroxyl groups. The metal atom usually makes four coordination bonds to the oxygen and nitrogen atoms. Preparation of complexes The salen anion forms complexes with most transition metals. These complexes are usually prepared by the reaction of H2salen ("proligand") with metal precursors containing built-in bases, such as alkoxides, metal amides, or metal acetate. The proligand may also be treated with a metal halide, with or without an added base. Lastl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal–organic Framework
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of compounds consisting of metal ions or cluster compound, clusters coordinated to organic compound, organic ligands to form one-, two-, or three-dimensional structures. The organic ligands included are sometimes referred to as "struts" or "linkers", one example being 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (BDC). More formally, a metal–organic framework is a crystalline material with organic ligands containing potential voids. In most cases for MOFs, the pores are stable during the elimination of the guest molecules (often solvents) and could be refilled with other compounds. Because of this property, MOFs are of interest for the storage of gases such as hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Other possible applications of MOFs are in gas purification, in gas separation, in Groundwater remediation, water remediation, in catalysis, as conducting solids and as supercapacitors. The synthesis and properties of MOFs constitute the primary focus of the disci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
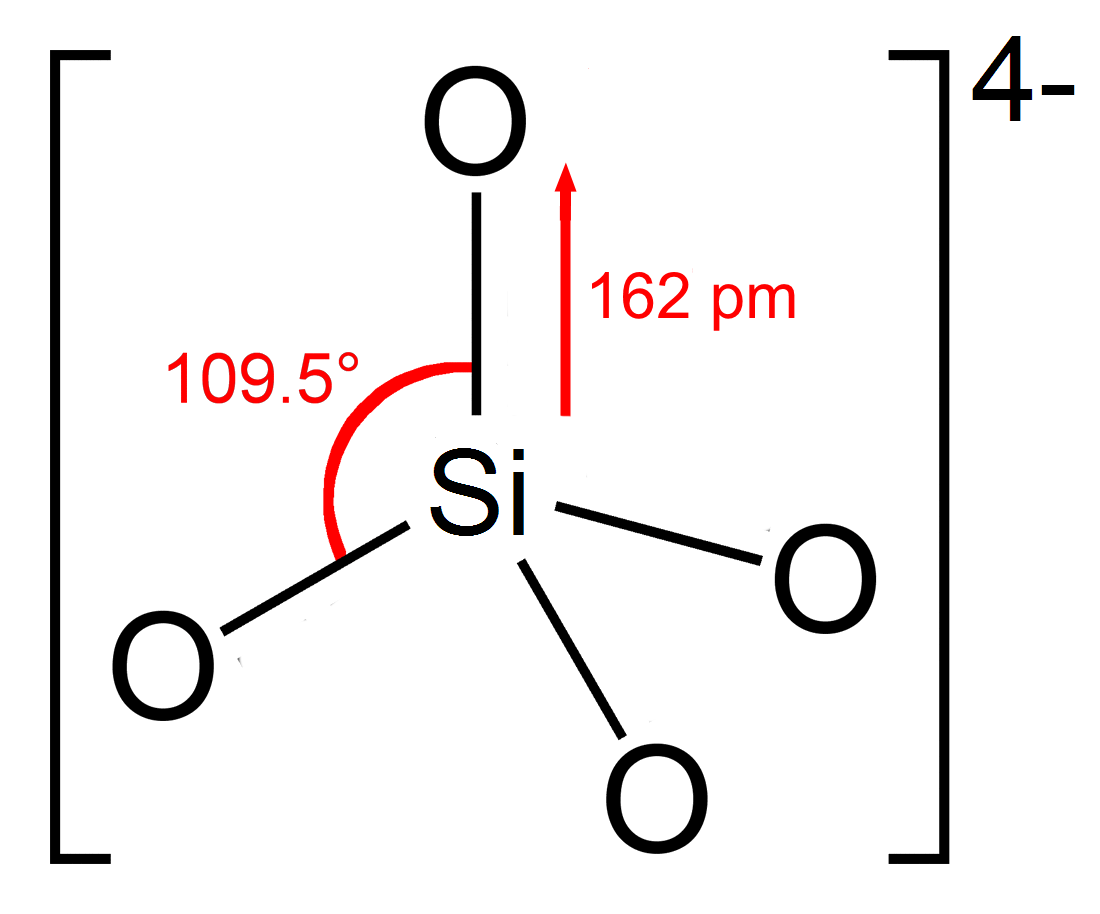
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sol–gel Process
In materials science, the sol–gel process is a method for producing solid materials from small molecules. The method is used for the fabrication of metal oxides, especially the oxides of silicon (Si) and titanium (Ti). The process involves conversion of monomers into a colloidal solution ('' sol'') that acts as the precursor for an integrated network (or ''gel'') of either discrete particles or network polymers. Typical precursors are metal alkoxides. Sol-gel process is used to produce ceramic nanoparticles. Stages In this chemical procedure, a " sol" (a colloidal solution) is formed that then gradually evolves towards the formation of a gel-like diphasic system containing both a liquid phase and solid phase whose morphologies range from discrete particles to continuous polymer networks. In the case of the colloid, the volume fraction of particles (or particle density) may be so low that a significant amount of fluid may need to be removed initially for the gel-like properti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |