|
Synod Of Epaone
The Council of Epaone or Synod of Epaone was held in September 517 at Epaone (or Epao, near the present Anneyron) in the Kingdom of Burgundy, Burgundian Kingdom. It was one of three national councils of bishops held around that time in former Roman Gaul: the council of Agde was held in 506 in the Visigothic Kingdom in the south and the council of Orléans (511), council of Orléans in 511 for the Kingdom of the Franks. The synod enacted the first legislation against wooden altars, forbidding the building of any but stone altars.Hassett, Maurice. "History of the Christian Altar." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 1. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1907. 29 January 2019 It also witnessed to the rise of the practice of mitigation of canonical penance in view of the changing times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anneyron
Anneyron () is a commune in the Drôme department in southeastern France. Population See also *Communes of the Drôme department The following is a list of the 363 communes of the Drôme department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Official site Communes of Drôme Dauphiné {{Drôme-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deaconess
The ministry of a deaconess is, in modern times, a usually non-ordained ministry for women in some Protestant, Oriental Orthodox, and Eastern Orthodox churches to provide pastoral care, especially for other women, and which may carry a limited liturgical role as well. The word comes from the Greek (), for "deacon", which means a servant or helper and occurs frequently in the Christian New Testament of the Bible. Deaconesses trace their roots from the time of Jesus Christ through to the 13th century in the West. They existed from the early through the middle Byzantine periods in Constantinople and Jerusalem; the office may also have existed in Western European churches. There is evidence to support the idea that the diaconate including women in the Byzantine Church of the early and middle Byzantine periods was recognized as one of the major non-ordained orders of clergy. The English separatists unsuccessfully sought to revive the office of deaconesses in the 1610s in their Ams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Church Councils
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church Councils Held In France
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the one, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Century In Francia
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smallest composite number, behind 4; its proper divisors are , and . Since 6 equals the sum of its proper divisors, it is a perfect number; 6 is the smallest of the perfect numbers. It is also the smallest Granville number, or \mathcal-perfect number. As a perfect number: *6 is related to the Mersenne prime 3, since . (The next perfect number is 28 (number), 28.) *6 is the only even perfect number that is not the sum of successive odd cubes. *6 is the root of the 6-aliquot tree, and is itself the aliquot sum of only one other number; the square number, . Six is the only number that is both the sum and the product of three consecutive positive numbers. Unrelated to 6's being a perfect number, a Golomb ruler of length 6 is a "perfect ruler". Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neander
Neander may refer to: ;Surname * August Neander (1789–1850), a German theologian and church historian * Ernst Neumann-Neander (1871–1954), founder of the now defunct Neander motorcycle manufacturer * Joachim Neander (1650–1680), Calvinist teacher * Michael Neander (1529–1581), professor of medicine at the University of Jena * Michael Neander (philologist) (1525–1595), philologist from Sorau, Germany ;Other uses * Neander crater on the Moon. * Neander Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Neander, character from Essay of Dramatick Poesie See also * Neandertal (valley) (formerly Neanderthal) in Germany * Neanderthal Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ag ... References {{surname Surnames of German origin de:Neander fr:Neander it:Neander nl:Neander ru:Neander pt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Josef Von Hefele
Karl Josef von Hefele (March 15, 1809 – June 6, 1893) was a Roman Catholic bishop and theologian of Germany. Biography Hefele was born at Unterkochen in Württemberg and was educated at Tübingen, where in 1839 he became professor-ordinary of Church history and patristics in the Roman Catholic faculty of theology, while collaborating along with William Robinson Clark to his major work. From 1842 to 1845 he sat in the National Assembly of Württemberg. In December 1869 he was enthroned bishop of Rottenburg. His literary activity, which had been considerable, was in no way diminished by his elevation to the episcopate. Among his numerous theological works may be mentioned his well-known edition of the Apostolic Fathers, issued in 1839; his ''Life of Cardinal Ximenes'', published in 1844 as ''Der Cardinal Ximenes und der kirchlichen Zustände Spaniens am Ende des 15. und am Anfange des 16. Jahrhunderts'' (Eng. trans. by John Dalton, 1860); and his still more celebrated ''Concil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harduin
Jean Hardouin ( en, John Hardwin; la, Johannes Harduinus; 1646 – 3 September 1729), was a French classical scholar. He is most known for his theory that most texts from Antiquity were forgeries. Biography He was born at Quimper in Brittany. Having acquired a taste for literature in his father's book-shop, he sought and obtained admission into the order of the Jesuits in around 1662 (when he was 16). In Paris, where he went to study theology. He ultimately became librarian of the Lycée Louis-le-Grand in 1683, and he died there. His first published work was an edition of Themistius (1684), which included no fewer than thirteen new orations. On the advice of Jean Garnier (1612–1681) he undertook to edit the ''Natural History'' of Pliny for the Dauphin series, a task which he completed in five years. Aside from editorial work, he became interested in numismatics, and published several learned works on this subject, all marked by a determination to be different from other int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Maassen
Friedrich Bernard Christian Maassen (24 September 1823 – 9 April 1900, age 76) was a German jurist, professor of law, and Roman Catholic scholar. Biography Maasen was born in Wismar, Mecklenburg-Schwerin. After studying the humanities in his native city, he studied jurisprudence at Jena, Berlin, Kiel and finally Rostock, where in 1849 as an advocate, he took his degree at the university there in 1851. He was active in the constitutional conflict of 1848 between the Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and the Diet, defending the rights of the representatives in three pamphlets, and, together with Franz von Florencourt, founded the anti-revolutionary ''"Norddeutscher Korrespondent"''. Shortly after his graduation he became a convert to Roman Catholicism. Later realizing that, as a Catholic, he was no longer eligible for public office in his native town, he travelled to Bonn, where he devoted himself to academic teaching. Maassen's magnum opus, ''Der Primat des Bischofs von Rom u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Embrun
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Embrun was located in southeastern France, in the mountains of the Maritime Alps, on a route that led from Gap by way of Briançon to Turin. It had as suffragans the Diocese of Digne, Diocese of Antibes and Grasse, Diocese of Vence, Diocese of Glandèves, Diocese of Senez and Diocese of Nice. Its see was the Cathedral of Nôtre Dame in Embrun. The former French Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Embrun was suppressed after the French Revolution. It was replaced, under the Civil Constitution of the Clergy (1790) by a diocese which had the same boundaries of the civil ''departement'' in which it was located. The diocese was called 'Haute-Alpes', with its center at Gap. When the Diocese of Gap was re-established in 1822 it comprised, besides the ancient Diocese of Gap, a large part of the ancient archdiocese of Embrun. The name of the metropolitan see of Embrun, however, had been absorbed in the title of the Archbishop of Aix-en-Provence and Arles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
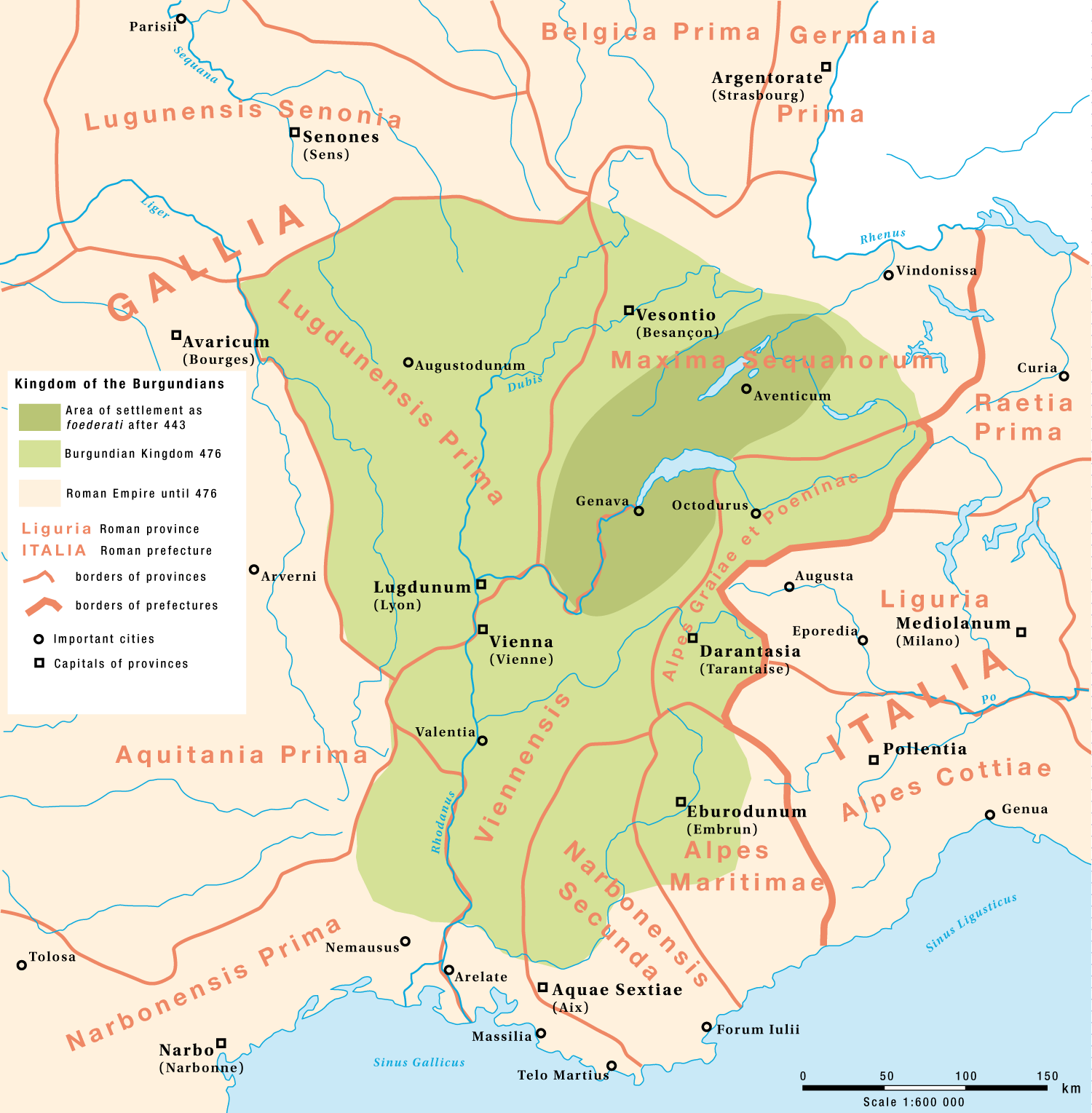
Kingdom Of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France, Italy and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and Lyon. As a political entity, Burgundy existed in a number of forms with different boundaries, notably, when it was divided into Upper and Lower Burgundy and Provence. Two of the entities, the first around the 6th century and the second around the 11th century, were called the Kingdom of Burgundy. At other times were the Kingdom of Provence, the Duchy of Burgundy and the County of Burgundy. Kingdom of the Burgundians (411–534) Burgundy is named after a Germanic tribe of Burgundians who originated in mainland Scandinavia, then settled on the island of Bornholm, whose name in Old Norse was ''Burgundarholmr'' ("Island of the Burgundians"). From there they migrated south through Germanic lands into Roman Gaul and settled in the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Gap
The Diocese of Gap and Embrun (Latin: ''Dioecesis Vapincensis et Ebrodunensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Gap et d'Embrun'') is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of Southern France."Diocese of Gap" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved 10 April 2017 The is , in the city of Gap. It has a co-cathedral< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)