|
Surena (4th-century)
Surena (also spelled Suren) was a 4th-century Iranian military officer active during the reign of the Sasanian king (shah) Shapur II (). He played an important role in the denial of the Roman invasion in 363 and the peace negotiations that followed. Biography Surena was a member of the House of Suren, one of the Seven Great Houses of Iran. The family, of Parthian origin, had been active in Iranian politics since the Arsacid Empire, and held parts of Sakastan as their personal fiefdom. Surena was seemingly a powerful figure in the country, being described as "second in power after the king." He is first mentioned in 363, when he on April 24 ambushed a patrol force led by Hormizd, a brother of Shapur II, who had entered the service of the Roman emperor Julian (). Hormizd only managed to escape due to the overflow of the Euphrates which proved too much for Surena and his men. The following day after the Roman sack of Pirisabora, Surena ambushed three squadrons of the Roman cavalr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities. The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe, from the Great Hungarian Plain in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the steppes and the wooded steppes and even the semi-deserts from the Great Hungarian Plain to the Ordos in northern China." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pirisabora
The siege of Pirisabora took place when the Roman Emperor Julian besieged the fortified city of Pirisabora under Mamersides in April 363. After two days of fierce fighting, the Sasanians and the citizens abandoned the circuit walls and took up a defensive position in the acropolis. After some failed attempts, the Romans began to construct a siege tower, after which Mamersides reached a compromise with Julian to hand over the fort in exchange for a safe withdrawal. Julian subsequently pillaged and burned the abandoned city. Background After settling political affairs in Constantinople, Emperor Julian gathered an army of 95,000 in Antioch for his invasion of the Sassanid Empire. Upon his arrival at Carrhae, Julian sent his generals, Procopius and Sebastianus, with 30,000 men into Armenia to join up with Arshak II's army of 24,000. At the same time the main body under Julian himself wheeled south, reaching the Euphrates at Callinicum, whence he directed his march south-east along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally Anglicisation, anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Ancient history, antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae'', chronicled in Latin the history of Rome from the accession of the Emperor Nerva in 96 to the death of Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378, although only the sections covering the period 353 to 378 survive. Biography Ammianus was born in the East Mediterranean, possibly in Syria Palaestina, Syria or Phoenice (Roman province), Phoenicia, around 330. His native language is unknown but he likely knew Greek as well as Latin. The surviving books of his history cover the years 353 to 378. Ammianus served as an officer in the army of the emperors Constantius II and Julian (emperor), Julian. He served in Gaul (Julian) and in the east (twice for Constantius, once under Julian). He professes to have been "a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nusaybin
Nusaybin (; '; ar, نُصَيْبِيْن, translit=Nuṣaybīn; syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, translit=Nṣībīn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is predominantly Kurds, Kurdish. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius ( grc, Μυγδόνιος). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian language, Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
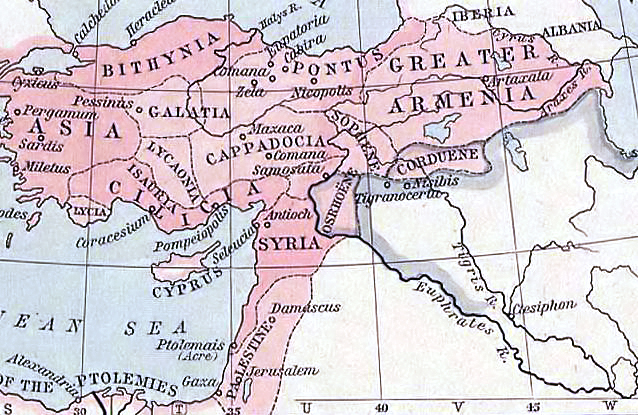
Kingdom Of Armenia (antiquity)
The Kingdom of Armenia, also the Kingdom of Greater Armenia, or simply Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք '; la, Armenia Maior), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire, was a monarchy in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into the successive reigns of three royal dynasties: Orontid (331 BC–200 BC), Artaxiad (189 BC–12 AD) and Arsacid (52–428). The root of the kingdom lies in one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia called Armenia (Satrapy of Armenia), which was formed from the territory of the Kingdom of Ararat (860 BC–590 BC) after it was conquered by the Median Empire in 590 BC. The satrapy became a kingdom in 321 BC during the reign of the Orontid dynasty after the conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great, which was then incorporated as one of the Hellenistic kingdoms of the Seleucid Empire. Under the Seleucid Empire (312–63 BC), the Armenian throne was divided in two—Armenia Maior and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavius Arinthaeus
Flavius Arintheus (or Arinthaeus; died AD 378) was a Roman army officer who started his career as a middle-ranking officer and rose to senior political and military positions. He served the emperors Constantius II, Julian, Jovian and Valens. He was appointed consul in 372 alongside Domitius Modestus. He served under Constantius during his campaign against the Alemanni, 354–5, under Julian in his Persian campaign, 363, and under Valens in the First Gothic War, 367–9, and Armenia, 370. He was one of the clique of senior officers who elected Jovian to the throne, and may have played a similar role in the election of Valentinian. He died in 378 while serving as ''magister peditum'', one of the two most senior military positions of the Roman Empire. Early career Probably a Goth, Arintheus began his career as a military officer. In 354–5 Arintheus served as a tribune, a middle-ranking officer, in Raetia. He belonged to one of the legions which accompanied Emperor Constantiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jovian (emperor)
Jovian ( la, Iovianus; 331 – 17 February 364) was Roman emperor from June 363 to February 364. As part of the imperial bodyguard, he accompanied Emperor Julian on his campaign against the Sasanian Empire and following the latter's death, Jovian was hastily declared emperor by his soldiers. With the army exhausted, provisions running low, and unable to cross the Tigris, he sought peace with the Sasanids on humiliating terms. After his arrival at Edessa, Jovian was petitioned by bishops over doctrinal issues concerning Christianity. His return to Constantinople would be cut short by his death at Dadastana. Jovian reigned eight months. Life Jovian was born at Singidunum, Moesia Superior (today Belgrade in Serbia), in 331, son of Varronianus, the commander of Constantius II's imperial bodyguards (''comes domesticorum''). He also joined the guards and in this capacity in 361, escorted Constantius' remains to the Church of the Holy Apostles. Jovian was married to Charito and they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor Shirakan
Nor Shirakan ( hy, Նոր Շիրական), Parskahayk ( hy, Պարսկահայք) or Persarmenia, was the seventh province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, situated on the western shore of Lake Urmia, bordered on Adiabene and Atropatene, now in northwestern Iran. Following the partition of Greater Armenia between the Roman Empire and Sassanid Empire in 387, the territory under Sassanid influence came to be known as Persarmenia. The region of Arzanene, traditionally part of Lesser Armenia, also became part of Persarmenia. Zarehavan was the centre of the province. Persarmenia had nine cantons:Frédéric Macler, 1989, Revue des études arméniennes: Volume 21, page 309, University of Michigan * Zaravand * Hér * Arna * Zarehavan * Tamber * Trabi * Ayli (Kurijan) * Mari * Arisi See also *List of regions of old Armenia This is a list of regions and or districts of ancient Armenia. A *Aghdznik *Aliovit * Amatunik * Angl * Andzevaciq * Andzith * Aragatzotn * Aranean * Aravelean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Samarra
The Battle of Samarra took place in June 363, during the invasion of the Sasanian Empire by the Roman Emperor Julian. After marching his army to the gates of Ctesiphon and failing to take the city, Julian, realizing his army was low on provisions and in enemy territory started marching towards Samarra. The battle began as a Sasanian attack on the Roman rearguard, but developed into a major battle. Julian was wounded during the battle, and later died without choosing a successor. Following Julian's death, the Romans elected Jovian as emperor. Stranded deep in Sasanian territory and suffering from a lack of supplies, Jovian was forced to accept terms for peace. Julian's campaign Julian invaded the Sasanian Empire with a force of 95,000 men, hoping to secure the eastern frontier and to replace Shah Shapur II with his brother Hormisdas. He split his force in two, one under his cousin Procopius numbering 30,000 men, which marched to northern Mesopotamia, and the other consistin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigranes
Pigranes was a 4th-century Sasanian military officer active during the reign of Shapur II (). According to Ammianus Marcellinus, on 29 May 363, when the forces of the Roman Emperor Julian () besieged the Sasanian capital of Ctesiphon Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ..., Pigranes along with his fellow officers Narseus and Surena were defeated and forced to flee to the interior of the city walls. Sources * People of the Roman–Sasanian Wars Generals of Shapur II 4th-century Iranian people Julian's Persian expedition {{Sasanian-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ctesiphon (363)
The Battle of Ctesiphon took place on 29 May 363 between the armies of Roman Emperor Julian and an army of the Sasanian Empire (during Shapur II's reign) outside the walls of the Persian capital Ctesiphon. The battle was a Roman victory, but eventually the Roman forces found themselves unable to continue their campaign as they were too far from their supply lines. Background On November 3, 361, Constantius II died in the city of Mopsucrene, leaving his cousin Flavius Claudius Julianus, known to history as Julian the Apostate, as sole Emperor of Rome. Arriving at Constantinople to oversee Constantius' burial, Julian immediately focused on domestic policy and began to greatly reform the Roman Imperial government by reorganizing, streamlining, and reducing the bureaucracy. Turning next to foreign policy, Julian saw the previously unchecked military incursions of Shapur II of Persia against the Eastern Roman provinces as posing the greatest external threat. After many failed ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.png)

