|
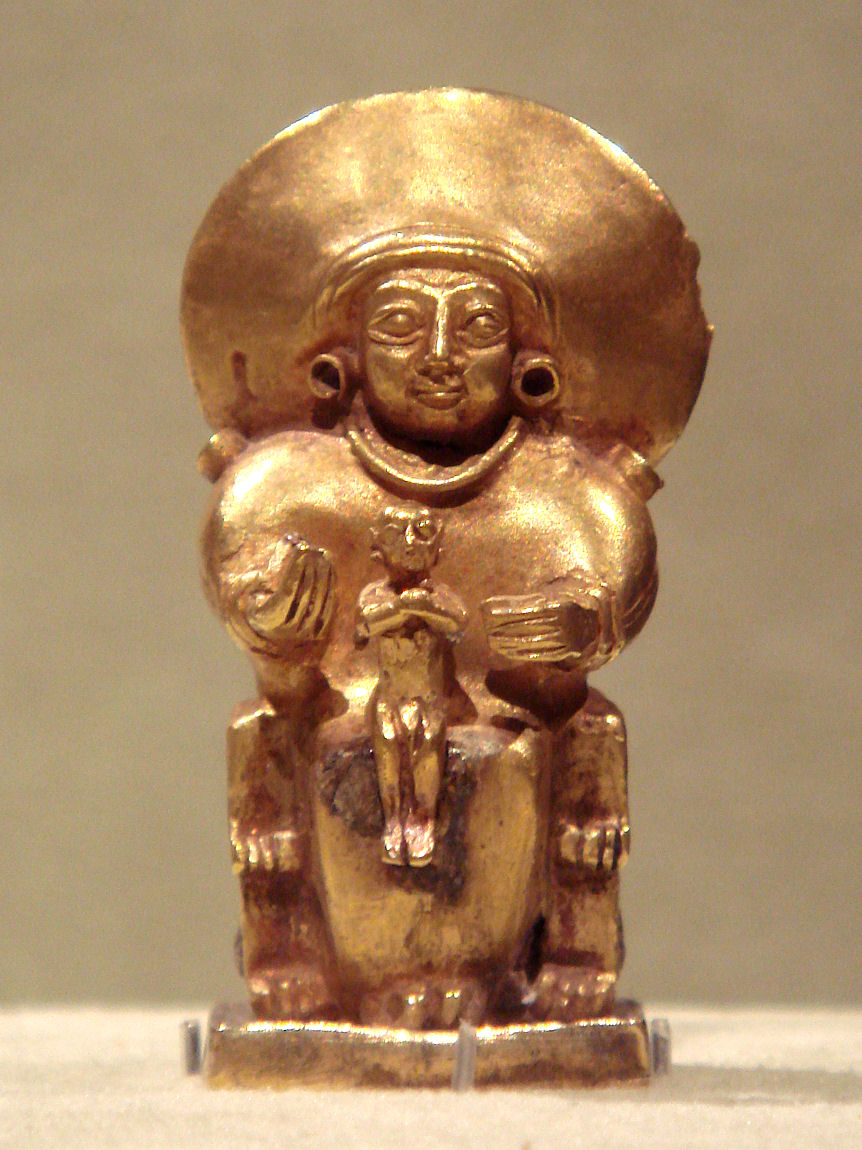
Sun Goddess Of Arinna
The Sun goddess of Arinna, also sometimes identified as Arinniti or as Wuru(n)šemu, is the chief goddess and companion of the weather god Tarḫunna in Hittite mythology. She protected the Hittite kingdom and was called the "Queen of all lands." Her cult centre was the sacred city of Arinna. In addition to the Sun goddess of Arinna, the Hittites also worshipped the Sun goddess of the Earth and the Sun god of Heaven, while the Luwians originally worshipped the old Proto-Indo-European Sun god Tiwaz. It appears that in the northern cultural sphere of the early Hittites, there was no male solar deity. Distinguishing the various solar deities in the texts is difficult since most are simply written with the Sumerogram dUTU (Solar deity). As a result, the interpretation of the solar deities remains a subject of debate. Family and myths The Sun goddess of Arinna and the weather god Tarḫunna formed a pair and together they occupied the highest position in the Hittite state's pant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hattian Language
Hattic, or Hattian, was a non-Indo-European agglutinative language spoken by the Hattians in Asia Minor in the 2nd millennium BC. Scholars call the language "Hattic" to distinguish it from Hittite, the Indo-European language of the Hittite Empire. The Hittites referred to the language as ''"hattili"'' (there are no attestations of the name of the language in Hattic itself). The name is doubtlessly related to the Assyrian and Egyptian designation of an area west of the Euphrates as "Land of the Hatti" (Khatti). The heartland of the oldest attested language of Anatolia, before the arrival of Hittite-speakers, ranged from Hattusa, then called "Hattus", northward to Nerik. Other cities mentioned in Hattic include Tuhumiyara and Tissaruliya. Hittite-speakers conquered Hattus from Kanesh to its south in the 18th century BC. They eventually absorbed or replaced the Hattic-speakers (Hattians) but retained the name ''Hatti'' for the region. The name of the inhabitants of that area is li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurunta
Kurunta (Cuneiform: ) was younger son of the early 13th century BC Hittite king Muwatalli II and cousin of Tudhaliya IV. Kurunta was thereby a Hittite prince and king of Tarhuntassa country. It has been suggested that he may have captured the Hittite capital for a very short time during the reign of the Hittite king Tuthaliya IV and declared himself a great king. Name His Luwian name ''Kurunta'' was after one of the patron gods in the Hittite pantheon. As is customary for late Hittite princes, the Kurunta had also a Hurrian name ''Ulmi-Teššup'' (spelled also''Ulmi-Teshup"''). The names of the gods and the monarchs are derived from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*ker-'', meaning 'head', 'horn'. In the Anatolian branch, the root originated Hittite ''kara=war-'' and Cuneiform Luwian ''zarwaniya'' ('pertaining to horn'). Life Most of the information about Kurunta is known from two treaties concluded between Hittite state and kingdom of Tarhuntassa. His name is also mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
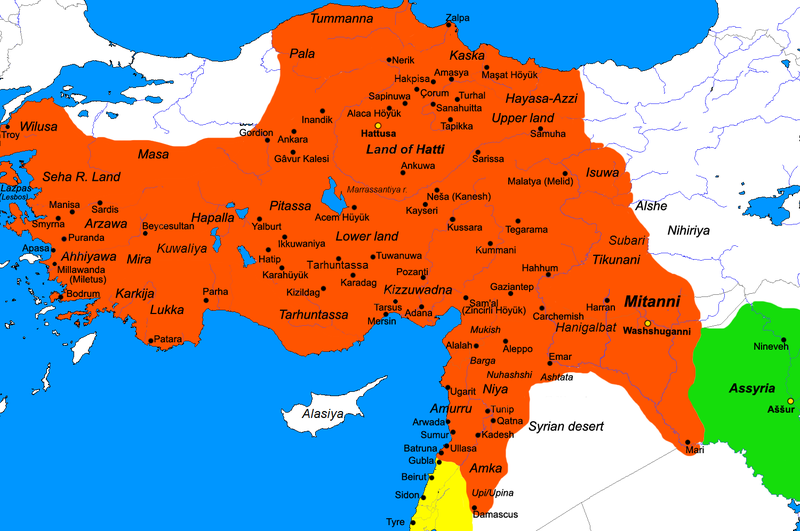
Ḫattuša
Hattusa (also Ḫattuša or Hattusas ; Hittite: URU''Ḫa-at-tu-ša'',Turkish: Hattuşaş , Hattic: Hattush) was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: ''Marashantiya''; Greek: '' Halys''). Hattusa was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. Surroundings The landscape surrounding the city included rich agricultural fields and hill lands for pasture as well as woods. Smaller woods are still found outside the city, but in ancient times, they were far more widespread. This meant the inhabitants had an excellent supply of timber when building their houses and other structures. The fields provided the people with a subsistence crop of wheat, barley and lentils. Flax was also harvested, but their primary source for clothing was sheep wool. They also hunted deer in the forest, but this was probably only a luxury reserved for the nobility. Domesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnuwanda I
Arnuwanda I was a king of the Hittite Empire. He became a ruler by marriage and was very religious. He ruled c. 1390–1380 BC (middle chronology). Biography Arnuwanda became a king by marriage. His wife was Ašmu-nikal, daughter of king Tudhaliya I (also known as Tudhaliya I/II). He became a successor of Tudhaliya as his son-in-law. He began his reign under a co-regency with Tudhaliya. During his time, the kingdom suffered what is known as the period of ‘concentric invasions’, when they were surrounded on all sides by enemies. A major enemy was the kingdom of Arzawa in the southwest. Arnuwanda may have led an unsuccessful expedition against Arzawa. At the time, Arzawa was led by king Tarhuntaradu, who was corresponding with the Egyptian Pharaoh Amenhotep III. Tarhuntaradu was a powerful leader, and the Egyptians clearly saw Arzawa as capable of controlling that whole area. Hattusa was sacked, and the court had to move to a temporary base, probably at Samuha. But later, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkert Haas
Volkert may refer to: People *Edward Charles Volkert (1871–1935), American painter *Georg Volkert (1945–2020), German footballer * Stephan Volkert (born 1971), German rower *Volkert Doeksen (born 1963), Dutch money manager *Volkert van der Graaf (born 1969), Dutch assassin *Volkert Kraeft (born 1941), German actor *Volkert Merl (born 1940), German racing driver *Volkert Overlander (1570–1630), Dutch noble, jurist, ship-owner and merchant *Volkert Simon Maarten van der Willigen (1822–1878), Dutch mathematician and physicist Companies *Volkert, Inc., a consulting firm headquartered in Mobile, Alabama Buildings *Volkert Van Buren House Volkert Van Buren House is a historic home located near Fulton, Oswego County, New York, Fulton in Oswego County, New York. It is a Federal architecture, Federal style structure constructed about 1832. ''See also:'' It was listed on the Nation ..., historic home in Oswego County, New York Surnames from given names {{Disambiguation, gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ḫattušili I
Hattusili I (''Ḫattušili'' I) was a king of the Hittite Old Kingdom. He reigned ca. 1650–1620 BCE as per middle chronology, the most accepted chronology nowadays, or alternatively ca. 1586–1556 BCE (short chronology). Excavations in Zincirli Höyük, Southern Turkey, suggest that Hattusili I destroyed a complex at that site in the mid to late 17th century BCE, which can confirm the middle chronology dating for his reign.Herrmann, Virginia, et al., (2020)"Iron Age Urbanization and Middle Bronze Age Networks at Zincirli Höyük: Recent Results from the Chicago-Tübingen Excavations" in ASOR 2020 Annual Meeting.Urbanus, Jason, (November/December 2019)"The Wrath of the Hittites" Archaeological Institute of America: "...The project leaders believe that they know who was responsible for the swath of destruction: Hattusili I (r. ca. 1650–1620 B.C.), one of the first kings of the Hittite Empire, which was expanding its territory from central Anatolia during the second millennium B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittite Texts
The corpus of texts written in the Hittite language is indexed by the ''Catalogue des Textes Hittites'' (CTH, since 1971). The catalogue is only a classification of texts; it does not give the texts. One traditionally cites texts by their numbers in CTH. Major sources for studies of selected texts themselves are the books of the StBoT series and the online ''Textzeugnisse der Hethiter''. CTH numbering scheme The texts are classified as follows: *Historical Texts (CTH 1–220) *Administrative Texts (CTH 221–290) *Legal Texts (CTH 291–298) *Lexical Texts (CTH 299–309) *Literary Texts (CTH 310–320) *Mythological Texts (CTH 321–370) *Hymns and Prayers (CTH 371–389) *Ritual Texts (CTH 390–500) *Cult Inventory Texts (CTH 501–530) *Omen and Oracle Texts (CTH 531–582) *Vows (CTH 583–590) *Festival Texts (CTH 591–724) *Texts in Other Languages (CTH 725–830) *Texts of Unknown Type (CTH 831–833) Selected texts Some Wikipedia articles dedicated to specific Hittite te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puduḫepa
Puduḫepa or Pudu-Kheba ( fl. 13th century BC) was a Hittite queen, her companion being the King Hattusili III Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal name of three Hittite kings: * Ḫattušili I (Labarna II) *Ḫattušili II *Ḫattušili III It was also the name of two Neo-Hittite kings: * Ḫattušili I (Labarn .... She has been referred to as "one of the most influential women known from the Ancient Near East." Biography Early life and marriage Puduḫepa was born at the beginning of the 13th century BC in the city of Lawazantiya in Kizzuwatna (i.e. Cilicia, a region south of the Hittite kingdom). Her father Bentepsharri was the head priest of the tutelary god, divinity of the city, Shaushka (identified with the Mesopotamian Ishtar), and Puduḫepa grew up to exercise the function of priestess of this same goddess. On his return from the Battle of Kadesh, the Hittite General officer, general Hattusili met Puduḫepa and, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ḫepat
Ḫebat ( xhu, 𒀭𒄭𒁁, ), also transcribed Khepat, was the mother goddess of the Hurrians, known as "the mother of all living". She was a popular deity, and her name appears in many Theophoric name, theophoric personal names. A king of Jerusalem mentioned in the Amarna letters was named Abdi-Heba, possibly meaning "Servant of Ḫepat". Origin Alfonso Archi assumes that her Hurrian name was derived from an earlier form known from Ebla: d''Ha-a-ba-du'', "she of Halab," already associated with a weather god (the Semitic Hadda rather than Hurrian Teshub) in some offering lists. Mythical family and associated deities Hurrians, who incorporated a number of preexisting Syrian deities into their own pantheon, regarded their head god Teshub as Hebat's husband. The mountain god Sarruma, already part of her circle in earlier times, was reinterpeted as their son as a result, and in cult he functioned as a dyad with his mother. They also had a daughter, Alanzu. Lluís Feliu in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurrian Religion
The Hurrian religion was the polytheistic religion of the Hurrians, a Bronze Age people of the Near East who chiefly inhabited the north of the Fertile Crescent. While the oldest evidence goes back to the third millennium BCE, is best attested in cuneiform sources from the second millennium BCE written not only in the Hurrian language, but also Akkadian, Hittite and Ugaritic. It was shaped by the contacts between Hurrians and various cultures they coexisted with. As a result, the Hurrian pantheon included both natively Hurrian deities and those of foreign origin, adopted from Mesopotamian, Syrian (chiefly Eblaite and Ugaritic), Anatolian and Elamite beliefs. The culture of the Hurrians were not entirely homogeneous, and different local religious traditions are documented in sources from Hurrian kingdoms such as Arrapha, Kizzuwatna and Mitanni, as well as from cities with sizeable Hurrian populations, such as Ugarit and Alalakh. Hurrian religion was one of the best attested influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |