|
Swee Lay Thein
Swee Lay Thein is a Malaysian haematologist and physician-scientist who is Senior Investigator at the National Institutes of Health. She works on the pathophysiology of haemoglobin disorders including sickle cell disease and thalassemia. Early life and education Thein was born in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. She studied medicine in both Malaysia and the United Kingdom. She graduated from the University of Malaya in 1976. She specialised in hematology at the Royal Postgraduate Medical School and the Royal Free Hospital. She moved to Oxford, where she worked at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Molecular Hematology Unit in the Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine and the John Radcliffe Hospital. She held various positions at Oxford, including a MRC Clinical Training position, a Wellcome Trust senior fellowship and an honorary consultancy. Research and career In 2000 Thein joined King's College London as a Professor of Molecular Haematology. She was made Clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Malaya
The University of Malaya ( ms, Universiti Malaya, UM; abbreviated as UM or informally the Malayan University) is a public research university located in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. It is the oldest and highest ranking Malaysian institution of higher education according to two international ranking agencies, and also the only university in the post-independent Malaya. The university has graduated six prime ministers of Malaysia, and other political, business, and cultural figures of national prominence. The predecessor of the university, King Edward VII College of Medicine, was established on 28 September 1905 in Singapore, then a territory of the British Empire. In October 1949, the merger of the King Edward VII College of Medicine and Raffles College created the university. Rapid growth during its first decade caused the university to organize as two autonomous divisions on 15 January 1959, one located in Singapore and the other in Kuala Lumpur. In 1960, the government of Malaysia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weatherall Institute Of Molecular Medicine
The MRC Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine at the University of Oxford is a research institute located at the John Radcliffe Hospital in Oxford. Founded in 1989 by Sir David Weatherall, the institute focuses on furthering our understanding of clinical medicine at a molecular level. It was one of the first institutes of its kind in the world to be dedicated to research in this area. The MRC WIMM is part of the Medical Sciences Division at the University of Oxford. It hosts over 500 staff and students from seven different departments working on five key areas of research: immunology and infection, haematology, rare diseases, cancer biology, stem cells and developmental biology. The institute houses the MRC Human Immunology Unit, MRC Molecular Haematology Unit and MRC WIMM Centre for Computational Biology. A third of the researchers are clinically qualified and have joint posts with the departments at the Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Research Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage Disequilibrium
In population genetics, linkage disequilibrium (LD) is the non-random association of alleles at different loci in a given population. Loci are said to be in linkage disequilibrium when the frequency of association of their different alleles is higher or lower than what would be expected if the loci were independent and associated randomly. Linkage disequilibrium is influenced by many factors, including selection, the rate of genetic recombination, mutation rate, genetic drift, the system of mating, population structure, and genetic linkage. As a result, the pattern of linkage disequilibrium in a genome is a powerful signal of the population genetic processes that are structuring it. In spite of its name, linkage disequilibrium may exist between alleles at different loci without any genetic linkage between them and independently of whether or not allele frequencies are in equilibrium (not changing with time). Furthermore, linkage disequilibrium is sometimes referred to as gamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCL11A
B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL11A'' gene. Function The ''BCL11A'' gene encodes for a regulatory C2H2 type zinc-finger protein, that can bind to the DNA. Five alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode distinct isoforms, have been reported. The protein associates with the SWI/SNF complex, that regulates gene expression via chromatin remodeling. ''BCL11A'' is highly expressed in several hematopoietic lineages, and plays a role in the switch from γ- to β-globin expression during the fetal to adult erythropoiesis transition. Furthermore, BCL11A is expressed in the brain, where it forms a protein complex with CASK to regulate axon outgrowth and branching. In the neocortex, BCL11A binds to the ''TBR1'' regulatory region and inhibits the expression of ''TBR1''. Clinical significance The corresponding ''Bcl11a'' mouse gene is a common site of retroviral integration in myeloid leukemia, and may functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately – new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Trait Locus
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation. Definition A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a region of DNA which is associated with a particular phenotypic trait, which varies in degree and which can be attributed to polygenic effects, i.e., the product of two or more genes, and their environment. . These QTLs are often found on different chromosomes. The number of QTLs which explain variation in the phenotypic trait indicates the genetic architecture of a trait. It may indicate that plant height is controlled by many genes of small effect, or by a few genes of large effect. Typically, QTLs underlie continuous traits (those traits which vary continuously, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage Analysis
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separated onto different chromatids during chromosomal crossover, and are therefore said to be more ''linked'' than markers that are far apart. In other words, the nearer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the chance of recombination between them, and the more likely they are to be inherited together. Markers on different chromosomes are perfectly ''unlinked'', although the penetrance of potentially deleterious alleles may be influenced by the presence of other alleles, and these other alleles may be located on other chromosomes than that on which a particular potentially deleterious allele is located. Genetic linkage is the most prominent exception to Gregor Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. The first experiment to demonstrate l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globin
The globins are a superfamily of heme-containing globular proteins, involved in binding and/or transporting oxygen. These proteins all incorporate the globin fold, a series of eight alpha helical segments. Two prominent members include myoglobin and hemoglobin. Both of these proteins reversibly bind oxygen via a heme prosthetic group. They are widely distributed in many organisms. Structure Globin superfamily members share a common three-dimensional fold. This 'globin fold' typically consists of eight alpha helices, although some proteins have additional helix extensions at their termini. Since the globin fold contains only helices, it is classified as an all-alpha protein fold. The globin fold is found in its namesake globin families as well as in phycocyanins. The globin fold was thus the first protein fold discovered (myoglobin was the first protein whose structure was solved). Helix packaging The eight helices of the globin fold core share significant nonlocal st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilization (or eleventh week gestational age) and continues until birth. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their final anatomical location. Etymology The word ''fetus'' (plural ''fetuses'' or '' feti'') is related to the Latin '' fētus'' ("offspring", "bringing forth", "hatching of young") and the Greek "φυτώ" to plant. The word "fetus" was used by Ovid in Metamorphoses, book 1, line 104. The predominant British, Irish, and Commonwealth spelling is ''fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foetal Haemoglobin
Fetal hemoglobin, or foetal haemoglobin (also hemoglobin F, HbF, or α2γ2) is the main oxygen carrier protein in the human fetus. Hemoglobin F is found in fetal red blood cells, and is involved in transporting oxygen from the mother's bloodstream to organs and tissues in the fetus. It is produced at around 6 weeks of pregnancy and the levels remain high after birth until the baby is roughly 2–4 months old. Hemoglobin F has a different composition from the adult forms of hemoglobin, which allows it to bind (or attach to) oxygen more strongly. This way, the developing fetus is able to retrieve oxygen from the mother's bloodstream, which occurs through the placenta found in the mother's uterus. In the newborn, levels of hemoglobin F gradually decrease and reach adult levels (less than 1% of total hemoglobin) usually within the first year, as adult forms of hemoglobin begin to be produced. Diseases such as beta thalassemias, which affect components of the adult hemoglobin, can del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
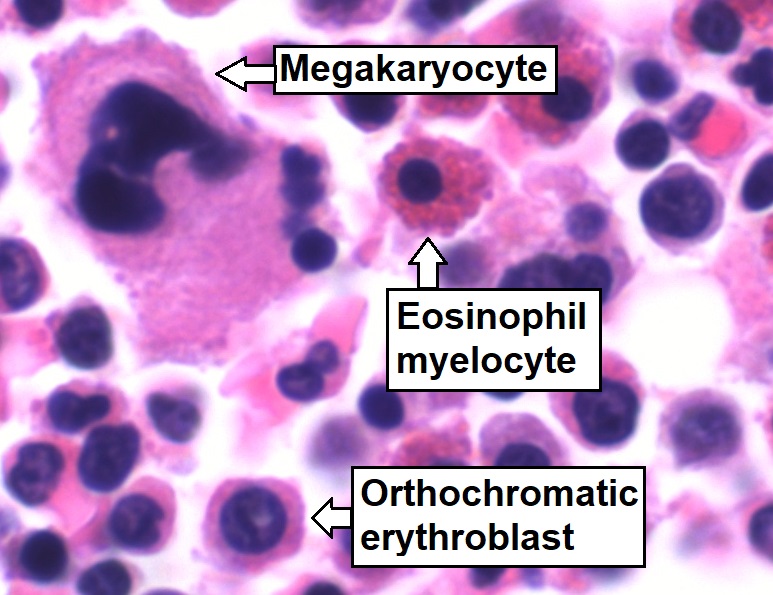
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |