|
Sunfix Glacier
Casey Inlet () is an ice-filled inlet at the terminus of Casey Glacier, between Miller Point and Cape Walcott, on the east coast of Palmer Land Palmer Land () is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica that lies south of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This application of Palmer Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between the Advisory Committee on Antarctic N .... It was photographed from the air by Sir Hubert Wilkins in 1928, Lincoln Ellsworth in 1935 and the United States Antarctic Service in 1940. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1947. The inlet takes its name from Casey Glacier. References * Inlets of Palmer Land {{PalmerLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casey Glacier
Casey Glacier () is a glacier wide, flowing east into Casey Inlet on the east coast of Palmer Land. It was discovered by Sir Hubert Wilkins on an aerial flight of December 20, 1928. Wilkins believed the feature to be a channel cutting completely across the Antarctic Peninsula, naming it Casey Channel after Rt. Hon. Richard G. Casey. Correlation of aerial photographs taken by Lincoln Ellsworth in 1935 and preliminary reports of the British Graham Land Expedition, 1934–37, led W.L.G. Joerg to interpret this glacier to be what Wilkins named Casey Channel. This interpretation is borne out by the results of subsequent exploration by members of the East Base of the United States Antarctic Service The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the A ... in 1940. See also * Hogmanay Pass R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Point
Miller Point is a black, rock cape rising to and forming the north side of the entrance to Casey Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by Sir Hubert Wilkins in a flight on December 20, 1928, and named by him for George E. Miller of Detroit, Michigan Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the .... It has since been more fully defined as a result of flights by Lincoln Ellsworth in 1935, and by the flights and sledge journey along this coast from East Base by members of the United States Antarctic Service in 1940. References Headlands of Palmer Land {{PalmerLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Walcott
Cape Walcott is a bold, ice-covered headland rising to 625 m on the north side of the entrance to Bertius Inlet, and forming the seaward extremity of Scripps Heights on the east coast of Palmer Land. Discovered by Sir Hubert Wilkins in 1928 and named by him for Frederic C. Walcott Frederic Collin Walcott (February 19, 1869April 27, 1949) was a United States senator from Connecticut. Biography Born in New York Mills, Oneida County, New York, the son of William Stuart Walcott and Emeline Alice Welch Walcott, Walcott atten ... of the Council of the American Geographical Society. Headlands of Palmer Land {{PalmerLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
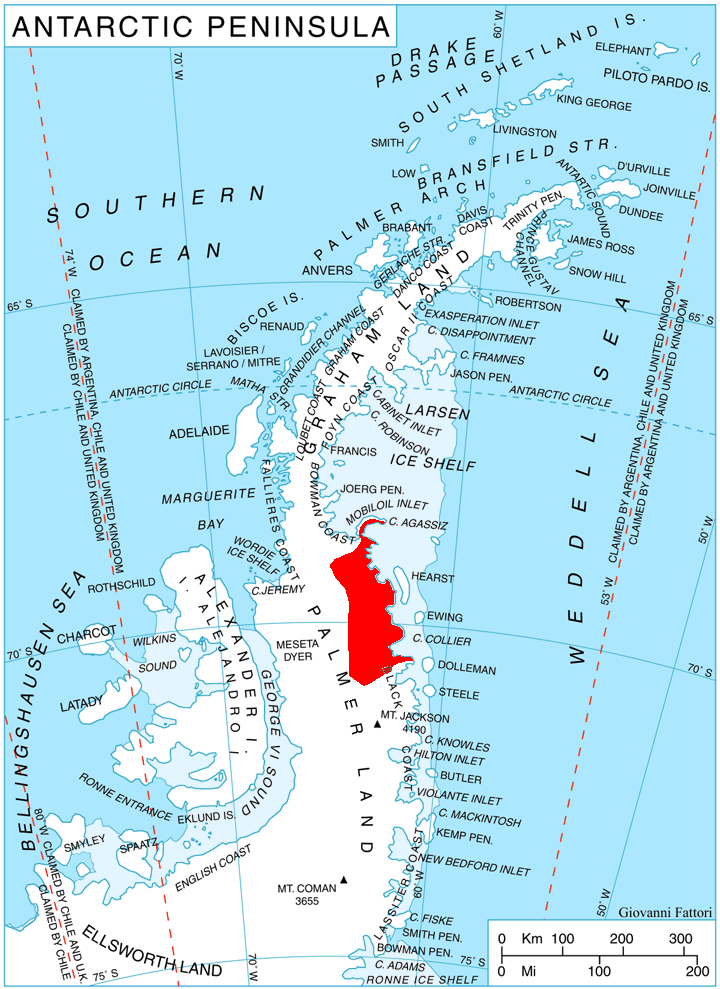
Palmer Land
Palmer Land () is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica that lies south of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This application of Palmer Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names and the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, in which the name Antarctic Peninsula was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69° S. Boundaries In its southern extreme, the Antarctic Peninsula stretches west, with Palmer Land eventually bordering Ellsworth Land along the 80° W line of longitude. Palmer Land is bounded in the south by the ice-covered Carlson Inlet, an arm of the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, which crosses the 80° W line. This is the base of Cetus Hill. This feature is named after Nathaniel Palmer, an American sealer who explored the Antarctic Peninsula area southward of Deceptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Hubert Wilkins
Sir George Hubert Wilkins MC & Bar (31 October 188830 November 1958), commonly referred to as Captain Wilkins, was an Australian polar explorer, ornithologist, pilot, soldier, geographer and photographer. He was awarded the Military Cross after he assumed command of a group of American soldiers who had lost their officers during the Battle of the Hindenburg Line, and became the only official Australian photographer from any war to receive a combat medal. He narrowly failed in an attempt to be the first to cross under the North Pole in a submarine, but was able to prove that submarines were capable of operating beneath the polar ice cap, thereby paving the way for future successful missions. The US Navy later took his ashes to the North Pole aboard the submarine USS ''Skate'' on 17 March 1959. Early life Hubert Wilkins was a native of Mount Bryan East, South Australia, the last of 13 children in a family of pioneer settlers and sheep farmers. He was born at Mount Bryan East, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Ellsworth
Lincoln Ellsworth (May 12, 1880 – May 26, 1951) was a polar explorer from the United States and a major benefactor of the American Museum of Natural History. Biography Lincoln Ellsworth was born on May 12, 1880, to James Ellsworth and Eva Frances Butler in Chicago, Illinois. He also lived in Hudson, Ohio, as a child. He attended The Hill School and took two years longer than usual to graduate, before entering the Sheffield Scientific School at Yale University. His academic performance was poor, and he subsequently enrolled at Columbia University and McGill before ending his academic career. Lincoln Ellsworth's father, James, a wealthy coal man from the United States, spent US$100,000 to fund Roald Amundsen's 1925 attempt to fly from Svalbard to the North Pole. Amundsen, accompanied by Lincoln Ellsworth, pilot Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen, flight mechanic Karl Feucht and two other team members, set out in two Dornier Wal flying boats, the N24 and N25, in an attempted to reach the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Service
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, and works with other federal agencies, the U.S. military, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey
The British Antarctic Survey (BAS) is the United Kingdom's national polar research institute. It has a dual purpose, to conduct polar science, enabling better understanding of global issues, and to provide an active presence in the Antarctic on behalf of the UK. It is part of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). With over 400 staff, BAS takes an active role in Antarctic affairs, operating five research stations, one ship and five aircraft in both polar regions, as well as addressing key global and regional issues. This involves joint research projects with over 40 UK universities and more than 120 national and international collaborations. Having taken shape from activities during World War II, it was known as the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey until 1962. History Operation Tabarin was a small British expedition in 1943 to establish permanently occupied bases in the Antarctic. It was a joint undertaking by the Admiralty and the Colonial Office. At the end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)