|
Symbolic Execution
In computer science, symbolic execution (also symbolic evaluation or symbex) is a means of analyzing a program to determine what inputs cause each part of a program to execute. An interpreter follows the program, assuming symbolic values for inputs rather than obtaining actual inputs as normal execution of the program would. It thus arrives at expressions in terms of those symbols for expressions and variables in the program, and constraints in terms of those symbols for the possible outcomes of each conditional branch. Finally, the possible inputs that trigger a branch can be determined by solving the constraints. The field of symbolic simulation applies the same concept to hardware. Symbolic computation applies the concept to the analysis of mathematical expressions. Example Consider the program below, which reads in a value and fails if the input is 6. int f() During a normal execution ("concrete" execution), the program would read a concrete input value (e.g., 5) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Control-flow Graph
In computer science, a control-flow graph (CFG) is a representation, using graph notation, of all paths that might be traversed through a program during its execution. The control-flow graph was conceived by Frances E. Allen, who noted that Reese T. Prosser used boolean connectivity matrices for flow analysis before. The CFG is essential to many compiler optimizations and static-analysis tools. Definition In a control-flow graph each node in the graph represents a basic block, i.e. a straight-line sequence of code with a single entry point and a single exit point, where no branches or jumps occur within the block. Basic blocks start with jump targets and end with jumps or branch instructions. Directed edges are used to represent jumps in the control flow. There are, in most presentations, two specially designated blocks: the ''entry block'', through which control enters into the flow graph, and the ''exit block'', through which all control flow leaves. Because of its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Concolic Testing
Concolic testing (a portmanteau of ''concrete'' and ''symbolic'', also known as dynamic symbolic execution) is a hybrid software verification technique that performs symbolic execution, a classical technique that treats program variables as symbolic variables, along a ''concrete execution'' ( testing on particular inputs) path. Symbolic execution is used in conjunction with an automated theorem prover or constraint solver based on constraint logic programming to generate new concrete inputs (test cases) with the aim of maximizing code coverage. Its main focus is finding bugs in real-world software, rather than demonstrating program correctness. A description and discussion of the concept was introduced in "DART: Directed Automated Random Testing" by Patrice Godefroid, Nils Klarlund, and Koushik Sen. The paper "CUTE: A concolic unit testing engine for C", by Koushik Sen, Darko Marinov, and Gul Agha, further extended the idea to data structures, and first coined the term ''concolic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symbolic Simulation
In computer science, a simulation is a computation of the execution of some appropriately modelled state-transition system. Typically this process models the complete state of the system at individual points in a discrete linear time frame, computing each state sequentially from its predecessor. Models for computer programs or VLSI logic designs can be very easily simulated, as they often have an operational semantics which can be used directly for simulation. Symbolic simulation is a form of simulation where many possible executions of a system are considered simultaneously. This is typically achieved by augmenting the domain over which the simulation takes place. A symbolic variable can be used in the simulation state representation in order to index multiple executions of the system. For each possible valuation of these variables, there is a concrete system state that is being indirectly simulated. Because symbolic simulation can cover many system executions in a single simul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abstract Interpretation
In computer science, abstract interpretation is a theory of sound approximation of the semantics of computer programs, based on monotonic functions over ordered sets, especially lattices. It can be viewed as a partial execution of a computer program which gains information about its semantics (e.g., control-flow analysis, control-flow, data-flow analysis, data-flow) without performing all the calculations. Its main concrete application is formal static code analysis, static analysis, the automatic information extraction, extraction of information about the possible executions of computer programs; such analyses have two main usages: * inside compilers, to analyse programs to decide whether certain Optimization (computer science), optimizations or Program transformation, transformations are applicable; * for debugging or even the certification of programs against classes of bugs. Abstract interpretation was formalized by the French computer scientist working couple Patrick Cousot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
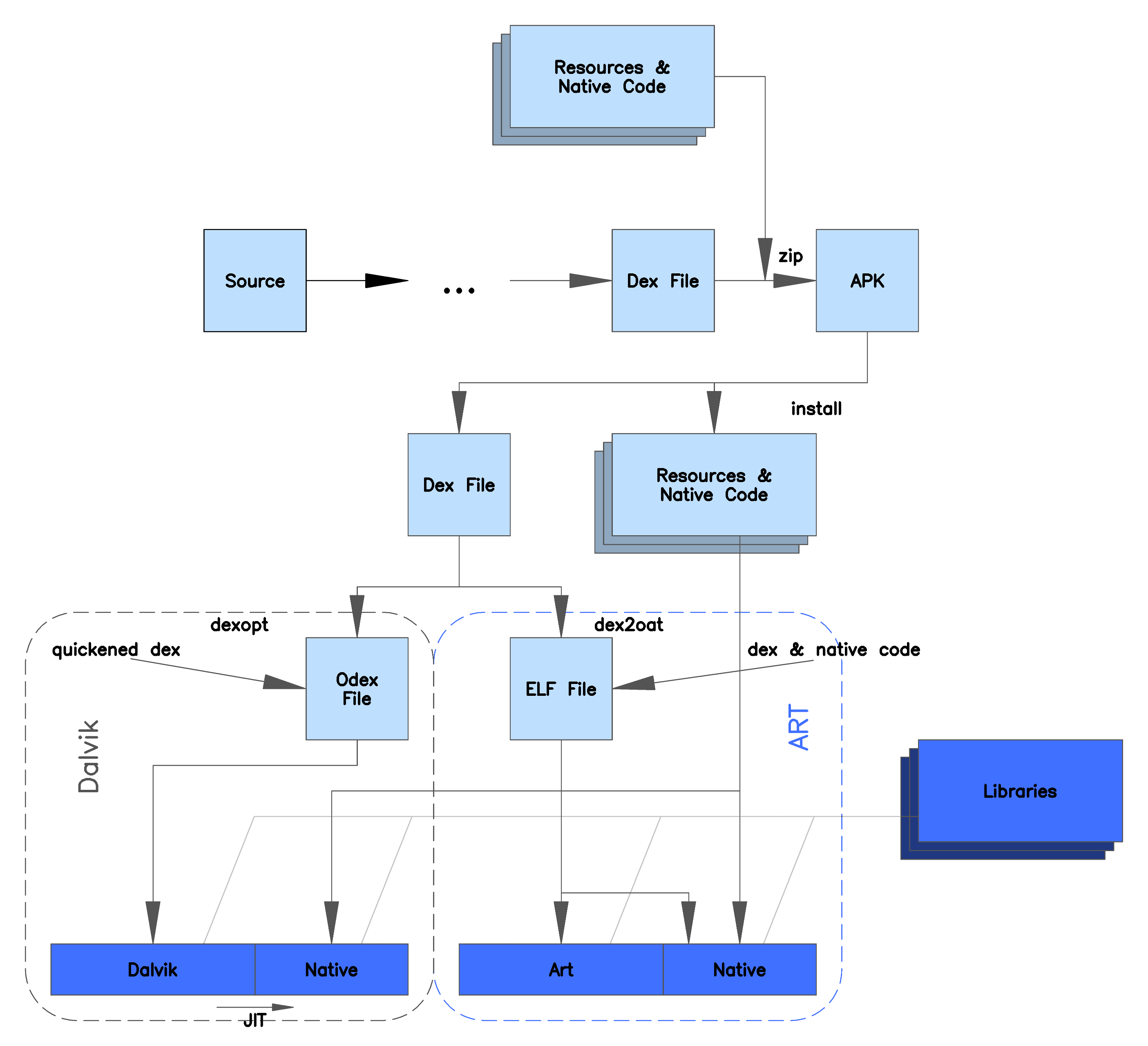
Dalvik (software)
Dalvik is a discontinued process virtual machine (VM) in the Android operating system that executes applications written for Android. (Dalvik bytecode format is still used as a distribution format, but no longer at runtime in newer Android versions.) Dalvik was an integral part of the Android software stack in the (now unsupported) Android versions 4.4 "KitKat" and earlier, which were commonly used on mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers, and more in some devices such as smart TVs and wearables. Dalvik is open-source software, originally written by Dan Bornstein, who named it after the fishing village of Dalvík in Eyjafjörður, Iceland. Programs for Android are commonly written in Java and compiled to bytecode for the Java Virtual Machine, which is then translated to Dalvik bytecode and stored in .dex (''Dalvik EXecutable'') and .odex (''Optimized Dalvik EXecutable'') files; related terms ''odex'' and ''de-odex'' are associated with respective by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ruby (programming Language)
Ruby is a general-purpose programming language. It was designed with an emphasis on programming productivity and simplicity. In Ruby, everything is an object (computer science), object, including primitive data types. It was developed in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro Matsumoto, Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto in Japan. Ruby is interpreted language, interpreted, high-level programming language, high-level, and Dynamic typing, dynamically typed; its interpreter uses garbage collection (computer science), garbage collection and just-in-time compilation. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural programming, procedural, object-oriented programming, object-oriented, and functional programming. According to the creator, Ruby was influenced by Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel (programming language), Eiffel, Ada (programming language), Ada, BASIC, and Lisp (programming language), Lisp. History Early concept According to Matsumoto, Ruby was conceived in 1993. In a 1999 post to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Racket (programming Language)
Racket is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language. The Racket language is a modern dialect of Lisp (programming language), Lisp and a descendant of Scheme (programming language), Scheme. It is designed as a platform for programming language theory, programming language design and implementation. In addition to the core Racket language, ''Racket'' is also used to refer to the family of programming languages and set of tools supporting development on and with Racket. Racket is also used for script (computing), scripting, computer science education, and research. The Racket platform provides an implementation of the Racket language (including a runtime system, libraries, and compiler supporting several compilation modes: machine code, machine-independent, interpreted, and JIT) along with the DrRacket integrated development environment (IDE) written in Racket. Racket is used by the ProgramByDesign outreach program, which aims to tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NET Framework
The .NET Framework (pronounced as "''dot net''") is a proprietary software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It was the predominant implementation of the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) until being superseded by the cross-platform .NET project. It includes a large class library called Framework Class Library (FCL) and provides language interoperability (each language can use code written in other languages) across several programming languages. Programs written for .NET Framework execute in a software environment (in contrast to a computer hardware, hardware environment) named the Common Language Runtime (CLR). The CLR is an process virtual machine, application virtual machine that provides services such as security, memory management, and exception handling. As such, computer code written using .NET Framework is called "managed code". FCL and CLR together constitute the .NET Framework. FCL provides the user interface, data access, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zig (programming Language)
Zig is an imperative, general-purpose, statically typed, compiled system programming language designed by Andrew Kelley. It is free and open-source software, released under an MIT License. A major goal of the language is to improve on the C language (also taking inspiration from Rust), with the intent of being even smaller and simpler to program in, while offering more functionality. The improvements in language simplicity relate to flow control, function calls, library imports, variable declaration and Unicode support. Further, the language makes no use of macros or preprocessor instructions. Features adopted from modern languages include the addition of compile time generic programming data types, allowing functions to work on a variety of data, along with a small set of new compiler directives to allow access to the information about those types using reflective programming (reflection). Like C, Zig omits garbage collection, and has manual memory management. To help eli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
WebAssembly
WebAssembly (Wasm) defines a portable binary-code format and a corresponding text format for executable programs as well as software interfaces for facilitating communication between such programs and their host environment. The main goal of WebAssembly is to facilitate high-performance applications on web pages, but it is also designed to be usable in non-web environments. It is an open standard intended to support any language on any operating system, and in practice many of the most popular languages already have at least some level of support. Announced in and first released in , WebAssembly became a World Wide Web Consortium recommendation on 5 December 2019 and it received the ''Programming Languages Software Award'' from ACM SIGPLAN in 2021. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) maintains the standard with contributions from Mozilla, Microsoft, Google, Apple, Fastly, Intel, and Red Hat. History The name WebAssembly is intended to suggest bringing assembly language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |