|
Swains Island
Swains Island (; Tokelauan: ''Olohega'' ; Samoan: ''Olosega'' ) is a remote coral atoll in the Tokelau Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. The island is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute between Tokelau and the United States, which has administered it as part of American Samoa since 1925. Privately owned by the family of Eli Hutchinson Jennings since 1856, Swains Island was used as a copra plantation until 1967. It has not been permanently inhabited since 2008 but has often been visited by members of the Jennings family, scientific researchers, and amateur radio operators.Swains Island Charles A. Veley, 27 November 2008.2012 Swains Island DXpedition /ref> [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Pedro Fernandes De Queirós
Pedro Fernandes de Queirós ( es, Pedro Fernández de Quirós) (1563–1614) was a Portuguese navigator in the service of Spain. He is best known for his involvement with Spanish voyages of discovery in the Pacific Ocean, in particular the 1595–1596 voyage of Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira, and for leading a 1605–1606 expedition that crossed the Pacific in search of Terra Australis. Early life Queirós (or Quirós as he signed) was born in Évora, Portugal in 1563. As the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós entered Spanish service as a young man and became an experienced seaman and navigator. In April 1595 he joined Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira on his voyage to colonize the Solomon Islands, serving as chief pilot. After Mendaña's death in October 1595, Queirós is credited with taking comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Noun
In linguistics, a collective noun is a word referring to a collection of things taken as a whole. Most collective nouns in everyday speech are not specific to one kind of thing. For example, the collective noun "group" can be applied to people ("a group of people"), or dogs ("a group of dogs"), or objects ("a group of stones"). Some collective nouns are specific to one kind of thing, especially terms of venery, which identify groups of specific animals. For example, "pride" as a term of venery always refers to lions, never to dogs or cows. Other examples come from popular culture such as a group of owls, which is called a "parliament". Different forms of English handle verb agreement with collective count nouns differently. For example, users of British English generally accept that collective nouns take either singular or plural verb forms depending on context and the metonymic shift that it implies. Derivation Morphological derivation accounts for many collective words and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales. Terminology The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japan, still dedicates a single factory ship for the industry. The vessels used by aboriginal whaling communities are much smaller and are used for various purposes over the course of the year. The ''whale catcher'' was developed during the age of steam, and then driven by diesel engines throughout much of the twentieth century. It was designed with a harpoon gun mounted at its bow and was fast enough to chase and catch rorquals such as the fin whale. At first, whale catchers either brought the whales they killed to a whaling station, a settlement ashore where the carcasses could be processed, or to its factory ship anchored in a sheltered bay or inlet. With the later development of the slipway at the ship's stern, whale catchers were able t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Australia. Divided into two parts, ''Tahiti Nui'' (bigger, northwestern part) and ''Tahiti Iti'' (smaller, southeastern part), the island was formed from volcanic activity; it is high and mountainous with surrounding coral reefs. Its population was 189,517 in 2017, making it by far the most populous island in French Polynesia and accounting for 68.7% of its total population. Tahiti is the economic, cultural and political centre of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity and an overseas country of the French Republic. The capital of French Polynesia, Papeete, is located on the northwest coast of Tahiti. The only international airport in the region, Faaā International Airport, is on Tahiti near Papeete. Tahiti was originally settled by Polyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachusetts. It is the only such consolidated town-county in Massachusetts. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,255, making it the least populated county in Massachusetts. Part of the town is designated the Nantucket CDP, or census-designated place. The region of Surfside on Nantucket is the southernmost settlement in Massachusetts. The name "Nantucket" is adapted from similar Algonquian names for the island, but is very similar to the endonym of the native Nehantucket tribe that occupied the region at the time of European settlement. Nantucket is a tourist destination and summer colony. Due to tourists and seasonal residents, the population of the island increases to at least 50,000 during the summer months. The average sale price ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby Jones. Funding for the original expedition was requested by President John Quincy Adams in 1828; however, Congress would not implement funding until eight years later. In May 1836, the oceanic exploration voyage was finally authorized by Congress and created by President Andrew Jackson. The expedition is sometimes called the U.S. Ex. Ex. for short, or the Wilkes Expedition in honor of its next appointed commanding officer, United States Navy Lieutenant Charles Wilkes. The expedition was of major importance to the growth of science in the United States, in particular the then-young field of oceanography. During the event, armed conflict between Pacific islanders and the expedition was common and dozens of natives were killed in act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Peacock (1813)
USS ''Peacock'' was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the War of 1812. ''Peacock'' was authorized by Act of Congress 3 March 1813, laid down 9 July 1813, by Adam and Noah Brown at the New York Navy Yard, and launched on 19 September 1813. The ''Peacock'' served in the War of 1812, capturing twenty ships. Subsequently, the ship served in the Mediterranean Squadron, and in the "Mosquito Fleet," which fought to suppress Caribbean piracy. She patrolled the South American coast during the colonial wars of independence. The ''Peacock'' was decommissioned in 1827 and broken up in 1828 to be rebuilt as USS ''Peacock'', intended as an exploration ship. It sailed as part of the United States Exploring Expedition in 1838. ''Peacock'' ran aground and broke apart on the Columbia Bar without loss of life in 1841. War of 1812 During the War of 1812, ''Peacock'' made three cruises under the command of Master Commandant Lewis Warrington. Departing New York 12 March 1814, sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German '' Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
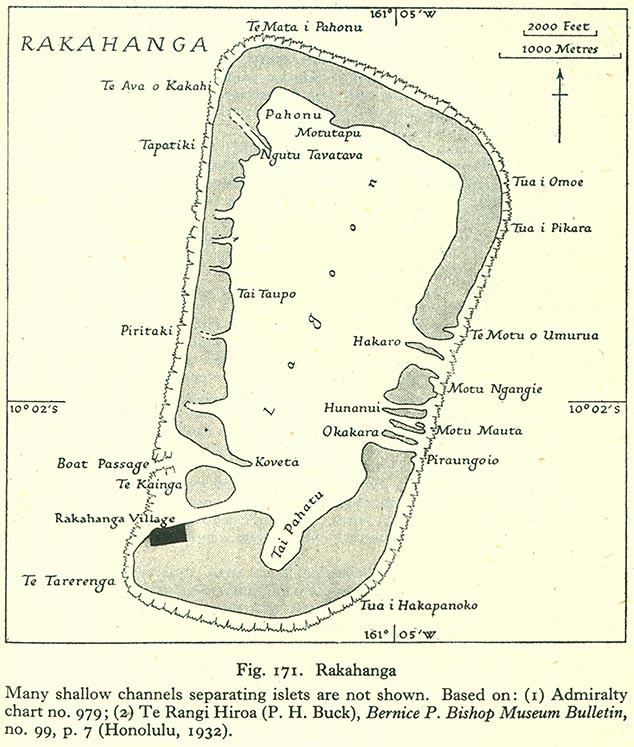
Rakahanga
Rakahanga is part of the Cook Islands, situated in the central-southern Pacific Ocean. The unspoilt atoll is from the Cook Islands' capital, Rarotonga, and lies south of the equator. Its nearest neighbour is Manihiki which is just away. Rakahanga's area is . Its highest point is approximately 5 metres above sea level. The population was 83 in the 2016 Census of Population & Dwellings. Since 2014 Rakahanga's power has been 100% solar generated. The Rakahanga-Manihiki language differs from Cook Islands Maori. Geography There are four main islands and seven motus or islets in the Rakahanga lagoon. The northern island is divided into three: Tetukono in the north and northeast, Tetaha Kiraro in the west, and Paerangi in the southwest; while the southern island is Rakahanga. The motus are: on the east, Te Motu o Umurua, Akaro, Motu Ngangie, Huananui, Motu Mahuta and Motu Okakara; while on the southwest side the islet of Te Kainga guards the widest passage into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and '' longitude'' are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or '' normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absolute measure of ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)