|
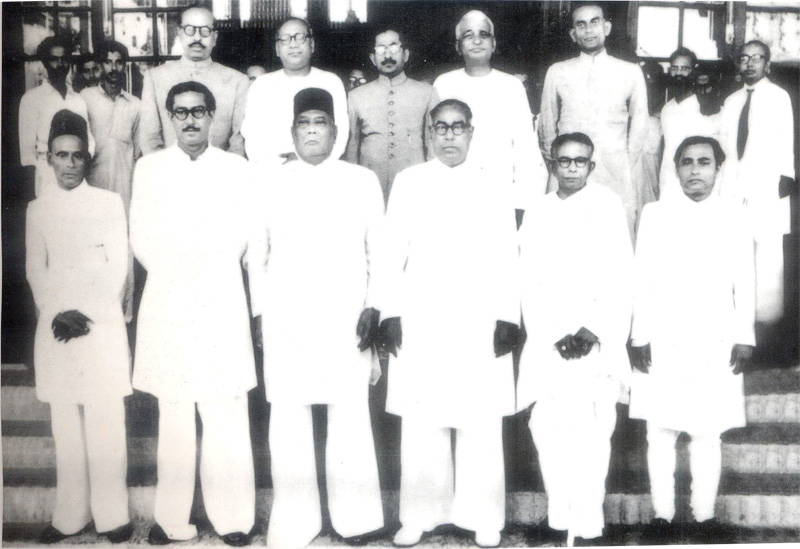
Syed Azizul Huq
Syed Azizul Huq ( bn, সৈয়দ আজিজুল হক; 1 October 1912 – 11 February 1992), also known by his daak naam Nanna Mia ( bn, নান্না মিঞা), was a Bangladeshi politician and former Member of Parliament from Barisal-2 in 1986 and 1988 Bangladeshi general election. He was a member of the Provincial Council of East Pakistan, Minister of Commerce and Minister of Industry. Early life and education Azizul Huq was born on 1 October 1912 to a Bengali Muslim family known as the Syeds of Chakhar in the Sharif Bari of Chakhar, Banaripara, then located under the Backergunge District of the Bengal Province. His father, Syed Motahar Husayn, was descended from Syed Ataullah, who had inherited jagirs in the Barisal region after marrying Dulal Bibi, the daughter of Mir Qutb. He graduated from Khalishakotha School in 1928 and later from Brojomohun College. In 1932, he received his Bachelor of Arts degree from Calcutta Islamia College. During his time th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jatiya Sangsad
The Jatiya Sangsad ( bn, জাতীয় সংসদ, lit=National Parliament, translit=Jatiyô Sôngsôd), often referred to simply as the ''Sangsad'' or JS and also known as the House of the Nation, is the supreme legislative body of Bangladesh. The current parliament of Bangladesh contains 350 seats, including 50 seats reserved exclusively for women. Elected occupants are called Member of Parliament, or MP. The 11th National Parliamentary Election was held on 30 December 2018. Elections to the body are held every five years, unless a parliament is dissolved earlier by the President of Bangladesh. The leader of the party (or alliance of parties) holding the majority of seats becomes the Prime Minister of Bangladesh, and so the head of the government. The President of Bangladesh, the ceremonial head of state, is chosen by Parliament. Since the December 2008 national election, the current majority party is the Awami League led by Sheikh Hasina. Etymology The Constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, starting in the early 13th century, wherein the powers to govern and collect tax from an estate was granted to an appointee of the state.Jāgīrdār system: INDIAN TAX SYSTEM Encyclopædia Britannica (2009) The tenants were considered to be in the servitude of the jagirdar. There were two forms of jagir, one being conditional and the other unconditional. The conditional jagir required the governing family to maintain troops and provide their service to the state when asked. The land grant w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1970 Pakistani General Election
General elections were held in Pakistan on 7 December 1970 to elect members of the National Assembly. They were the first general elections since the independence of Pakistan and ultimately the only ones held prior to the independence of Bangladesh. Voting took place in 300 general constituencies, of which 162 were in East Pakistan and 138 in West Pakistan. A further thirteen seats were reserved for women (seven of which were in East Pakistan and six of which were in West Pakistan), who were to be elected by members of the National Assembly. The elections were a fierce contest between two social democratic parties, the west-based Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP) and the east-based Awami League. The Awami League was the sole major party in the east wing, while in the west wing, the PPP faced severe competition from the conservative factions of Muslim League, the largest of which was Muslim League (Qayyum), as well as Islamist parties like Jamaat-e-Islami (JI), Jamiat Ulema-e-I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayub Khan (general)
Muhammad Ayub Khan (Urdu: ; 14 May 1907 – 19 April 1974), was the second President of Pakistan. He was an army general who seized the presidency from Iskander Mirza in a coup in 1958, the first successful coup d'état in the country's history. Popular demonstrations and labour strikes supported by the protests in East Pakistan ultimately led to his forced resignation in 1969. During his presidency, differences between East and West Pakistan arose to an enormous degree, that ultimately led to the Independence of East Pakistan. Trained at the British Royal Military College, Ayub Khan fought in World War II as a colonel in the British Indian Army before deciding to transfer to the Pakistan Army in the aftermath of the partition of India in 1947. His assignments included command of the 14th Division in East-Bengal. He was elevated to become the first native Commander-in-Chief of the Pakistan Army in 1951 by Prime Minister Liaquat Ali Khan, succeeding General Douglas Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Pakistan
The Constitution of Pakistan ( ur, ), also known as the 1973 Constitution, is the supreme law of Pakistan. Drafted by the government of Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, with additional assistance from the country's Pakistani political parties, opposition parties, it was approved by the Parliament of Pakistan, Parliament on 10 April and ratified on 14 August 1973. The Constitution is intended to guide Pakistan's law, political culture, and system. It sets out the state's outline, the fundamental rights of the population, the state's law and orders, and also the structure and establishment of the institutions and the armed forces. The first three chapters establish the rules, mandate, and Separation of powers, separate powers of the three branches of the government: a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature; an executive branch governed by the Prime Minister of Pakistan, Prime Minister as chief executive; and an apex federal judiciary headed by Supreme Court of Pakistan, Supreme Court. The Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Hussain Sarkar
Abu Hussain Sarkar ( bn, আবু হোসেন সরকার; 1894 – 17 April 1969) was a Bengali politician and lawyer. He served as the fourth chief minister of East Pakistan. Under his ministry, the Bangla Academy was inaugurated and 21 February was recognised as '' Shohid Dibosh'' in memory of the Bengali Language Movement. Early life and education Sarkar was born in 1894, to a Bengali Muslim family in Sadullapur, Gaibandha, which was then under the Rangpur District of the Bengal Presidency. He was involved in the Swadeshi movement, which disrupted his education and led to his arrest in 1911. He was later released and passed his matriculation in 1915. He then studied further, gaining a Bachelor of Law degree. Career Sarkar started his law practice in the Rangpur bar. He joined the Indian National Congress but left it over differences. In 1935, he joined A K Fazlul Huq's Krishak Praja Party. He contested in the 1937 Bengal legislative elections, winning in the Gaib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Front (East Pakistan)
The United Front was a coalition of political parties in East Bengal which contested and won Pakistan's first provincial general election to the East Bengal Legislative Assembly. The coalition consisted of the Awami Muslim League, the Krishak Praja Party, the Ganatantri Dal (Democratic Party) and Nizam-e-Islam. The coalition was led by three major Bengali populist leaders- A. K. Fazlul Huq, Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy and Maulana Bhashani. The election resulted in a crushing defeat for the Muslim League. Veteran student leader of East Pakistan Khaleque Nawaz Khan defeated sitting Prime Minister of East Pakistan Mr. Nurul Amin in Nandail Constituency of Mymensingh district and created history in political arena. Nurul Amin's crushing defeat to a 27 years old young Turk of United Front effectively eliminated the Muslim League from political landscape of the then East Pakistan. United Front parties securing a landslide victory and gaining 223 seats in the 309-member assembly. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barisal District
Barisal District, officially spelled Barishal District from April 2018, is a district in south-central Bangladesh, formerly called Bakerganj district, established in 1797. Its headquarters are in the city of Barisal, which is also the headquarters of Barisal Division.''About Barisal'' Local Government Engineering Department, Local Government Division, Ministry of Local Government, Rural Development & Cooperatives; retrieved 14 May 2014. History Barisal District is a district in southern Bangladesh and is also the headquarter of Barisal Division. Barisal District traces its origins to Bakerganj district which was established in 1797. It was placed in |
1954 East Bengal Legislative Assembly Election
Legislative elections were held in East Bengal between 8 and 12 March 1954, the first since Pakistan became an independent country in 1947. The opposition United Front led by the Awami League and Krishak Sramik Party won a landslide victory with 223 of the 309 seats.Nair, p165 The Muslim League Chief Minister of East Pakistan Nurul Amin was defeated in his own constituency by Khaleque Nawaz Khan by over 7,000 votes, with all the Muslim League ministers losing their seats.Nair, p167 Background The Bengal Assembly had been elected as part of the provincial elections in British India in 1946. Its term was extended several times, with around 34 seats left vacant as by-elections were not held. Electoral system The East Bengal Legislative Assembly consisted of 309 seats, of which 228 were reserved for Muslims, 36 for scheduled castes, 12 for women (nine Muslims, one general and two scheduled caste), two for Buddhists and one for Christians.Nair, p166 There were also 30 general sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolkata Municipal Corporation
Kolkata Municipal Corporation (abbreviated KMC; also Calcutta Municipal Corporation) is the local government of the Indian city of Kolkata, the state capital of West Bengal. This civic administrative body administers an area of . Its motto, ''Purosri Bibardhan'', is inscribed on its emblem in Bengali script. Geography The Kolkata Municipal Corporation is located at in Kolkata, West Bengal. Department Structure Kolkata Municipal Corporation was established in 1876. Under the guidance of the first Minister of Local Self-Government in Bengal, Sir Surendranath Banerjee, the Calcutta Municipal Act of 1923 made provision for the enfranchisement of women and the election of a Mayor of Kolkata annually. Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das was the first Mayor of Kolkata Municipal Corporation with Subhas Chandra Bose as his Chief Executive Officer. Later mayors include Deshapriya Jatindra Mohan Sengupta, Subhas Chandra Bose, Bidhan Chandra Roy, Nalini Ranjan Sarkar, Abul Kasem Fazlul Haque, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Law
Bachelor of Laws ( la, Legum Baccalaureus; LL.B.) is an undergraduate law degree in the United Kingdom and most common law jurisdictions. Bachelor of Laws is also the name of the law degree awarded by universities in the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong S.A.R., Macau S.A.R., Malaysia, Bangladesh, India, Japan, Pakistan, Kenya, Ghana, Nigeria, South Africa, Botswana, Israel, Brazil, Tanzania, Zambia, and many other jurisdictions. In the United States, the Bachelor of Laws was also the primary law degree historically, but was phased out in favour of the Juris Doctor degree in the 1960s. Canadian practice followed suit in the first decade of the 21st century, phasing out the Bachelor of Laws for the Juris Doctor. History of academic degrees The first academic degrees were all law degrees in medieval universities, and the first law degrees were doctorates. The foundations of the first universities were the glossators of the 11th century, which were also schools of law. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta Islamia College
Maulana Azad College, formerly Islamia College, is a public institute of liberal arts, commerce and science in India, located in central Kolkata, West Bengal, India. The college is fully government-administered. It is located near the junction of Rafi Ahmed Kidwai Road and SN Banerjee Road, popularly called "Lotus crossing". It is affiliated to the University of Calcutta. The college also offers numerous courses in languages associated with Muslim culture, such as Urdu, Arabic, and Persian. The college offers both post-graduate (English, Zoology and Urdu) and under-graduate courses in a number of subjects in the three streams of arts, science and commerce. It is accredited an ('A') grade by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC). The college has been given the status of 'Centre of Potential for Excellence' by UGC. The college has produced distinguished and notable nationalists, politicians, educationists, judges, ministers, novelists, IAS, IPS and WBCS officers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)