|
Summerour Mound Site
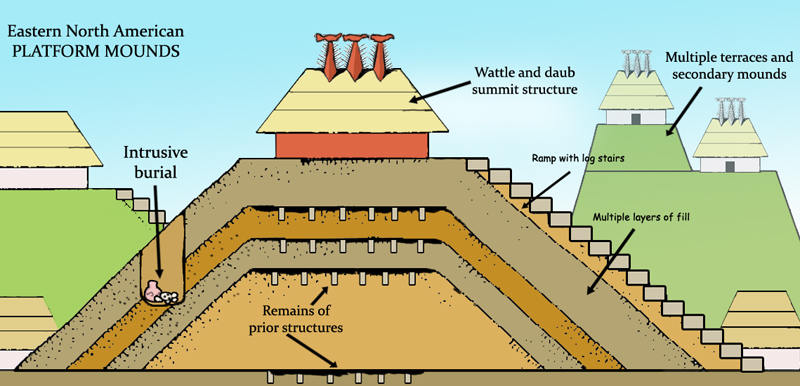
The Summerour Mound site ( 9FO16) is an archaeological site located in Forsyth County, Georgia. It was formerly on a floodplain of the west bank of the Chattahoochee River in northern Georgia. It is now flooded under the Buford Reservoir, also known as Lake Lanier. This mound site, previously unreported, was discovered and excavated in 1951–54 by Joseph Caldwell in association with a Smithsonian Institution River Survey. He described the platform mound at the site as "considerably spread out in cultivation and ... now an oval, with a nearly level summit plateau about long, wide, and high." Caldwell found a temple or other public structure on the mound summit. It was rectangular, long by wide, the outer walls constructed of small posts set in wall trenches. The mound was originally classified as Early Mississippian culture. Materials and records related to the mound have been restudied and the consensus is that it was likely earlier, part of the Late Woodland period. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forsyth County, Georgia
Forsyth County ( or ) is a County (United States), county in the north-central portion of the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. Suburban and exurban in character, Forsyth County lies within the Atlanta Metropolitan Area. The county's only Municipal corporation, incorporated city and county seat is Cumming, Georgia, Cumming. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 251,283. Forsyth was the fastest-growing county in Georgia and the 15th fastest-growing county in the United States between 2010 and 2019. Forsyth County's rapid population growth can be attributed to its proximity to high-income employment opportunities in nearby Alpharetta, Georgia, Alpharetta and northern Fulton County, Georgia, Fulton County, its equidistant location between the big-city amenities of bustling Atlanta, Georgia, Atlanta and the recreation offerings of the scenic Blue Ridge Mountains, its plentiful supply of large, relatively affordable new-construction homes, and Forsyth County Schools, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the origin of the proto-Iroquoian language was likely the Appalachian region, and the split betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenimer Site
The Kenimer site (9Wh68) is an archaeological site near Sautee Nacoochee, Georgia in White County. The site contains two earthwork mounds located on top of a natural hilltop. Site description The Kenimer site is located on an erosional remnant hill just to the north of and overlooking the Nacoochee Valley. It overlooks the junction of the Chattahoochee River and Sautee Creek, which is about to the southeast. Mound A, the largest of the site's two mounds is above the level of the flood plain of the rivers and approximately above sea level. Georgia State Route 17 is positioned to the north of Mound A. Because the mounds are located on an irregularly shaped natural hill their exact dimensions are hard to determine and vary from side to side. The summit of Mound A is approximately square. On its high northeastern side, it is more than in height, and, on its western side adjacent to Mound B, it is in height. Mound B is located to the west of Mound A and is oriented with bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joe Bell Site
The Joe Bell site ( 9MG28) is an archaeological site located in Morgan County, Georgia underneath Lake Oconee, but prior to the 1970s, it was located south of the mouth of the Apalachee River on the western bank of the Oconee River. The junction of these two rivers could be seen from the site. This site was first visited by Marshall Williams in 1968 at the suggestion of the site’s landowner, Joe Bell, who had discovered various artifacts while the site was being regularly plowed. Because of Interstate construction, Marshall Williams and Mark Williams discovered this site during surface surveys and excavations of the plowed areas. The site was excavated and analyzed by Mark Williams as part of his PhD dissertation. During the 1969 excavations, four areas within the site were designated for excavation. In Areas 1-3 various five foot square units were excavated. No excavations were done in Area 4 in 1969. Large quantities of small potsherds were discovered during these excavations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyar Site
The Dyar site ( 9GE5) is an archaeological site in Greene County, Georgia, in the north central Piedmont physiographical region. The site covers an area of 2.5 hectares. It was inhabited almost continuously from 1100 to 1600 by a local variation of the Mississippian culture known as the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. Although submerged under Lake Oconee, the site is still important as one of the first explorations of a large Mississippian culture mound. The Dyar site is thought to have been one of the principal towns of the paramount chiefdom of Ocute, perhaps Cofaqui. Site description The platform mound located at the site was described in 1975 as being in the shape of a truncated cone approximately high and with a base in diameter. On the eastern edge of the mound in the central area of the site was a plaza surrounded by domestic structures making up an oval shaped village of 2.13 hectares. Mound Platform mounds are built up in a series of stages that can span ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mississippian Sites
This is a list of Mississippian sites. The Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, inland-Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally. Its core area, along the Mississippi River and its major tributaries, stretched from sites such as Cahokia in modern Illinois, the largest of all the Mississippian sites, to Mound Bottom in Tennessee, to the Winterville site in the state of Mississippi. The typical form were earthwork platform mounds, with flat tops, often the sites for temples or elite residences. Other mounds were built in conical or ridge-top forms. The culture reached peoples in settlements across the continent: Temple mound complexes were constructed also in areas ranging from Aztalan in Wisconsin to Crystal River in Florida, and from Fort Ancient, now in Ohio, to Spiro in Oklahoma. Mississippian cultural influences extended as far north and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramics Of Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
Native American pottery is an art form with at least a 7500-year history in the Americas. Pottery is fired ceramics with clay as a component. Ceramics are used for utilitarian cooking vessels, serving and storage vessels, pipes, funerary urns, censers, musical instruments, ceremonial items, masks, toys, sculptures, and a myriad of other art forms. Due to their resilience, ceramics have been key to learning more about pre-Columbian indigenous cultures. Materials and techniques The clay body is a necessary component of pottery. Clay must be mined and purified in an often laborious process, and certain tribes have ceremonial protocols to gathering clay. Different tribes have different processes for processing clay, which can include drying in the sun, soaking in water for days, and repeatedly running through a screen or sieve. Acoma and other Pueblo pottery traditionally pound dry clay into a powder and then remove impurities by hand, then running the dry powder through a screen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Randolph Kelly
Arthur Randolph Kelly (October 27, 1900 – November 4, 1979) was an American professional archaeologist. He made numerous contributions to archeology in Georgia, which began with directing excavations at the Macon Plateau Site in 1933, part of the federal archeology program that provided jobs while undertaking studies of important sites. During his career, he also worked at the Etowah Mound and Village site, Lamar Mounds, the Lake Douglas Mound, the Oliver and Walter F. George River Basin surveys, the Estatoe Mound, the Chauga Mound, and the Bell Field Mound, among others in Georgia. After completing his graduate education with master's and doctoral degrees at Harvard University, Kelly had a career spanning academic service, and professional excavations under the Smithsonian Institution and other organizations. He also directed operations at national monuments for the National Park Service and served as its chief archeologist for several years. In 1947 he was selected by Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta Museum Of History
The Augusta Museum of History is a history museum located in Augusta, Georgia, U.S. The museum was founded in 1937 to preserve and share the history of Augusta and its surrounding area. On display are numerous artifacts, images, and dioramas that showcase the broad spectrum of the region's history. The Museum of History is the only Museum in the CSRA (Central Savannah River Area - includes four counties in Georgia: Burke, Columbia, McDuffie and Richmond and two counties in South Carolina - Aiken and Edgefield) accredited by the American Alliance of Museums. Permanent Collection *Augusta's Story – This exhibit explores the 12,000-year journey of the region's history. It is composed of artifacts from the prehistoric times to James Brown, the Godfather of Soul. Artifacts include a diorama of Stallings Island culture, slave-made pottery from the antebellum era, 12-pounder bronze Napoleon Cannon tube, and an 1869 steam fire engine that shows the destruction of the 1916 fire. An inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Echota
New Echota was the capital of the Cherokee Nation (1794–1907), Cherokee Nation in the Southeast United States from 1825 until their Cherokee removal, forced removal in the late 1830s. New Echota is located in present-day Gordon County, Georgia, Gordon County, in northwest Georgia, 3.68 miles north of Calhoun, Georgia, Calhoun. It is south of Resaca, Georgia, Resaca, next to present day New Town, Georgia, New Town, known to the Cherokee as ''Ustanali''. The site has been preserved as a state park and a historic site. It was designated in 1973 as a National Historic Landmark District. The site is at the confluence of the Coosawattee River, Coosawattee and Conasauga River, Conasauga rivers, which join to form the Oostanaula River, a tributary of the Coosa River. It is near Town Creek. Archeological evidence has shown that the site of New Echota had been occupied by ancient indigenous cultures for thousands of years prior to the historic Cherokee Native Americans in the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vann Tavern (1908–1999), American historian
{{disambiguation, geo, given name ...
Vann may refer to: * ''Salvadora oleoides'' is a small bushy evergreen tree found in India, Pakistan, and southern Iran * Vann Peak, Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica People with the name * Vann (surname), an English surname (including a list of people with the surname) * Vann McElroy (born 1960), former National Football League player * Ho Vann, politician elected to the National Assembly of Cambodia in 2003 * Vann Molyvann (1926-2017), Cambodian architect * John Paul Vann (1924-1972), U.S. civilian commander during the Vietnam War * L. Vann Pettaway (born c. 1957), former men's basketball coach at Alabama Agricultural and Mechanical University * C. Vann Woodward Comer Vann Woodward (November 13, 1908 – December 17, 1999) was an American historian who focused primarily on the American South and race relations. He was long a supporter of the approach of Charles A. Beard, stressing the influence of un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |