|
Synod Of Ingelheim
The Universal Synod of Ingelheim began on June 7, 948 in the then church of Saint Remigius in Ingelheim. Being summoned by Pope Agapetus II its primary goal was to resolve a long running Schism concerning the archiepiscopal see of Reims. The synod was presided by Marinus of Bomarzo, then the Roman Church's librarian. In the run up to the convocation there were two earlier synods, in Verdun in November 947 and in Mouzon in the beginning of 948, both considering the same problem but unable to resolve it. Topics Since 931 the archiepiscopal see was claimed by Hugh of Vermandois and Artald of Reims. Hugh was supported by his uncle, Hugh the Great while Artald was supported by both Louis IV. and Otto the Great. The aforementioned appeared at the synod in person while Hugh the Great was absent and not even substituted for. A clerk of Hugh of Vermandois named Sigbaldus then presented a letter stating that Guy, Bishop of Soissons, Hildegarius of Beauvais, Raoul Iof Laon and the rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Remigius
Remigius (french: Remi or ; – January 13, 533), was the Bishop of Reims and "Apostle of the Franks". On 25 December 496, he baptised Clovis I, King of the Franks. The baptism, leading to about 3000 additional converts, was an important event in the Christianization of the Franks. Because of Clovis's efforts, a large number of churches were established in the formerly pagan lands of the Frankish empire, establishing a distinct Catholic variety of Christianity for the first time in Germanic lands, most of whom had been converted to Arian Christianity. Life Remigius was born, traditionally, at Cerny-en-Laonnois, near Laon, Picardy, into the highest levels of Gallo-Roman society. He is said to have been son of Emilius, count of Laon (who is not otherwise attested) and of Celina, daughter of the Bishop of Soissons, which Clovis had conquered in 487. He studied at Reims and soon became so noted for his learning and sanctity, and his high status, that he was elected Bishop of Reims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose of the institutional act is to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular, those of being in communion with other members of the congregation, and of receiving the sacraments. It is practiced by all of the ancient churches (such as the Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodox churches and the Eastern Orthodox churches) as well as by other Christian denominations, but it is also used more generally to refer to similar types of institutional religious exclusionary practices and shunning among other religious groups. The Amish have also been known to excommunicate members that were either seen or known for breaking rules, or questioning the church, a practice known as shun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaldag
Adaldag (c. 90028 April 988; also Adelgis, Adelger, and Adalgag) was the seventh archbishop of Hamburg-Bremen, from 937 until his death. He was of noble birth, a relation and pupil of Adalward, Bishop of Verden, and became canon of Hildesheim. Otto I made him his chancellor and notary immediately after his accession, and on the death of Archbishop Unni in 936 nominated him to the vacant see. None of the early incumbents of the see ruled for so long, and none did so much for the diocese, though his success was partly the fruit of his predecessors’ labors and of peculiarly favorable circumstances. Under Adaldag the metropolitan see obtained its first suffragans, by the erection of the bishoprics of Ribe, Schleswig, and Århus; and that of the Slavic territories of Aldenburg (today's Oldenburg in Holstein) was also placed under Hamburg. Not to be confused with Oldenburg in Oldenburg, which had formerly belonged to the diocese of Verden. He resisted successfully a renewal of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert (archbishop Of Trier)
Robert, also spelled Ruotbert or Rotbert (died 19 May 956), was the archbishop of Trier from 931 until his death. He played a leading role in the politics of both Germany and France, and especially of the Lotharingian territory in between. He was a patron of scholars and writers and a reformer of monasteries. Rise If Robert was the canonical age of thirty when elected bishop, he would have been born in 901 or earlier. This is most likely, since he was already the chancellor of the see of Trier under his predecessor, Rudgar. (In 938 he granted a lifetime '' precaria'' to his predecessor's niece, Ada, and her two sons.) Robert was originally from the Batavian region, perhaps a member of the Saxon nobility. His brother, Ansfried the elder, was said to have been the count of fifteen counties, including Toxandria, and his nephew's daughter was said to be related to the Unrochinger family. Robert was described by some records as a kinsman of Bruno the Great, a member of the Ottonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick, Archbishop Of Mainz
Frederick (died October 954) was the Archbishop of Mainz from 937, following the late Hildebert, until his death. He was a son of Reginar, Duke of Lorraine. Immediately, Frederick acted as an opponent of Otto the Great, one of the most consistent opponents he faced. In 939, he joined the rebellion of Eberhard III of Franconia, Gilbert of Lorraine, and Henry I of Bavaria. He was imprisoned in Hammelburg for a while. He plotted with Henry to assassinate Otto in Easter 941 in Quedlinburg, but they were discovered and put in captivity in Ingelheim, being released and pardoned only after doing penance at Christmas of that year. Frederick refused to accompany Otto to Italy in 951. He participated in another rebellion with Liudolf, Duke of Swabia, and Conrad, Duke of Lorraine Conrad ( – 10 August 955), called the Red (german: Konrad der Rote), was Duke of Lorraine from 944 until 953. He became the progenitor of the Imperial Salian dynasty. Life He was the son of Werner V (die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regesta Imperii
Papal regesta are the copies, generally entered in special registry volumes, of the papal letters and official documents that are kept in the papal archives. The name is also used to indicate subsequent publications containing such documents, in chronological order, with summaries of their essential contents, for which English diplomatics usually use the term "calendar". Early history The growth of the correspondence of the Holy See is evident even by the end of the 2nd century. Probably from a very early date a copy was made of papal documents before their dispatch, and that the collection of these documents was preserved at the seat of the central administration of the Roman Church. At that time high officials of the Roman State administration, the imperial chancery, the Senate, the consuls, the provincial governments, had all official documents entered in such volumes and preserved in the archives. The books in which these documents were entered were called ''commentarii reges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
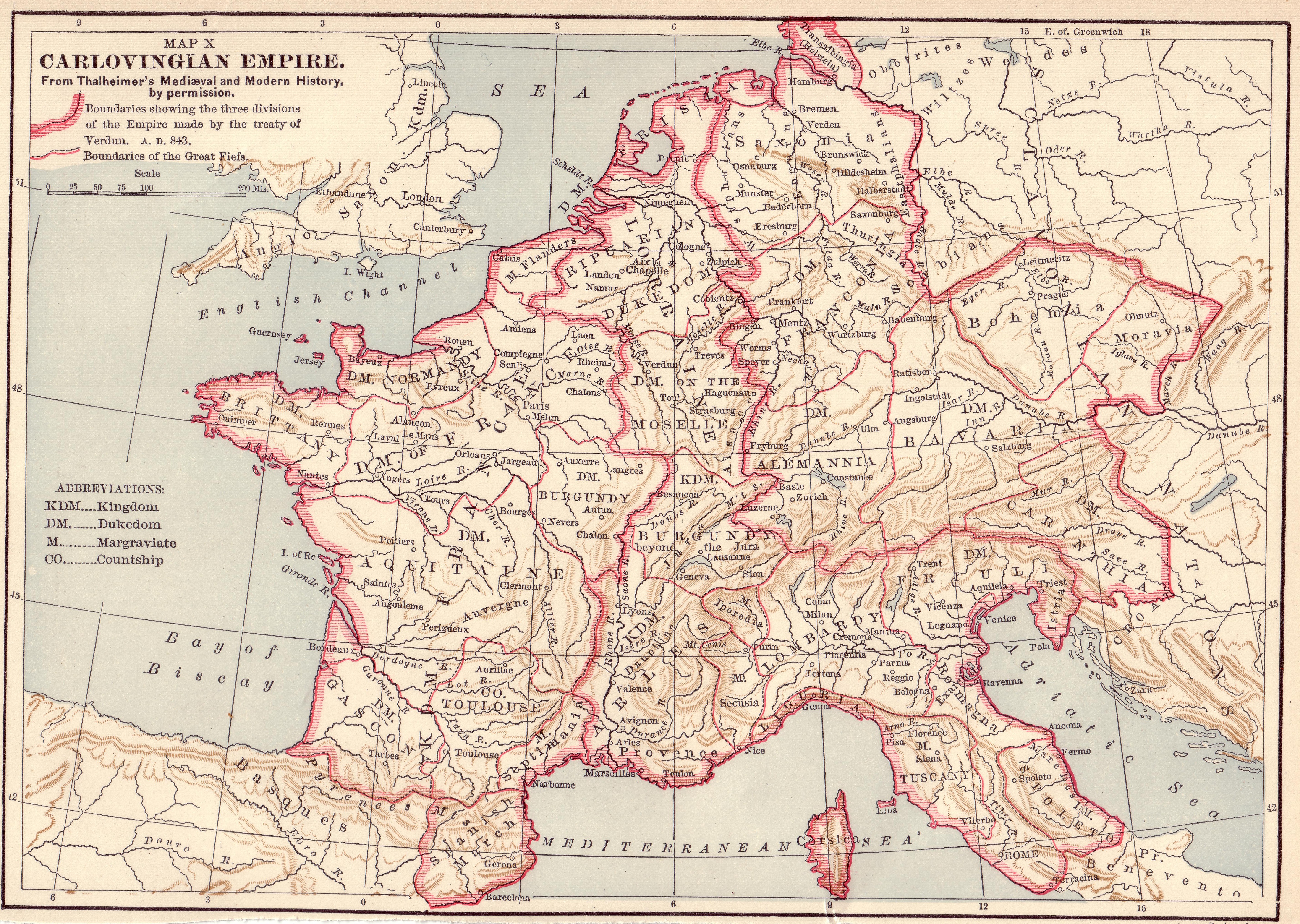
West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. It is considered the first polity in French history. West Francia extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France, but it did not extend as far east. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine, the County and Kingdom of Burgundy (the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace and Provence in the east and southeast for example. It also did not include the Brittany peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing power of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire into three kingdoms. The east–west division, enforced by the Germanic languages, Germanic-Latin language split, "gradually hardened into the establishment of separate kingdoms", with East Francia becoming the Kingdom of Germany and West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France. Terminology The term ''orientalis Francia'' originally referred to Franconia and ''orientales Franci'' to its inhabitants, the ethnic Franks living east of the Rhine. The use of the term in a broader sense, to refer to the eastern kingdom, was an innovation of Louis the German's court. Since eastern Francia could be identified with old Austrasia, the Frankish heartland, Louis's choice of terminology hints at his ambitions. Under his grandson, Arnu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginbrand Of Aarhus
Reginbrand (d. 988) was a bishop of the Ancient See of Aarhus. He was ordained by bishop Adaldag of Hamburg-Bremen in 948 in the first ordination of bishops in the Scandinavian countries. The ordination had the explicit support of the pope who wished to expand Christianity into northern Europe. Adaldag ordained three bishops for the Jutland region; Harald to Slesvig, Ljufdag to Ribe and Reginbrand to Aarhus. The meeting was attended by Otto the Great and Louis IV along with 34 German, French and Danish bishops, in the St. Remigius Kirche in Ingelheim am Rhein. The ordination of Reginbrand is seen as an important point in the history of Jutland and Aarhus. It happened two decades before Harald Bluetooth Harald "Bluetooth" Gormsson ( non, Haraldr Blátǫnn Gormsson; da, Harald Blåtand Gormsen, died c. 985/86) was a king of Denmark and Norway. He was the son of King Gorm the Old and of Thyra Dannebod. Harald ruled as king of Denmark from c. ... officially christened Denma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Schleswig
The List of the Bishops of Schleswig contains the names of the bishops of the see in Schleswig ( da, Slesvig, en, italic=yes, Sleswick) in chronological order. Also Lutheran bishops, who officiated after 1542, superintendents and general superintendents are listed. Note Between 947 and 948 Archbishop Adaldag of Hamburg-Bremen founded the three suffragan dioceses of , Århus, and Ribe (Ripen). In 1104 the Schleswig see was redeployed in ecclesiastical hierarchy to become a suffragan to the Archdiocese of Lund. Since 1542 the bishops were Lutherans, partially even lacking theological qualification but only collecting the prebends from the episcopal estates. Therefore, they were assisted by Lutheran (general) superintendents for the pastoral care. Most parishioners adopted Lutheranism too. After 1624 nobody was invested as Bishop of Schleswig any more. General superintendents fulfilled the pastoral functions as to Lutheran faithful. Between 1854 and 1864 the Lutheran church in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oredo Of Schleswig
Oredo is a Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. Its headquarter is in Benin City. Its capital city is Benin City which also is the capital city of Edo State, Nigeria. Benin City is also the capital city of the Benin Empire. The Oba of Benin, Omo N'Oba Ewuare II's palace is located here. There are four major markets in Oredo Local Government Area; Oba market, New Benin market, New market and Ekiosa market. Residents include the Oba of Benin, Omo N'Oba N'Edo Uku Akpolokpolo Oba Ewuare II and Gabriel Osawaru Igbinedion, the Esama Of Benin Kingdom. Geography It has an area of 249km and a population of 374,671 at the 2006 census. The postal code A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal a ... of the area is 300. Oredo Marriage Registry The Oredo marriage regis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |