|
Swedish Volunteer Corps (Winter War)
The Swedish Volunteer Corps ( sv, Svenska frivilligkåren) during the Winter War numbered 9,640 officers and men. Sweden was officially non-belligerent during the war, so the Corps was used by Finland. The Swedish volunteers were in the front lines in the northern Salla area starting from February 28, 1940. Their losses included 33 dead, 10 missing, 50 wounded, and 130 disabled by frostbite. There were also 25 aircraft that served in the Swedish Voluntary Air Force, F19. Swedish volunteers also defended Turku in an anti-aircraft battery. By the end of the war, the Volunteer Corps was composed of 8,260 Swedes, plus 725 Norwegians, and 600 Danes. They demonstrated a strong Nordic unity that was symbolized in their "four brother hands" insignia which represented Finland, Sweden, Norway, and Denmark. Commanders *1940: General Ernst Linder Organization Swedish Volunteer Corps - ''Svenska Frivilligkåren'' ** I. stridsgruppen (Lieutenant-Colonel Magnus Dyrssen, Captain Carl C:so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
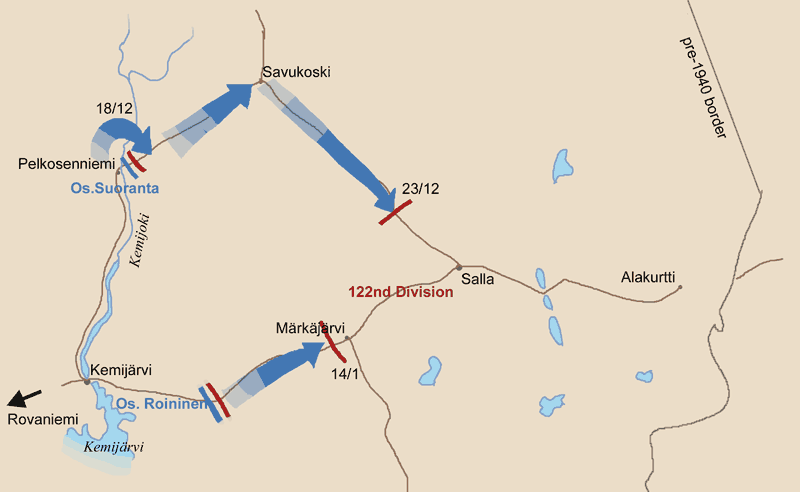
Salla Phase2
Salla (''Kuolajärvi'' until 1936) ( smn, Kyelijävri) is a municipality of Finland, located in Lapland. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . The nearby settlement of Sallatunturi is home to the Salla Ski Resort. History Salla is in the Eastern Lapland and as a border area was affected by the Second World War. Red Army troops invaded Finland at Salla during the Winter War but were stopped by the Finnish Army (see Battle of Salla). Parts of the municipality were ceded to the Soviet Union after the war. The ceded part is sometimes called "Old Salla" or ''Vanha Salla''. During the Continuation War the old town of Salla was on the Soviet side of the border. The German XXXVI Corps attacked the Soviet positions in an operation code-named '' Polarfuchs''. With the help of the Finnish 6th Division it managed to occupy all of the ceded territories. At the end of the war the German troops were pushed out of Lap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
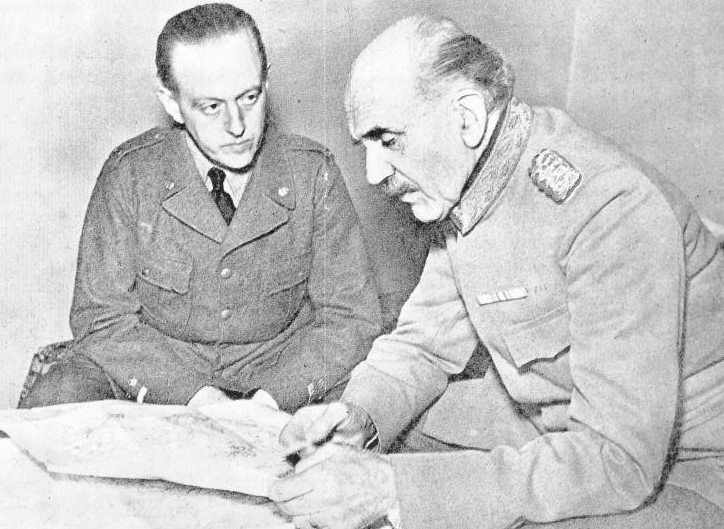
Viking Tamm
Lieutenant General Viking Sebastian Henricsson Tamm (21July 1896 – 25November 1975) was a Swedish Army officer. In addition to the years he served in the Swedish Army, Tamm led a group of Swedish officers who developed the Ethiopian military school's officer training (1934–36 and 1945–46) and he was a volunteer in the Winter War in Finland in 1940 commanding the II. Battlegroup of the Swedish Volunteer Corps. Back in Sweden he eventually became Chief of the Army Staff and the General Staff Corps (1948–53) and commander of the I Military District (1953–61) before retiring as a Lieutenant General in 1961. Early life Tamm was born on 21 July 1896 in Stockholm, Sweden, the son of the bank director and later finance minister Henric Tamm and his wife Louise Tham. Career Tamm was commissioned as an officer with the rank of second lieutenant in 1916 and was assigned to Svea Life Guards (I 1). He was promoted to lieutenant in 1919. Tamm attended the Royal Swedish Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden And The Winter War
The Winter War was fought in the four months following the Soviet Union's invasion of Finland on November 30, 1939. This took place three months after the German invasion of Poland that triggered the start of World War II in Europe. Sweden did not become actively involved in the conflict, but did indirectly support Finland. The Swedish Volunteer Corps provided 9,640 officers and men. The Swedish Voluntary Air Force also provided 25 aircraft that destroyed twelve Soviet aircraft while only losing six planes with only two to actual enemy action and four to accidents. Sweden also provided a portion of the weapons and equipment used by the Finns throughout the war. Background to Swedish policy According to the dominant view in Sweden's foreign ministry, Finland's foreign policy had, since its independence and 1918 civil war, been "unsteady and adventurous". In addition, Finland's domestic politics were viewed with great suspicion by Swedish Social Democrats. After the Socialists' de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet-Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1944, as part of World War II.; sv, fortsättningskriget; german: Fortsetzungskrieg. According to Finnish historian Olli Vehviläinen, the term 'Continuation War' was created at the start of the conflict by the Finnish government, to justify the invasion to the population as a continuation of the defensive Winter War and separate from the German war effort. He titled the chapter addressing the issue in his book as "Finland's War of Retaliation". Vehviläinen asserted that the reality of that claim changed when the Finnish forces crossed the 1939 frontier and started annexation operations. The US Library of Congress catalogue also lists the variants War of Retribution and War of Continuation (see authority control)., group="Note" In Soviet historiography, the war was called the Finnish Front of the Great Patriotic War.. Alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morjärv
Morjärv (Kalix language: ''morajärv'') is a locality situated in Kalix Municipality, Norrbotten County, Sweden Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ... with 201 inhabitants in 2010. References Populated places in Kalix Municipality Norrbotten {{Norrbotten-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergeant (Sweden And Finland)
Sergeant (''kersantti'' in Finnish) is a Swedish (OR6) and Finnish (OR5) military rank above överfurir in Sweden and alikersantti in Finland; and below översergeant in Sweden and ylikersantti in Finland.http://www.goarmy.com/about/ranks_and_insignia.jsp USA enlisted ranks Finland Enlisted NCOs usually start from sergeant (OR5), in infantry platoons sergeants may serve as squad leaders (6-8 men), deputy platoon commanders (~30 men) or rarely even a platoon commanders, or at company level as Company Sergeant Majors. In the Finnish army, conscripts are first trained for 2 months in basic training and about 30% are selected for junior NCO training (''aliupseerikoulu'' or ''AUK''), which lasts 4 months. Upon completion, they are promoted to ''alikersantti'' and posted to companies for 6 months as squad leaders. Usually, the best-performing ''alikersantti'' in a platoon is promoted to ''kersantti'' a few weeks before discharge, and in meantime acts as a deputy platoon commander as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Överstelöjtnant
Lieutenant colonel (LtCol) ( sv, Överstelöjtnant, Övlt) is a field grade officer rank in the Swedish Armed Forces, just above the rank of major and just below the rank of colonel. It is equivalent to the naval rank of commander in the Swedish Navy. History Lieutenant colonel denotes the closest below the colonel's regimental officer rank. The term is almost as old as colonel and initially referred to his closest aides. Nowadays, the lieutenant colonel in a regiment in most armies has become the colonel's closest assistant. In Sweden, in peacetime he is sometimes battalion commander; in war as well as during major troop exercises he often commands regiments. Lieutenant colonels serves as commanding officer of a battalion or second-in-command of a brigade. As staff officers, lieutenant colonels serves as section heads, heads of function or qualified staff officer. Lieutenant colonels belong to skill levels C (Advanced) or D (Expert). Rank insignia Collar patches File:OF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private (rank)
A private is a soldier, usually with the lowest rank in many armies. Soldiers with the rank of Private may be conscripts or they may be professional (career) soldiers. The term derives from the medieval term "private soldiers" (a term still used in the British Army), contrasting mercenary soldiers and denoting individuals who were either exclusively hired, conscripted, or mustered into service by a feudal nobleman commanding a battle group of an army. Asia Indonesia In Indonesia, this rank is referred to as '' Tamtama'' (specifically ''Prajurit'' which means soldier), which is the lowest rank in the Indonesian National Armed Forces and special Police Force. In the Indonesian Army, Indonesian Marine Corps, and Indonesian Air Force, "Private" has three levels, which are: Private (''Prajurit Dua''), Private First Class (''Prajurit Satu''), and Master Private (''Prajurit Kepala''). After this rank, the next promotion is to Corporal. File:prada pdh ad.png, Private (''Prajurit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fänrik
''Fänrik'' () ( en, second lieutenant in the Swedish Army/Air Force, Acting sub-lieutenant in the Navy) is a company grade officer rank. In the army/airforce, it ranks above sergeant and below lieutenant. In the navy, it ranks above sergeant and below sub-lieutenant. It is equivalent to the specialist officers rank of . means standard-bearer and has been used as a name for the lowest officer rank in the Swedish infantry since the 16th century, with the exception of the years 1835–1914. Army/Air Force/Navy (second lieutenant) is a rank in the Swedish Army, Swedish Air Force and in the Swedish Navy (Coastal Artillery 1902–2000, Amphibious Corps 2000–present). History was already during the latter part of the Middle Ages the name of the officer at the or , who carried the colour. Later the was relieved of this duty, and he became the closest man of the (commander) or captain. During the 17th century, the lieutenant, who had previously been the assistant of the , rose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Armed Forces
The Swedish Armed Forces ( sv, Försvarsmakten, "the Defense Force") is the government agency that forms the armed forces of Sweden, tasked with the defense of the country as well as with promoting Sweden's wider interests, supporting international peacekeeping, and providing humanitarian aid. It consists of the Swedish Army, the Swedish Air Force and the Swedish Navy, as well as a military reserve force, the Home Guard. Since 1994, all Swedish military branches are organized within a single unified government agency, headed by the Supreme Commander, even though the individual services maintain their distinct identities. The Swedish Armed Forces is made up of 23,600 active personnel, 11,200 military reserves, 24,000 Home Guard and 5,200 conscripts (set to increase to 8,000 conscripts by 2024) as of 2022. Units of the Swedish Armed Forces are currently on deployment in several international operations either actively or as military observers, including Afghanistan as part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Air Force
The Swedish Air Force ( sv, Svenska flygvapnet or just ) is the air force branch of the Swedish Armed Forces. History The Swedish Air Force was created on 1 July, 1926 when the aircraft units of the Army and Navy were merged. Because of the escalating international tension during the 1930s the Air Force was reorganized and expanded from four to seven squadrons. World War II When World War II broke out in 1939 further expansion was initiated and this substantial expansion was not finished until the end of the war. Although Sweden never entered the war, a large air force was considered necessary to ward off the threat of invasion and to resist pressure through military threats from the great powers. By 1945 the Swedish Air Force had over 800 combat-ready aircraft, including 15 fighter divisions. A major problem for the Swedish Air Force during World War II was the lack of fuel. Sweden was surrounded by countries at war and could not rely on imported oil. Instead domestic oil s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |