|
Synchroidae
The Synchroidae are a small family of tenebrionoid beetle Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...s with no vernacular common name. The family consists of three extant genera, '' Mallodrya'', '' Synchroa'', and '' Synchroina'', with a total of nine species., which are found in North America, East Asia and Southeast Asia. The larvae of species of ''Synchroa'' are known to feed on rotting cambium tissue found in deciduous trees, with adults being nocturnal.Ślipinśki, Adam and Lawrence, John F.. "11.16. Synchroidae Lacordaire, 1859". ''Volume 2 Morphology and Systematics (Elateroidea, Bostrichiformia, Cucujiformia partim)'', edited by Willy Kükenthal, Richard A.B. Leschen, Rolf G. Beutel and John F. Lawrence, Berlin, New York: De Gruyter, 2011, pp. 667-669. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchroa
''Synchroa'' is a genus of synchroa bark beetles in the family Synchroidae. There are about six described species in ''Synchroa''. Species These six species belong to the genus ''Synchroa'': * '' Synchroa chinensis'' Nikitsky, 1999 * '' Synchroa elongatula'' Nikitsky, 1999 * '' Synchroa melanotoides'' Lewis, 1895 * '' Synchroa punctata'' Newman, 1838 * '' Synchroa quiescens'' Wickham, 1911 * '' Synchroina tenuipennis'' Fairmaire, 1898 g Data sources: i=ITIS, c=Catalogue of Life, g=GBIF, b=Bugguide.net References Further reading * External links * Tenebrionoidea {{synchroidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenebrionoidea
The Tenebrionoidea are a very large and diverse superfamily of beetles. It generally corresponds to the Heteromera of earlier authors. Taxonomy Tenebrionoidea contains the following families: * Aderidae Winkler 1927 (ant-like leaf beetles) * Anthicidae Latreille 1819 (ant-like flower beetles) *† Apotomouridae Bao et al. 2018 * Archeocrypticidae Kaszab 1964 * Boridae C. G. Thomson 1859 * Chalcodryidae Watt 1974 * Ciidae Leach 1819 (minute tree-fungus beetles) (= Cisidae) * Melandryidae Leach 1815 (false darkling beetles) * Meloidae Gyllenhal 1810 (blister beetles) * Mordellidae Latreille 1802 ( tumbling flower beetles) * Mycetophagidae Leach 1815 ( hairy fungus beetles) * Mycteridae Blanchard 1845 * Oedemeridae Latreille 1810 ( false blister beetles) * Promecheilidae Lacordaire, 1859 * Prostomidae C. G. Thomson 1859 * Pterogeniidae Crowson 1953 * Pyrochroidae Latreille 1807 ( fire-colored beetles, etc.) * Pythidae Solier 1834 * Ripiphoridae Gemminger and Harold 1870 ( wedg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallodrya
''Mallodrya'' is a genus of synchroa bark beetles in the family Synchroidae The Synchroidae are a small family of tenebrionoid beetle Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from .... There is one described species in ''Mallodrya'', ''M. subaenea''. References Further reading * Tenebrionoidea Articles created by Qbugbot {{synchroidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal life-forms; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ladybugs) eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Beetles typically have a particularly hard e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
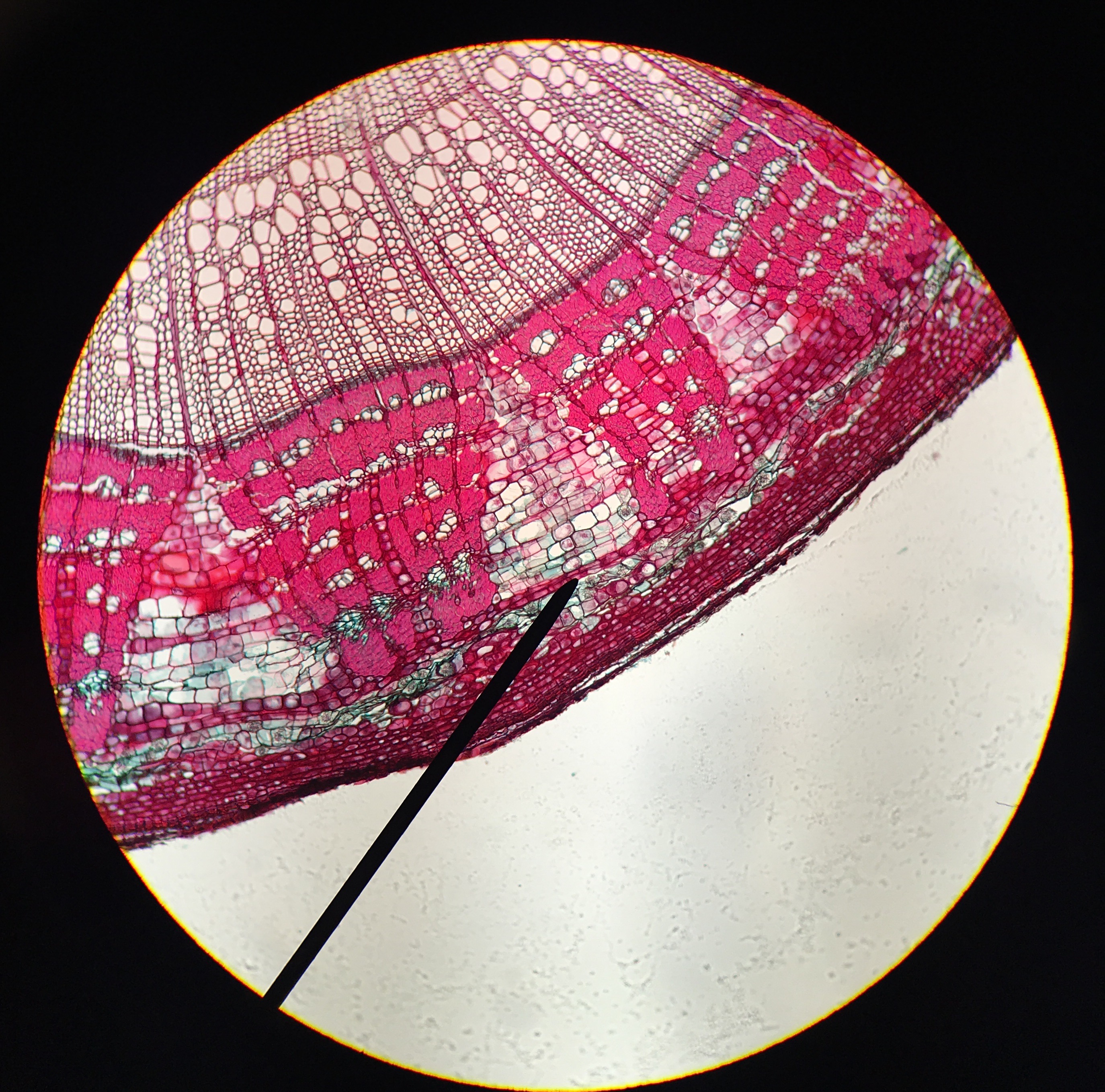
Cambium
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or cooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |