|
Super High Speed Silver-37
In shogi, Super High Speed Silver-37 or Ultra Quick Right Silver (超速3七銀 or 超速▲3七銀 ''chōsoku san-nana gin'') is a rapid attacking formation used with a Static Rook opening by Black often against White's Cheerful Central Rook. It was developed by then-3-dan Yoshitaka Hoshino, who went on to become the second apprentice professional to win the Masuda Award in 2010. Black aims to advance their right silver through 37 to 46. White likewise can answer Black's advancing silver by moving their left silver to 44. See also * Static Rook * Cheerful Central Rook In shogi, Cheerful Central Rook (ゴキゲン中飛車 ''gokigen nakabisha'', also Gokigen Central Rook or Go-As-You-Please Central Rook) is a type of Central Rook opening in which the Central Rook player's bishop diagonal remains open. This is ... Bibliography 2014年6月26日 第4期リコー杯女流王座戦二次予選 清水市代女流六段 対 真田彩子女流二段16手目の棋 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
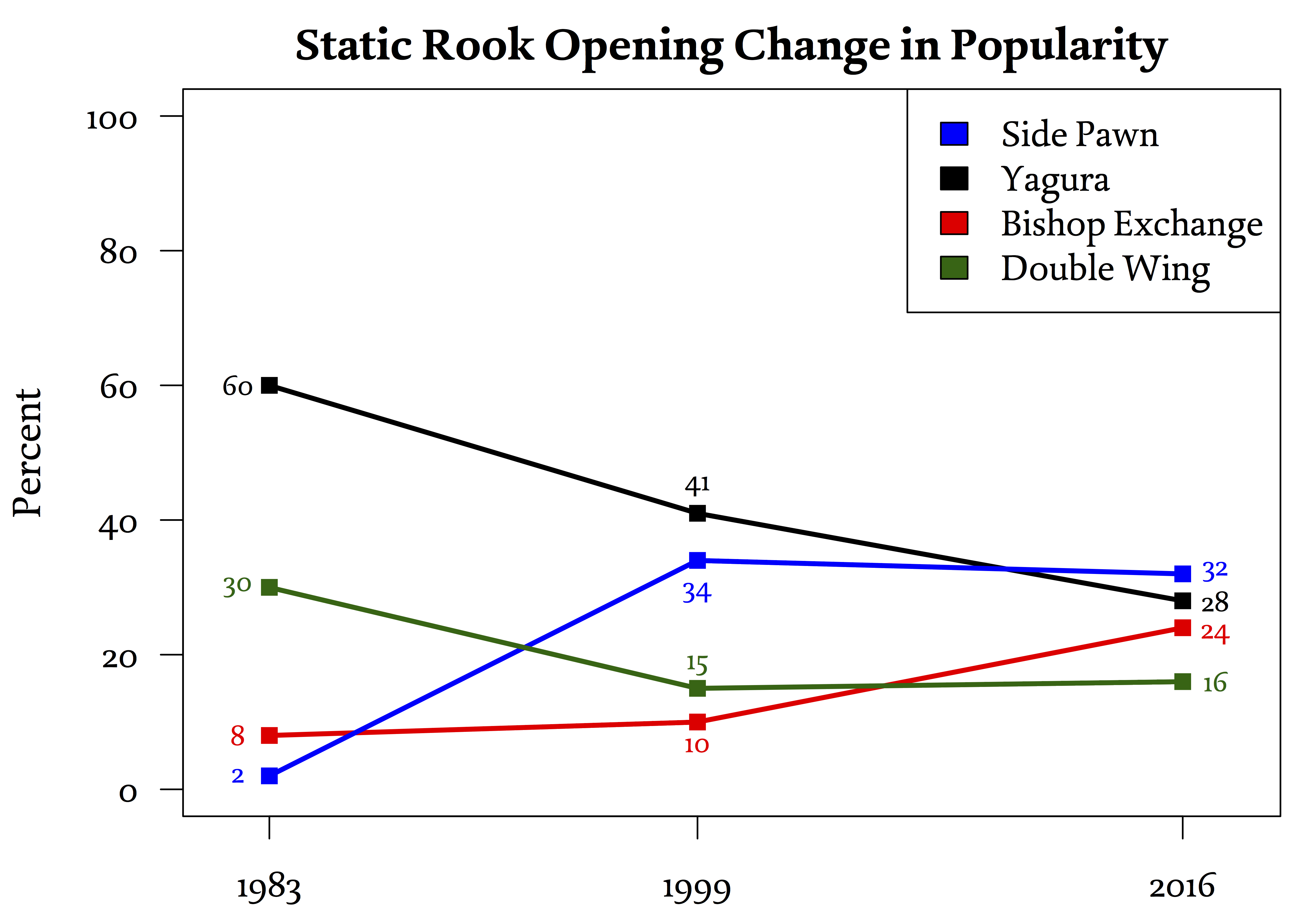
Static Rook
Static Rook (居飛車 ''ibisha'') openings in shogi typically have the player's rook at its start position, which is the second file (on the 28 square) for Black and the eighth file (on the 82 square) for White. Explanation Static Rook is a set of openings in which the rook remains on its starting square, which is the 28 square if played by Black and the 82 square if played by White. It is also possible to include other openings where the rook moves to another file that is still on the players right side of the board, such as the third file or the fourth file. The reason for including these other openings where the rook is not technically ''static'' is because the typical castle fortifications constructed to the protect the Static Rook player's king are usually the same for these openings. Nonetheless, some shogi theory does categorize these openings with right side rook movement into the same group as Ranging Rook openings despite the disparity in castle formation. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheerful Central Rook
In shogi, Cheerful Central Rook (ゴキゲン中飛車 ''gokigen nakabisha'', also Gokigen Central Rook or Go-As-You-Please Central Rook) is a type of Central Rook opening in which the Central Rook player's bishop diagonal remains open. This is a more aggressive strategy since the bishops may be exchanged at any time during the opening. (See: Ranging Rook#Types of Ranging Rook.) Cheerful Central Rook is played against a Static Rook opponent. White's variation 1.P-76 P-34 2.P-26. Open bishop diagonals. Black plays Static Rook. 2...P-54. White pushes the central pawn – the signature move of Cheerful Central Rook. 3.P-25. Rook pawn advance. 3...R-52. Central Rook move. Early pawn push After White swings their rook to the central file, pushing the second file pawn by Black (4.P-24) in order to trade the pawns off and get a pawn in hand is thought to be a mistake (although not quite a blunder) here since it will result in a position judged to be better for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshitaka Hoshino
is a Japanese professional shogi player ranked 5-dan. He also holds an Esports professional shogi player license from the (JeSU). Early life Hoshino was born in Ageo, Saitama on August 10, 1988. He became interested in shogi when he was about five years old with his first opponent being his mother, and entered the Japan Shogi Association's apprentice school at the rank of 6-kyū under the guidance of shogi professional in 2001. He was promoted to the rank of apprentice professional 3-dan in 2007, and finally obtained full professional status and the rank of 4-dan in 2014 after tying Hiroshi Miyamoto for first place in the 54th 3-dan League (October 2013March 2014) with a record of 13 wins and 5 losses. Hoshino later stated in a October 2021 interview that his primary motivation for becoming a shogi professional was not money or to have a career, but rather because he felt that "his life would end" and the mental strain would be great if he quit. Professional shogi player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Shogi Awards
The Annual Shogi Awards (将棋大賞 ''shōgi taishō'') are a number of prizes awarded yearly by the Japan Shogi Association to professional and amateur shogi players who have achieved particular success. The first Annual Shogi Awards were presented in 1974. Winners Below is a table of the awards given and the award winners for each year. Kōzō Masuda Awards The Kōzō Masuda Award (升田幸三賞 ''Masuda Kōzō shō'') and the Kōzō Masuda Special Prize (升田幸三賞特別賞 ''Masuda Kōzō shō takubetsu shō'') are two prizes awarded to professional or amateur players who have made an outstanding contribution to the development and evolution of shogi openings by way of innovation or excellence in shogi theory or tactics. The awards are named after the innovative player, Kōzō Masuda. The Masuda Award is given out yearly since 1995 while the Masuda Special Prize is awarded infrequently. Winners Masuda Award * 1995 (22nd Annual Shogi Awards) Kunio Naitō for the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Openings
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Abstract strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century Mercenary#15th to 18th centuries, mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |