|
Sun City Girls (album)
''Sun City Girls'' is the eponymously titled debut studio album of American experimental rock band Sun City Girls, released in 1984 by Placebo Records. Track listing Personnel Adapted from the ''Sun City Girls'' liner notes. ;Sun City Girls * Alan Bishop – bass guitar, guitar, alto saxophone, trumpet, dulcimer, tape, percussion, vocals * Richard Bishop – lap steel guitar, piano, organ, melodica, flute, percussion * Charles Gocher – drums, horns, guitar, percussion, bongos, güiro, bells, triangle, whistle, xylophone, vocals ;Production and additional personnel * Tom Barnes – engineering * The Cat – production * Greg Hynes – production * Sandy Lamont – engineering * M.A.C. – cover art * Sun City Girls Sun City Girls were an American experimental rock band, formed in 1979 in Phoenix, Arizona. From 1981, the group consisted of Alan Bishop (bass guitar, vocals), his brother Richard Bishop (guitar, piano, vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun City Girls
Sun City Girls were an American experimental rock band, formed in 1979 in Phoenix, Arizona. From 1981, the group consisted of Alan Bishop (bass guitar, vocals), his brother Richard Bishop (guitar, piano, vocals), and Charles Gocher (drums, vocals). Their name was inspired by Sun City, Arizona, an Arizona retirement community. In 2007, Gocher died following a long battle with cancer, bringing an end to the group. In a 26-year career, they produced 50 albums, 23 cassettes, 6 feature-length videos, and many other recordings. Operating in indie rock and underground music circles, Sun City Girls recorded numerous critically acclaimed albums, released in small editions by labels like Placebo, Majora, Eclipse Records, Amarillo Records, and their own Abduction Records, and has garnered a devoted cult following. Their music was hugely eclectic and varied, spreading across genres such as spoken word, free improvisation, jazz and rock, along with a recurring interest in world music. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melodica
The melodica is a handheld free-reed instrument similar to a pump organ or harmonica. It features a musical keyboard on top, and is played by blowing air through a mouthpiece that fits into a hole in the side of the instrument. The keyboard usually covers two or three octaves. Melodicas are small, lightweight, and portable, and many are designed for children to play. They are popular in music education programs, especially in Asia. The modern form of the instrument was invented by Hohner in the late 1950s, though similar instruments have been known in Italy since the 19th century. Description The mouthpiece can be a short rigid or semi-flexible plastic piece or a long flexible plastic tube (designed to allow the player to either hold the keyboard so the keys can be seen or lay the keyboard horizontally on a flat surface for two-handed playing). A foot pump can also be used as an alternative to breathing into the instrument. Melodica keyboards typically ascend from a low F note. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinyl Record
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The groove usually starts near the periphery and ends near the center of the disc. At first, the discs were commonly made from shellac, with earlier records having a fine abrasive filler mixed in. Starting in the 1940s polyvinyl chloride became common, hence the name vinyl. The phonograph record was the primary medium used for music reproduction throughout the 20th century. It had co-existed with the phonograph cylinder from the late 1880s and had effectively superseded it by around 1912. Records retained the largest market share even when new formats such as the compact cassette were mass-marketed. By the 1980s, digital media, in the form of the compact disc, had gained a larger market share, and the record left the mainstream in 1991. Since the 1990s, records co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
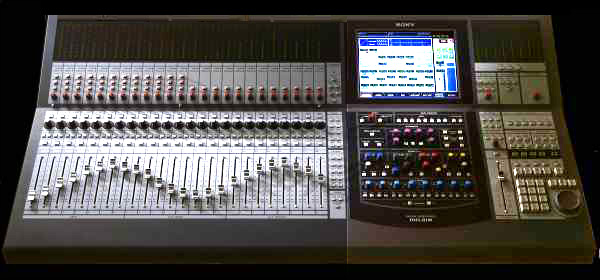
Audio Mixing (recorded Music)
In sound recording and reproduction, audio mixing is the process of optimizing and combining multitrack recordings into a final mono, stereo or surround sound product. In the process of combining the separate tracks, their relative levels are adjusted and balanced and various processes such as equalization and compression are commonly applied to individual tracks, groups of tracks, and the overall mix. In stereo and surround sound mixing, the placement of the tracks within the stereo (or surround) field are adjusted and balanced. Audio mixing techniques and approaches vary widely and have a significant influence on the final product. Audio mixing techniques largely depend on music genres and the quality of sound recordings involved. The process is generally carried out by a mixing engineer, though sometimes the record producer or recording artist may assist. After mixing, a mastering engineer prepares the final product for production. Audio mixing may be performed on a mixing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cover Art
Cover art is a type of artwork presented as an illustration or photograph on the outside of a published product such as a book (often on a dust jacket), magazine, newspaper ( tabloid), comic book, video game (box art), music album (album art), CD, videotape, DVD, or podcast. The art has a primarily commercial function, for instance to promote the product it is displayed on, but can also have an aesthetic function, and may be artistically connected to the product, such as with art by the creator of the product. Album cover art Album cover art is artwork created for a music album. Notable album cover art includes Pink Floyd's ''The Dark Side of the Moon, King Crimson's In the Court of the Crimson King,'' the Beatles' '' Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band'', ''Abbey Road'' and their self-titled "White Album" among others. Albums can have cover art created by the musician, as with Joni Mitchell's ''Clouds'', or by an associated musician, such as Bob Dylan's artwork for the cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Engineering
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to: Sound * Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound *Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum * Digital audio, representation of sound in a form processed and/or stored by computers or digital electronics *Audio, audible content (media) in audio production and publishing *Semantic audio, extraction of symbols or meaning from audio * Stereophonic audio, method of sound reproduction that creates an illusion of multi-directional audible perspective * Audio equipment Entertainment *AUDIO (group), an American R&B band of 5 brothers formerly known as TNT Boyz and as B5 * ''Audio'' (album), an album by the Blue Man Group * ''Audio'' (magazine), a magazine published from 1947 to 2000 *Audio (musician), British drum and bass artist * "Audio" (song), a song by LSD Computing *, an HTML element, see HTML5 audio See also *Acoustic (other) *Audible (other) *A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylophone
The xylophone (; ) is a musical instrument in the percussion family that consists of wooden bars struck by mallets. Like the glockenspiel (which uses metal bars), the xylophone essentially consists of a set of tuned wooden keys arranged in the fashion of the keyboard of a piano. Each bar is an idiophone tuned to a pitch of a musical scale, whether pentatonic or heptatonic in the case of many African and Asian instruments, diatonic in many western children's instruments, or chromatic for orchestral use. The term ''xylophone'' may be used generally, to include all such instruments such as the marimba, balafon and even the semantron. However, in the orchestra, the term ''xylophone'' refers specifically to a chromatic instrument of somewhat higher pitch range and drier timbre than the marimba, and these two instruments should not be confused. A person who plays the xylophone is known as a ''xylophonist'' or simply a ''xylophone player''. The term is also popularly used to refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whistle
A whistle is an instrument which produces sound from a stream of gas, most commonly air. It may be mouth-operated, or powered by air pressure, steam, or other means. Whistles vary in size from a small slide whistle or nose flute type to a large multi-piped church organ. Whistles have been around since early humans first carved out a gourd or branch and found they could make sound with it. In prehistoric Egypt, small shells were used as whistles. Many present day wind instruments are inheritors of these early whistles. With the rise of more mechanical power, other forms of whistles have been developed. One characteristic of a whistle is that it creates a pure, or nearly pure, tone. The conversion of flow energy to sound comes from an interaction between a solid material and a fluid stream. The forces in some whistles are sufficient to set the solid material in motion. Classic examples are Aeolian tones that result in galloping power lines, or the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle (musical Instrument)
The triangle is a musical instrument in the percussion family, and is classified as an idiophone in the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system. Triangles are made from a variety of metals including aluminum, beryllium copper, brass, bronze, iron, and steel. The metal is formed into a triangle shape by bending or casting methods. The instrument is usually held by a loop of some form of thread or wire at the top curve. The triangle theoretically has indefinite pitch, and produces a plurality of overtones when struck with an appropriate beater. History Iconography is the primary source for knowledge of the history of the triangle, and provides insight into the musical and social context in which the instrument developed. Some scholars believe the triangle to be a direct descendant of the ancient Egyptian sistrum. Others do not go quite so far, referring to the triangle as being "allied" with the sistrum throughout history, but not a direct descendant. It is thought that if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell (instrument)
A bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell (jingle bell). Bells are usually cast from bell metal (a type of bronze) for its resonant properties, but can also be made from other hard materials. This depends on the function. Some small bells such as ornamental bells or cowbells can be made from cast or pressed metal, glass or ceramic, but large bells such as a church, clock and tower bells are normally cast from bell metal. Bells intended to be heard over a wide area can range from a single bell hung in a turret or bell-gable, to a musical ensemble such as an English ring of bells, a carillon or a Russian zvon which are tuned to a common scale and instal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Güiro
The güiro () is a Puerto Rican percussion instrument consisting of an open-ended, hollow gourd with parallel notches cut in one side. It is played by rubbing a stick or tines (see photo) along the notches to produce a ratchet sound. The güiro is commonly used in Puerto Rican, Cuban and other forms of Latin American music, and plays a key role in the typical rhythm section of important genres like son, trova and salsa. Playing the güiro usually requires both long and short sounds, made by scraping up and down in long or short strokes. The güiro, like the maracas, is often played by a singer. It is closely related to the Cuban guayo, Dominican güira, and Haitian graj which are made of metal. Other instruments similar to the güiro are the Colombian guacharaca, the Brazilian reco-reco, the quijada (cow jawbone) and the frottoir (French) or fwotwa (French Creole) ( washboard). Etymology In the Arawakan language, a language of the indigenous people of Latin America and sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bongo Drum
Bongos ( es, bongó) are an Afro-Cuban percussion instrument consisting of a pair of small open bottomed hand drums of different sizes. They are struck with both hands, most commonly in an eight-stroke pattern called ''martillo'' (hammer). The larger drum is called a hembra (Spanish for female) and the smaller drum is called the macho (Spanish for male). They are mainly employed in the rhythm section of son cubano and salsa ensembles, often alongside other drums such as the larger congas and the stick-struck timbales. This brought bongos into our cultural vocabulary, from Beatniks to Mambo to the current revival of Cuban folkloric music. Bongo drummers (''bongoseros'') emerged as the only drummers of son cubano ensembles in eastern Cuba toward the end of the 19th century. It is believed that Bongos evolved from the Abakua Drum trio 'Bonko' and its lead drum 'Bonko Enmiwewos'. These drums are still a fundamental part of the Abakua Religion in Cuba. If joined with a wooden peck in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

