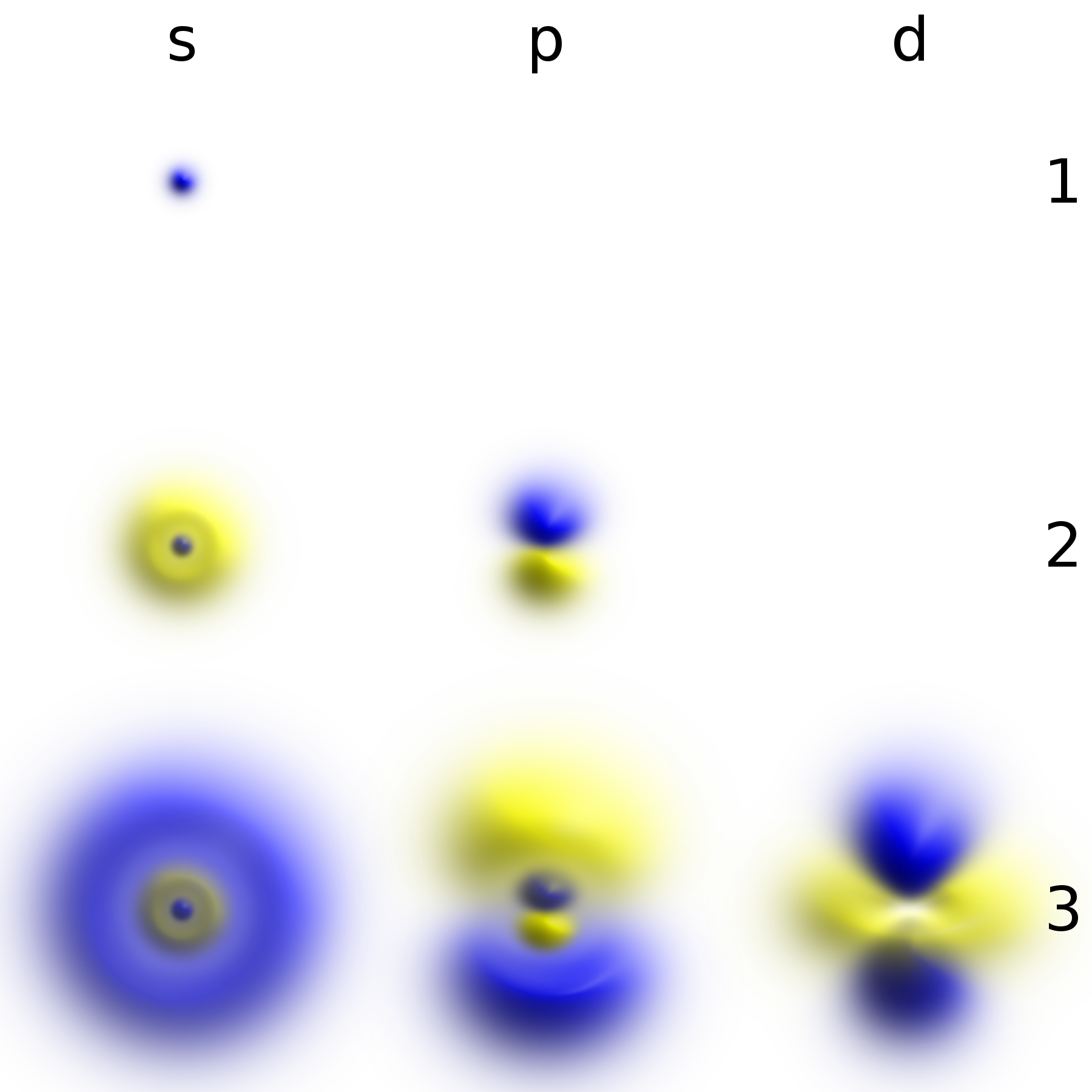
|
Supersymmetric WKB Approximation
In physics, the supersymmetric WKB (SWKB) approximation is an extension of the WKB approximation that uses principles from supersymmetric quantum mechanics to provide estimations on energy eigenvalues in quantum-mechanical systems. Using the supersymmetric method, there are potentials V(x) that can be expressed in terms of a superpotential, W(x), such that : V(x) = W^2(x)-\frac W'(x) The SWKB approximation then writes the Born–Sommerfeld quantization condition from the WKB approximation in terms of W(x). The SWKB approximation for unbroken supersymmetry, to first order in \hbar is given by : \frac\int_b^a dx \, \sqrt = n\pi where E_n is the estimate of the energy of the n-th excited state, and a and b are the classical turning points, given by : W^2(a) = W^2(b) = E_n The addition of the supersymmetric method provides several appealing qualities to this method. First, it is known that, by construction, the ground state energy will be exactly estimated. This is an improvem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WKB Approximation
In mathematical physics, the WKB approximation or WKB method is a method for finding approximate solutions to linear differential equations with spatially varying coefficients. It is typically used for a semiclassical calculation in quantum mechanics in which the wavefunction is recast as an exponential function, semiclassically expanded, and then either the amplitude or the phase is taken to be changing slowly. The name is an initialism for Wentzel–Kramers–Brillouin. It is also known as the LG or Liouville–Green method. Other often-used letter combinations include JWKB and WKBJ, where the "J" stands for Jeffreys. Brief history This method is named after physicists Gregor Wentzel, Hendrik Anthony Kramers, and Léon Brillouin, who all developed it in 1926. In 1923, mathematician Harold Jeffreys had developed a general method of approximating solutions to linear, second-order differential equations, a class that includes the Schrödinger equation. The Schrödinger equati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics
In theoretical physics, supersymmetric quantum mechanics is an area of research where supersymmetry are applied to the simpler setting of plain quantum mechanics, rather than quantum field theory. Supersymmetric quantum mechanics has found applications outside of high-energy physics, such as providing new methods to solve quantum mechanical problems, providing useful extensions to the WKB approximation, and statistical mechanics. Introduction Understanding the consequences of supersymmetry (SUSY) has proven mathematically daunting, and it has likewise been difficult to develop theories that could account for symmetry breaking, ''i.e.'', the lack of observed partner particles of equal mass. To make progress on these problems, physicists developed ''supersymmetric quantum mechanics'', an application of the supersymmetry superalgebra to quantum mechanics as opposed to quantum field theory. It was hoped that studying SUSY's consequences in this simpler setting would lead to new un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Eigenvalue
A stationary state is a quantum state with all observables independent of time. It is an eigenvector of the energy operator (instead of a quantum superposition of different energies). It is also called energy eigenvector, energy eigenstate, energy eigenfunction, or energy eigenket. It is very similar to the concept of atomic orbital and molecular orbital in chemistry, with some slight differences explained below. Introduction A stationary state is called ''stationary'' because the system remains in the same state as time elapses, in every observable way. For a single-particle Hamiltonian, this means that the particle has a constant probability distribution for its position, its velocity, its spin, etc. (This is true assuming the particle's environment is also static, i.e. the Hamiltonian is unchanging in time.) The wavefunction itself is not stationary: It continually changes its overall complex phase factor, so as to form a standing wave. The oscillation frequency of the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum-mechanical
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limits to how a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limits to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics
In theoretical physics, supersymmetric quantum mechanics is an area of research where supersymmetry are applied to the simpler setting of plain quantum mechanics, rather than quantum field theory. Supersymmetric quantum mechanics has found applications outside of high-energy physics, such as providing new methods to solve quantum mechanical problems, providing useful extensions to the WKB approximation, and statistical mechanics. Introduction Understanding the consequences of supersymmetry (SUSY) has proven mathematically daunting, and it has likewise been difficult to develop theories that could account for symmetry breaking, ''i.e.'', the lack of observed partner particles of equal mass. To make progress on these problems, physicists developed ''supersymmetric quantum mechanics'', an application of the supersymmetry superalgebra to quantum mechanics as opposed to quantum field theory. It was hoped that studying SUSY's consequences in this simpler setting would lead to new un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersymmetry
In a supersymmetric theory the equations for force and the equations for matter are identical. In theoretical and mathematical physics, any theory with this property has the principle of supersymmetry (SUSY). Dozens of supersymmetric theories exist. Supersymmetry is a spacetime symmetry between two basic classes of particles: bosons, which have an integer-valued spin and follow Bose–Einstein statistics, and fermions, which have a half-integer-valued spin and follow Fermi–Dirac statistics. In supersymmetry, each particle from one class would have an associated particle in the other, known as its superpartner, the spin of which differs by a half-integer. For example, if the electron exists in a supersymmetric theory, then there would be a particle called a ''"selectron"'' (superpartner electron), a bosonic partner of the electron. In the simplest supersymmetry theories, with perfectly " unbroken" supersymmetry, each pair of superpartners would share the same mass and intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert Einstein was concerned wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Physics
Mathematical physics refers to the development of mathematics, mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The ''Journal of Mathematical Physics'' defines the field as "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and for the formulation of physical theories". An alternative definition would also include those mathematics that are inspired by physics (also known as physical mathematics). Scope There are several distinct branches of mathematical physics, and these roughly correspond to particular historical periods. Classical mechanics The rigorous, abstract and advanced reformulation of Newtonian mechanics adopting the Lagrangian mechanics and the Hamiltonian mechanics even in the presence of constraints. Both formulations are embodied in analytical mechanics and lead to understanding the deep interplay of the notions of symmetry (physics), symmetry and conservation law, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |