|
Synergetics (Fuller)
Synergetics is the empirical study of systems in transformation, with an emphasis on whole system behaviors unpredicted by the behavior of any components in isolation. R. Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983) named and pioneered the field. His two-volume work ''Synergetics: Explorations in the Geometry of Thinking'', in collaboration with E. J. Applewhite, distills of a lifetime of research into book form. Since systems are identifiable at every scale, Synergetics is necessarily interdisciplinary, embracing a broad range of scientific and philosophical topics, especially in the area of geometry, wherein the tetrahedron features as Fuller's model of the simplest system. Despite mainstream endorsements such as the prologue by Arthur Loeb, and positive dust cover blurbs by U Thant and Arthur C. Clarke, along with the posthumous naming of the carbon allotrope "buckminsterfullerene", Synergetics remains an off-beat subject, ignored for decades by most traditional curricula and academic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law. There is no general agreement on how the terms ''evidence'' and ''empirical'' are to be defined. Often different fields work with quite different conceptions. In epistemology, evidence is what justifies beliefs or what determines whether holding a certain belief is rational. This is only possible if the evidence is possessed by the person, which has prompted various epistemologists to conceive evidence as private mental states like experiences or other beliefs. In philosophy of science, on the other hand, evidence is understood as that which ''Scientific method#Confirmation, confirms'' or ''disconfirms'' Hypothesis#Scientific hypothesis, scientific hypotheses and arbitrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Frame
In architecture and structural engineering, a space frame or space structure ( 3D truss) is a rigid, lightweight, truss-like structure constructed from interlocking struts in a geometric pattern. Space frames can be used to span large areas with few interior supports. Like the truss, a space frame is strong because of the inherent rigidity of the triangle; flexing loads (bending moments) are transmitted as tension and compression loads along the length of each strut. History Alexander Graham Bell from 1898 to 1908 developed space frames based on tetrahedral geometry. Bell's interest was primarily in using them to make rigid frames for nautical and aeronautical engineering, with the tetrahedral truss being one of his inventions. Max Mengeringhausen developed the space grid system called MERO (acronym of ''MEngeringhausen ROhrbauweise'') in 1943 in Germany, thus initiating the use of space trusses in architecture. The commonly used method, still in use has individual tubular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
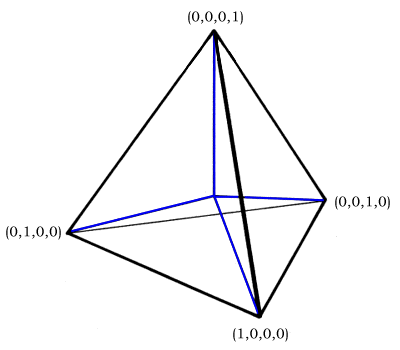
Quadray Coordinates
Quadray coordinates, also known as caltrop, tetray or Chakovian coordinates, were developed by Darrel Jarmusch and others, as another take on simplicial coordinates, a coordinate system using a simplex or tetrahedron as its basis polyhedron.Urner, Kirby. "Teaching Object-Oriented Programming with Visual FoxPro." ''FoxPro Advisor'' (Advisor Media, March, 1999), page 48 ff. Geometric definition The four basis (but not necessarily unit) vectors stem from the center of a regular tetrahedron and go to its four corners. Their coordinate addresses are (1, 0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1, 0) and (0, 0, 0, 1) respectively. These may be positively scaled without rotation (e.g. negation) and linearly combined to span conventional ''XYZ'' space, with at least one of the four coordinates unneeded (set to zero). Pedagogical significance A typical application might set the edges of the basis tetrahedron as unit. The tetrahedron it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesic Dome
A geodesic dome is a hemispherical thin-shell structure (lattice-shell) based on a geodesic polyhedron. The triangular elements of the dome are structurally rigid and distribute the structural stress throughout the structure, making geodesic domes able to withstand very heavy loads for their size. History The first geodesic dome was designed after World War I by Walther Bauersfeld, chief engineer of the Carl Zeiss optical company, for a planetarium to house his planetarium projector. An initial, small dome was patented and constructed by the firm of Dykerhoff and Wydmann on the roof of the Zeiss plant in Jena, Germany. A larger dome, called "The Wonder of Jena", opened to the public in July 1926. Twenty years later, Buckminster Fuller coined the term "geodesic" from field experiments with artist Kenneth Snelson at Black Mountain College in 1948 and 1949. Although Fuller was not the original inventor, he is credited with the U.S. popularization of the idea for which he rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dymaxion House
The Dymaxion House was developed by inventor and architect Buckminster Fuller to address several perceived shortcomings with existing homebuilding techniques. Fuller designed several versions of the house at different times — all of them factory manufactured kits, assembled on site, intended to be suitable for any site or environment and to use resources efficiently. A key design consideration was ease of shipment and assembly. As he did when naming many of his inventions, Fuller combined the words dynamic, maximum, and tension to arrive at the term ''Dymaxion''. History The Dymaxion House was completed in 1930 after two years of development, and redesigned in 1945. Buckminster Fuller wanted to mass-produce a bathroom and a house. His first "Dymaxion" design was based on the design of a grain bin. During World War II, the U.S. Army commissioned Fuller to send these housing units to the Persian Gulf. In 1945, science-fiction writer Robert A. Heinlein placed an order for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Nine (tensegrity Sphere)
Cloud Nine is the name Buckminster Fuller gave to his proposed airborne habitats created from giant geodesic spheres, which might be made to levitate by slightly heating the air inside above the ambient temperature. Geodesic spheres (structures of triangular components arranged to make a sphere) become stronger as they become bigger, because of how they distribute stress over their surfaces. As a sphere gets bigger, the volume it encloses grows much faster than the mass of the enclosing structure itself. Fuller suggested that the mass of a mile-wide geodesic sphere would be negligible compared to the mass of the air trapped within it. He suggested that if the air inside such a sphere were heated even by one degree higher than the ambient temperature of its surroundings, the sphere could become airborne. He calculated that such a balloon could lift a considerable mass, and hence that 'mini-cities' or airborne towns of thousands of people could be built in this way. A Cloud Nine co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy And Life
Research concerning the relationship between the thermodynamic quantity entropy and the evolution of life began around the turn of the 20th century. In 1910, American historian Henry Adams printed and distributed to university libraries and history professors the small volume ''A Letter to American Teachers of History'' proposing a theory of history based on the second law of thermodynamics and on the principle of entropy. The 1944 book ''What is Life?'' by Nobel-laureate physicist Erwin Schrödinger stimulated further research in the field. In his book, Schrödinger originally stated that life feeds on negative entropy, or negentropy as it is sometimes called, but in a later edition corrected himself in response to complaints and stated that the true source is free energy. More recent work has restricted the discussion to Gibbs free energy because biological processes on Earth normally occur at a constant temperature and pressure, such as in the atmosphere or at the bottom of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synergy
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts. The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' from ', , meaning "working together". History In Christian theology, synergism is the idea that salvation involves some form of cooperation between divine grace and human freedom. The words ''synergy'' and ''synergetic'' have been used in the field of physiology since at least the middle of the 19th century: SYN'ERGY, ''Synergi'a'', ''Synenergi'a'', (F.) ''Synergie''; from ''συν'', 'with', and ''εργον'', 'work'. A correlation or concourse of action between different organs in health; and, according to some, in disease. :—Dunglison, Roble''Medical Lexicon''Blanchard and Lea, 1853 In 1896, Henri Mazel applied the term "synergy" to social psychology by writing ''La synergie sociale'', in which he argued that Darwinian theory failed to account of "social synergy" or "social love", a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century. Biography Coxeter was born in Kensington to Harold Samuel Coxeter and Lucy (). His father had taken over the family business of Coxeter & Son, manufacturers of surgical instruments and compressed gases (including a mechanism for anaesthetising surgical patients with nitrous oxide), but was able to retire early and focus on sculpting and baritone singing; Lucy Coxeter was a portrait and landscape painter who had attended the Royal Academy of Arts. A maternal cousin was the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott. In his youth, Coxeter composed music and was an accomplished pianist at the age of 10. Roberts, Siobhan, ''King of Infinite Space: Donald Coxeter, The Man Who Saved Geometry'', Walker & Company, 2006, He felt that mathematics and music were intimately related, outlining his ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |