|
Suwannee Valley Culture
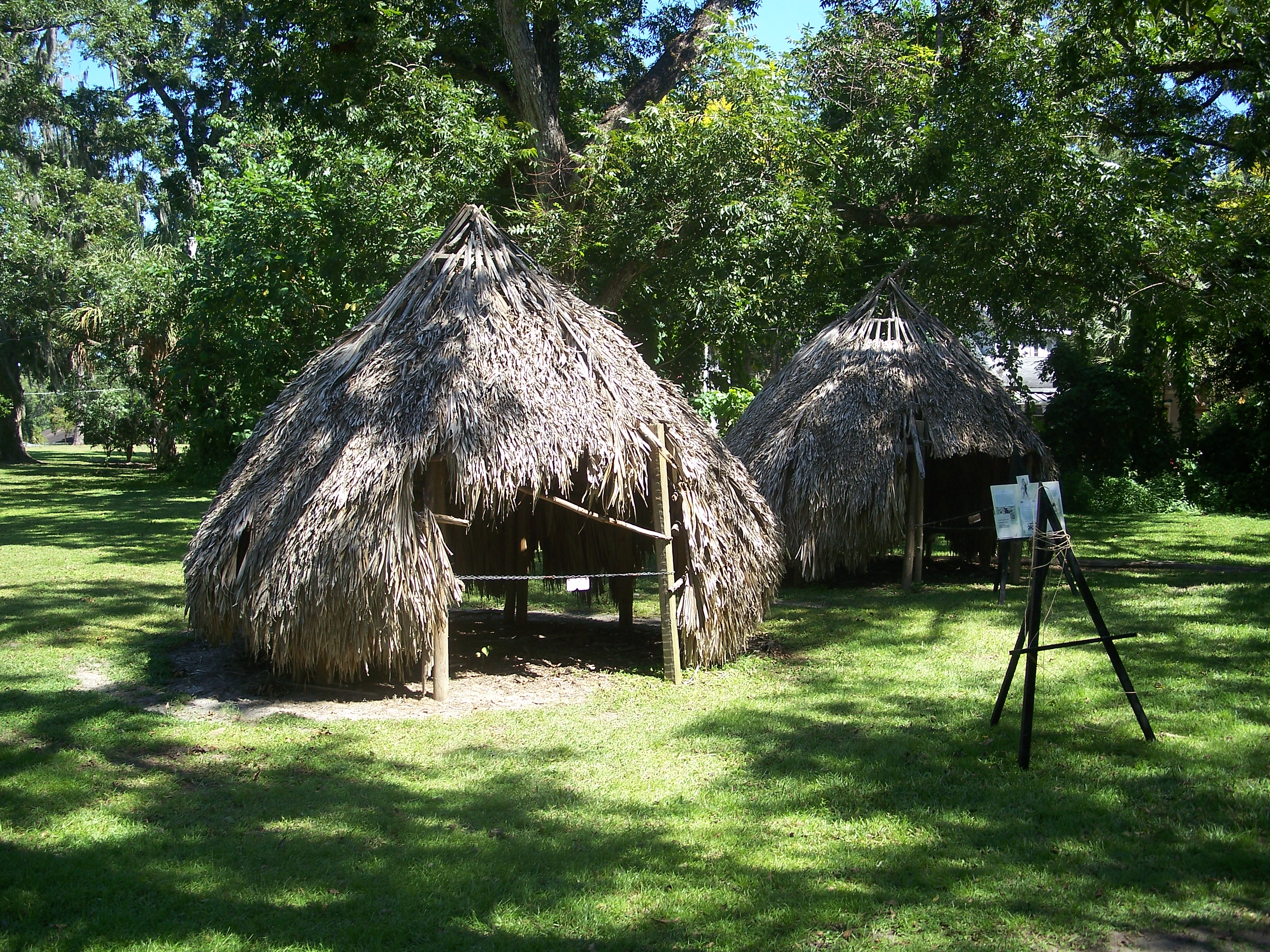
The Suwannee Valley culture is defined as a Late Woodland Southeast period archaeological culture in north Florida, dating from around 750 to European contact. The core area of the culture was found in an area roughly corresponding to present-day Suwannee and southern and central Columbia counties. It was preceded by the McKeithen Weeden Island culture and followed by the Spanish mission period Leon-Jefferson culture. Definition The Suwannee Valley culture was defined in the 1990s, as excavations revealed a unique ceramic assemblage. The core area of the Suwannee Valley culture was roughly bounded on the north, west and southwest by a great bend in the Suwannee River, and on the south by the Santa Fe River. The Suwannee Valley culture probably included the south bank of the Santa Fe River, in northern Alachua County, Florida, where it bordered the similar Alachua culture. It also extended westwards to the Aucilla River, beyond which lay the Fort Walton (950-Spanish mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Trinomial
A Smithsonian trinomial (formally the Smithsonian Institution Trinomial System, abbreviated SITS) is a unique identifier assigned to archaeological sites in many states in the United States. They are composed of one or two digits coding for the state, typically two letters coding for the county or county-equivalent within the state, and one or more sequential digits representing the order in which the site was listed in that county. The Smithsonian Institution The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ... developed the site number system in the 1930s and 1940s, but it no longer maintains the system. Trinomials are now assigned by the individual states. The 48 states then in the union were assigned numbers in alphabetical order. Alaska was assigned number 49 and Hawaii was assigne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American History Of Florida
Native may refer to: People * Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes Other uses * Northeast Arizona Technological Institute of Vocational Education (NATIVE), a technology school district in the Arizona portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Columbian Cultures
This list of pre-Columbian cultures includes those civilizations and cultures of the Americas which flourished prior to the European colonization of the Americas. Cultural characteristics Many pre-Columbian civilizations established permanent or urban settlements, agriculture, and complex societal hierarchies. In North America, indigenous cultures in the Lower Mississippi Valley during the Middle Archaic period built complexes of multiple mounds, with several in Louisiana dated to 5600–5000 BP (3700 BC–3100 BC). Watson Brake is considered the oldest, multiple mound complex in the Americas, as it has been dated to 3500 BC. It and other Middle Archaic sites were built by pre-ceramic, hunter-gatherer societies. They preceded the better known Poverty Point culture and its elaborate complex by nearly 2,000 years. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of North America
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Frank Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions.Jackson and Fogelson 3 Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represent the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formative Period In The Americas
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a political-ideological aristocracy relative to the general group. Concept In anthropological theory, one model of human social development rooted in ideas of cultural evolution describes a chiefdom as a form of social organization more complex than a tribe or a band society, and less complex than a state or a civilization. Within general theories of cultural evolution, chiefdoms are characterized by permanent and institutionalized forms of political leadership (the chief), centralized decision-making, economic interdependence, and social hierarchy. Chiefdoms are described as intermediate between tribes and states in the progressive scheme of sociopolitical development formulated by Elman Service: ''band - tribe - chiefdom - state''. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Missions In Florida
Beginning in the second half of the 16th century, the Kingdom of Spain established a number of Christian missions, missions throughout Spanish Florida, ''La Florida'' in order to convert the Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianity, to facilitate control of the area, and to prevent its colonization by other countries, in particular, Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France. Spanish Florida originally included much of what is now the Southeastern United States, although Spain never exercised long-term effective control over more than the northern part of what is now the State of Florida from present-day St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine to the area around Tallahassee, Florida, Tallahassee, southeastern Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, and some coastal settlements, such as Pensacola, Florida. A few short-lived missions were established in other locations, including Mission Santa Elena in present-day South Carolina, around the Florid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yustaga
The Yustaga were a Timucua people of what is now northwestern Florida during the 16th and 17th centuries. The westernmost Timucua group, they lived between the Aucilla and Suwannee Rivers in the Florida Panhandle, just east of the Apalachee people. A dominant force in regional tribal politics, they may have been organized as a loose regional chiefdom consisting of up to eight smaller local chiefdoms.Worth vol. II, p. 5. The Yustaga were closely associated with the Northern Utina people living on the other side of the Suwannee River, though they appear to have spoken a different dialect of the Timucua language, perhaps Potano. The Yustaga were among the first Timucua to encounter Europeans, as their location near the Apalachee ensured that several explorers passed through their territory looking for that group. After decades of resistance they were brought into the Spanish mission system in the 1620s. Like all Timucua groups, they experienced significant demographic decline in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Utina
The Northern Utina, also known as the Timucua or simply Utina, were a Timucua people of northern Florida. They lived north of the Santa Fe River and east of the Suwannee River, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language known as "Timucua proper". They appear to have been closely associated with the Yustaga people, who lived on the other side of the Suwannee. The Northern Utina represented one of the most powerful tribal units in the region in the 16th and 17th centuries, and may have been organized as a loose chiefdom or confederation of smaller chiefdoms. The Fig Springs archaeological site may be the remains of their principal village, Ayacuto, and the later Spanish mission of San Martín de Timucua. The Northern Utina had sporadic contact with the Europeans beginning in the first half of the 16th century. In 1539 Spanish conquistador Hernando de Soto passed through the Northern Utina region, where he captured and subsequently executed Aguacaleycuen, who may have been the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


