|
Swedish–Geatish Wars
The Swedish-Geatish wars refer to semi-legendary 6th century battles between Swedes and Geats that are described in the Anglo-Saxon epic ''Beowulf''. Little has survived of such battles in the Norse sagas, and later 11th century-13th century wars between Swedes and Geats, notably involving the Geatish clans House of Stenkil and House of Sverker, are referred to as Swedish civil wars. The first war in ''Beowulf'' The Anglo-Saxon epic relates that the Swedes did not keep the peace when the Geatish king Hreðel had died, because the Swedish king Ongenþeow's sons (i.e. Ohthere and Onela) had grown up and were eager to fight. The Geats under their new king Hæþcyn captured the Swedish queen, but old king Ongenþeow saved her, at a hill fort called Hrefnesholt, although they lost her gold. Ongenþeow killed Hæþcyn, and besieged the Geats at Hrefnesholt. The Geats were, however, rescued by Hygelac, Hæþcyn's brother, who arrived the next day with reinforcements. Having lost t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Brávellir
The Battle of Brávellir or the Battle of Bråvalla was a legendary battle, said to have taken place c.770, that is described in the sagas as taking place on the Brávellir between Sigurd Hring, king of Sweden and the Geats of Västergötland, and his uncle Harald Wartooth, king of Denmark and the Geats of Östergötland. Sources The battle is recounted in several sources such as the Norse sagas '' Hervarar saga ok Heiðreks'', '' Bósa saga ok Herrauðs'' and '' Sǫgubrot af nokkrum fornkonungum'', but it is most extensively described in the nationalistic Danish history ''Gesta Danorum'' by Saxo Grammaticus. Cause Harald had inherited Sweden from his maternal grandfather Ivar Vidfamne, but ruled Denmark and East Götaland, whereas his subordinate king, Sigurd Hring, was the ruler of Sweden and West Götaland. According to legend, Harald realised that he was now old and might die of old age and therefore not go to Valhalla. He consequently asked Sigurd if he would let him leave th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
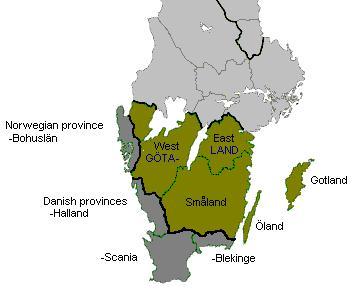
Götaland
Götaland (; also '' Geatland'', '' Gothia'', ''Gothland'', ''Gothenland'' or ''Gautland'') is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border. Götaland once consisted of petty kingdoms, and their inhabitants were called ''Gautar'' in Old Norse. However, the term mainly referred to the population of modern Västergötland. It is agreed that these were the same as the ''Geats'', the people of the hero Beowulf in England's national epic, ''Beowulf''. The modern state of Sweden started forming when some provinces of Götaland gradually became more and more politically intertwined with those of Svealand. This process can be traced back to at least the 11th century, and would continue for several hundred years. Other parts of modern Götaland were at that time either Danish or Norwegian. The province of Smålan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetic Licence
Artistic license (alongside more contextually-specific derivative terms such as poetic license, historical license, dramatic license, and narrative license) refers to deviation from fact or form for artistic purposes. It can include the alteration of grammar or language, or the rewording of pre-existing text. History The artistic license may also refer to the ability of an artist to apply smaller distortions, such as a poet ignoring some of the minor requirements of grammar for poetic effect. For example, Mark Antony's "Friends, Romans, Countrymen, lend me your ears" from Shakespeare's ''Julius Caesar'' would technically require the word "and" before "countrymen", but the conjunction "and" is omitted to preserve the rhythm of iambic pentameter (the resulting conjunction is called an asyndetic tricolon). Conversely, on the next line, the end of "I come to bury Caesar, not to praise him" has an extra syllable because omitting the word "him" would make the sentence unclear, but ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-legendary Kings Of Sweden
The legendary kings of Sweden () according to legends were rulers of Sweden and the Swedes who preceded Eric the Victorious and Olof Skötkonung, the earliest reliably attested Swedish kings. Though the stories of some of the kings may be embellished tales of local rulers or chiefs that actually existed. For example, Hygelac (500 A.D.) is believed to have historical basis due to his name being attested in Frankish, English, Danish and Icelandic sources. But the historicity of most legendary kings remains impossible to verify due to a lack of sources.Dick, Harrison 2011 http://blog.svd.se/historia/2011/10/13/varfor-jag-inte-tror-pa-sagokungar/ The modern Swedish monarchy considers Eric the Victorious to have been the first King of Sweden. In medieval Swedish lists of kings, the figure generally represented as the first king of Sweden is Olof Skötkonung, the first Christian king of Sweden and the first Swedish king to mint coins. The earlier kings are for the most part only attes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hreðel
Hrethel ( ang, Hrēðel; gem-x-proto, Hrōþilaz, italic=no) is a king of the Geats''. Name Hrethel's name appears with both the root vowel and and with both the consonant (i.e. the phoneme , pronounced in Old English) and (which would ordinarily represent the phoneme ). This is thought to be due to an early manuscript of ''Beowulf'' writing the root vowel using the early graphs (for the vowel resulting from the i-mutation of Common Germanic ) and (for the phoneme , pronounced ). Later scribes misread the former as and failed to recognise that the latter represented the sound rather than . The name also appears as a genitive weak noun, in the half-line "þæt is Hrǣdlan lāf" ('that is Hrǣdla's bequest'). Rendered in ordinary Late West Saxon spelling and in nominative form, this form of the name would presumably have been *''Hrēðla''. Role in ''Beowulf'' Hrethel is married to a sister or daughter of Swerting (Hygelac is the nefa of Swerting) and he has three sons: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geatish King
Geatish kings ( la, Rex Getarum/Gothorum; sv, Götakungar), ruling over the provinces of Götaland (Gautland/Geatland), appear in several sources for early Swedish history. Today, most of them are not considered historical. This list follows the generally accepted identification between the names Götar (Swedish language, modern Swedish), Gautar (Old Norse) and Geatas (Old English language, Old English), which is based both on tradition, literary sources and on etymology. However, unlike some translations it does not identify this tribe with the Goths. Both Old Norse and Old English records clearly separate the Geats from the Goths, while still depicting them as closely related to each other. From the Middle Ages until 1974, the king of Sweden claimed the title King of the Geats as "King of Sweden and Geats/Goths" or King of the Goths, "Rex Sweorum et Gothorum". Monarchy of Denmark, Danish monarchs used the similar title "King of the Goths" from 1362 until 1972. Legendary kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Literature
Old English literature refers to poetry and prose written in Old English in early medieval England, from the 7th century to the decades after the Norman Conquest of 1066, a period often termed Anglo-Saxon England. The 7th-century work ''Cædmon's Hymn'' is often considered as the oldest surviving poem in English, as it appears in an 8th-century copy of Bede's text, the ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People''. Poetry written in the mid 12th century represents some of the latest post-Norman examples of Old English. Adherence to the grammatical rules of Old English is largely inconsistent in 12th-century work, and by the 13th century the grammar and syntax of Old English had almost completely deteriorated, giving way to the much larger Middle English corpus of literature. In descending order of quantity, Old English literature consists of: sermons and saints' lives; biblical translations; translated Latin works of the early Church Fathers; chronicles and narrative history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
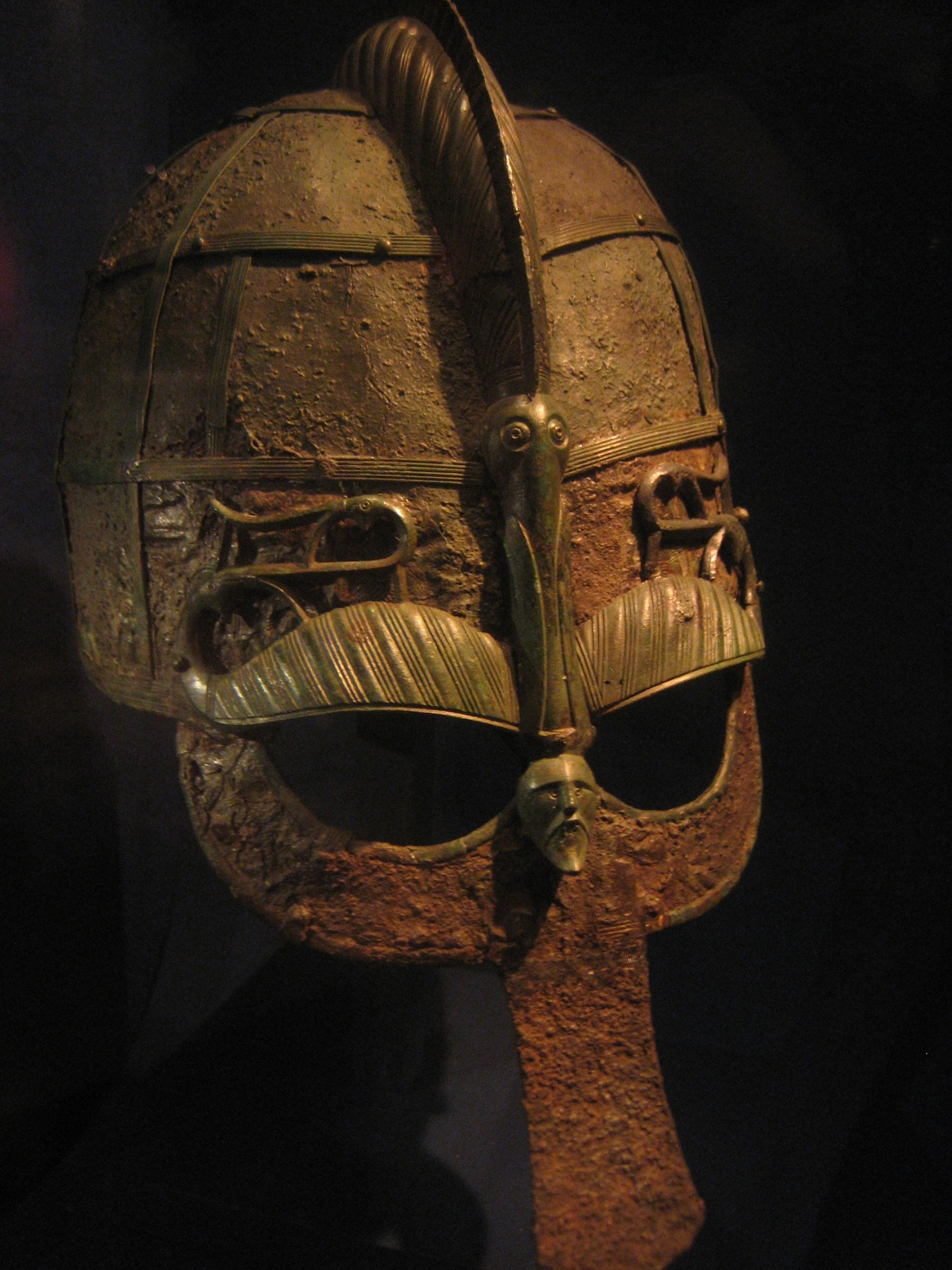
Vendel Era Helmet (950)
Vendel is a village at Tierp Municipality in Uppland, Sweden. The village overlooks Vendelsjön, a long inland stretch of water near the Vendel river which has its confluence with the river Fyris. Vendel was the site of an ancient royal estate, part of ''Uppsala öd'', a network of royal estates meant to provide income for the medieval Swedish kings. A large number of archaeological finds have been found here, which have given their name to the Vendel Period. Vendel Church (''Vendels kyrka'') was probably begun to be built in Romanesque style during the latter half of the 13th century. Around 1450, the church was vaulted with brick vaults. The church is most noted for its murals by Johannes Iwan who worked in Uppland during the 15th century. Archaeological research In 1881 to 1883, several excavations by Swedish archaeologist Hjalmar Stolpe (1841–1905) revealed 14 graves in and just beyond the south-east corner of the churchyard. Several of the burials were contained in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendel Era Helmet (942)
Vendel is a village at Tierp Municipality in Uppland, Sweden. The village overlooks Vendelsjön, a long inland stretch of water near the Vendel river which has its confluence with the river Fyris. Vendel was the site of an ancient royal estate, part of ''Uppsala öd'', a network of royal estates meant to provide income for the medieval Swedish kings. A large number of archaeological finds have been found here, which have given their name to the Vendel Period. Vendel Church (''Vendels kyrka'') was probably begun to be built in Romanesque style during the latter half of the 13th century. Around 1450, the church was vaulted with brick vaults. The church is most noted for its murals by Johannes Iwan who worked in Uppland during the 15th century. Archaeological research In 1881 to 1883, several excavations by Swedish archaeologist Hjalmar Stolpe (1841–1905) revealed 14 graves in and just beyond the south-east corner of the churchyard. Several of the burials were contained in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Sverker
The House of Sverker were a powerful political force in medieval Sweden, contesting for royal power. Their origins were in Östergötland. After the extinction of the House of Stenkil and the ascension of Sverker I of Sweden in 1130, a civil war commenced. In the beginning, there were several pretenders, of whom Sverker I emerged as victorious, for a time. The antagonists in long run were finally the House of Sverker in Östergötland and the House of Eric in Västergötland and Uppland (Saint Eric was killed and buried in the latter province, others in the dynasty were buried in Varnhem Abbey in the former province as later also Birger Jarl was, a relative to the dynasty), which alternated on the throne for several generations, until in the 1220s the Eric dynasty got the upper hand, and the Sverker dynasty became extinct (at least in the male line). As usual in medieval succession rivalries, the outcome combined the blood of rival lines, as in 1250 Valdemar of the Folkungs (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |